-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Muscle: Its Properties, Types and Functions
You all know about different types of movements. We all love to see the fascinating movements of the gymnasts. Have you ever wondered how gymnasts move like this? Which organs are responsible for these different types of movements in them?

GIF: Movements
The answer is that the movement occurs due to the coordinated effort of the muscular system, skeletal system and the nervous system. Human beings are able to show a variety of movements with the help of the above organ systems.
If we talk about unicellular organisms, such as Euglena, the movement occurs through flagella and hence it is known as flagellar movement. This type of movement helps in the swimming of spermatozoa as well as it maintains the water canal system in sponges. Let’s understand now a little more about the muscular system in this article.
Table of Contents
- What is muscle?
- Unique properties of muscles
- Types of muscles
- Functions of muscles
- Practice Questions
- FAQs
What is Muscle?
Muscle is a specialized tissue that originates from the mesoderm. About 40 - 50% of the body weight of a human adult is contributed by muscles. Muscles are composed of cells known as myocytes. These cells provide contractibility and allow the muscle to gain the ability to contract. It is a property to shorten and return back to its original state. Myocytes shorten to ⅓ to ½ of their length. The stimulus of contraction is conducted to the neighboring cells. In an adult human, 320 pairs of muscles are present.

Structure of Muscle
Each muscle is composed of many long and cylindrical cells called muscle fibres. They are formed from the myoblasts. They are arranged parallel to each other. Sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of muscle fibres. Endoplasmic reticulum is called sarcoplasmic reticulum. Sarcoplasm possesses fine threads called myofibrils. The cell membrane of muscle fibre is called sarcolemma. They possess one or more nuclei.
Unique Properties of Muscles
The unique properties that a muscle possesses are enlisted below:
Contractility
This property allows a muscle to shorten and return to its original state.

Excitability
It is the ability of a muscle to respond towards a signal.
Elasticity
It is a muscle’s ability to recoil or return to its original length.
Extensibility
It is a muscle’s ability to stretch itself.

Types of Muscles
There are three types of muscle tissue based structure, function and location as follows:
- Smooth muscle tissue
- Cardiac muscle tissue
- Skeletal muscle tissue
Smooth Muscle Tissue
The smooth muscle tissue has tapering ends at both ends. They have smooth appearance i.e. the striations of light and dark bands are absent. The smooth muscle tissue helps in the transportation of food in the digestive tract and transport of gametes in the female reproductive system.
Common Names of the Smooth Muscle
These muscles are also known with different names, such as:
- Visceral muscle - They form the lining of hollow organs.
- Non-striated muscle - This is because the striations are absent in these muscles.
- Non-striped muscle - They have smooth appearance because of the absence of alternative light and dark bands.
- Involuntary muscle: They are not under the conscious control of a person,.

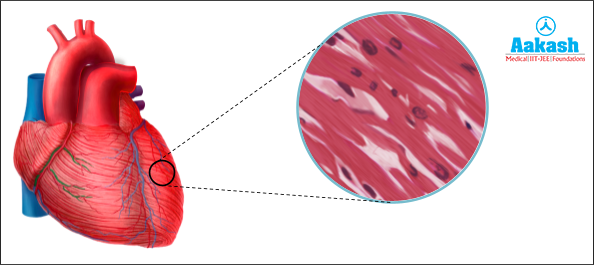
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue is only present in the heart. It is a contractile tissue that helps in the beating of the heart. It is responsible for the continuous rhythmic heart movement due to which blood is pumped by the heart. This muscle tissue helps in maintaining the cardiac cycle.
Common Names of the Smooth Muscle
These muscles are also known with different names, such as:
- Striated muscle - As they possess alternate light and dark bands.
- Involuntary muscle - The activities of cardiac muscle are not under the conscious control of a person.
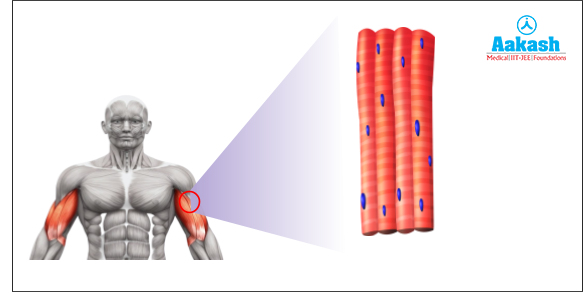
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue is closely associated with the skeletal components of the body. The movements are under the control of the conscious control of a person. Therefore, they are known as voluntary muscles. It allows the movement of the body parts. They have striated appearance under the microscope.
Common Names of the Smooth Muscle
These muscles are also known with different names, such as:
- Striped muscles - This is because they have a striated appearance.
- Striated muscles - They have alternate light and dark bands that give a striated appearance.
- Voluntary muscles - The activities of skeletal muscle tissue are under the conscious control of a person.
Functions of Muscle
Muscles perform a diverse range of functions in the human body. Some of the functions are described below:
- Muscles present in the mouth help in breathing, speaking and swallowing.
- They help in the churning movements in the stomach.
- They help in the peristaltic movement of the digestive tract.
- They help in the transportation of gametes in the female reproductive tract.
- They help get rid of waste from the body.
- Cardiac muscles help to pump blood.
- They help in moving, sitting, lying and standing.
- They help in facial expressions.
- They assist the skeletal system to give a proper shape to the body.
- They help to face flight, fright and fight situations.
- Myometrium of the uterus helps in childbirth.
Practice Problems of Muscle
Q1. From the given options, find the incorrect statement.
- Heart muscles are striated and involuntary
- Muscles of hands and legs are striated and voluntary
- Muscles of the alimentary canal are striated and involuntary
- Muscles of the reproductive tract are unstriated and involuntary
Solution: In the alimentary canal, smooth muscles are present and these are unstriated and involuntary muscles. The smooth muscles transport the food in the digestive tract. Hence, the correct option is c.
Q2. Muscles are originated from ______________-.
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- Any of the above
Solution: Muscle is a specialised tissue that originates from mesoderm. They are made up of special cells called myocytes. The muscles are the structures that are responsible for movement of different body parts. Hence, the correct option is c.
Q3. The activities of visceral muscles are not under the control of the nervous system. These muscles are known as _________________.
Answer: Those muscles that are not under the control of the nervous system are known as involuntary muscles. These muscles are also known as smooth muscles.
From the following muscles, which are involved in the locomotion and changing of body posture?
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Skeletal muscle
- Both B and CS
Solution: Skeletal muscle is involved in the locomotory actions and changing of body posture. These muscle tissues are closely associated with the skeletal components of the body. Hence, the correct option is c.
FAQs of Muscle
Question1. Name the muscle that has characteristic striations and is involuntary?
Answer: Cardiac muscles or muscles of the heart are striated and involuntary. These muscles have alternate light and dark bands and the activities are not under the conscious control of the person.
Question2. Which muscles are responsible for the movement of food in the digestive tract and transportation of gametes in the genital tract?
Answer Smooth muscle cells are responsible for the transportation of food and gametes in the digestive tract and genital tract, respectively. These muscles are smooth in appearance and do not possess dark and light bands.
Question3. How can a person make our muscles strong?
Answer: A person can make our muscles strong by doing muscular exercise, such as push-ups, body weight exercises, resistance training and many more. These are known as muscle strengthening exercises.
Question4. How many muscles are present in the human body?
Answer: In an adult human, 640 muscles are present in pairs. They are present in 320 pairs. These muscles constitute 40 - 50% of the body weight.
Related Topics to Muscles in Bioloy
NCERT Biology Class 11 Chapters



