-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Classification of Carbohydrates and Their Structure - Carbohydrates, Classification, Structure, Practice Problem and FAQs
You must have tried a variety of food like beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, spaghetti, peas, whole grains, barley, oats, brown rice, corn, and cherry pie in your diet plan. But, what is important is a balanced died. Do you remember the composition of a balanced diet?
Carbohydrate-rich foods are an essential component of a balanced diet. Carbohydrates provide glucose to the body, which is converted into energy for bodily functions and physical activity. From health point of view, we can consider two carbohydrate sources. One which is digested to give glucose and the other not so easily digestible. Carbohydrates from unprocessed or lightly cooked whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and beans promote good health by providing vitamins, minerals, fibre, and a variety of important phytonutrients. White bread, pastries, sodas, and other highly refined or processed foods are all unhealthy sources of carbohydrates. These foods contain easily digestible carbohydrates, which may contribute to weight gain, impede weight loss, and encourage heart diseases and diabetes.
There is a lot to know about these carbohydrates.

Table of content
- Introduction of Carbohydrates
- Classification of Carbohydrates and their Structure
- Practice Problem
- Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
Introduction of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates of sucrose, cellulose, starch, glucose, etc were isolated in Germany Their reactions with phenyl hydrazine to produce crystalline phenylosazone were carried out Fischer inicatingby reacting two phenyl hydrazine with the aldehyde group and the carbon adjacent to the aldehyde group.
Carbohydrates, which include sugars, fibres, and starches, are essential nutrients. Plants are the primary producers of carbohydrates. They are found in grains, vegetables, fruits, milk, and other dairy products. They are the fundamental food group required for a healthy lifestyle. Carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms make up carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates got their common name from the fact that they frequently have the formula CX(H2O)Y. They appeared to be 'carbon hydrates.' For example, the formula of glucose, C6H12O6, clearly fits into the general formula of carbohydrates, i.e., CX(H2O)Y.
So, can we say that all of the compounds that fit into the formula of CX(H2O)Y are carbohydrates?
'No,' is the answer to this question. There are compounds,-
- Falling under the formula but do not exhibit the properties of carbohydrates..
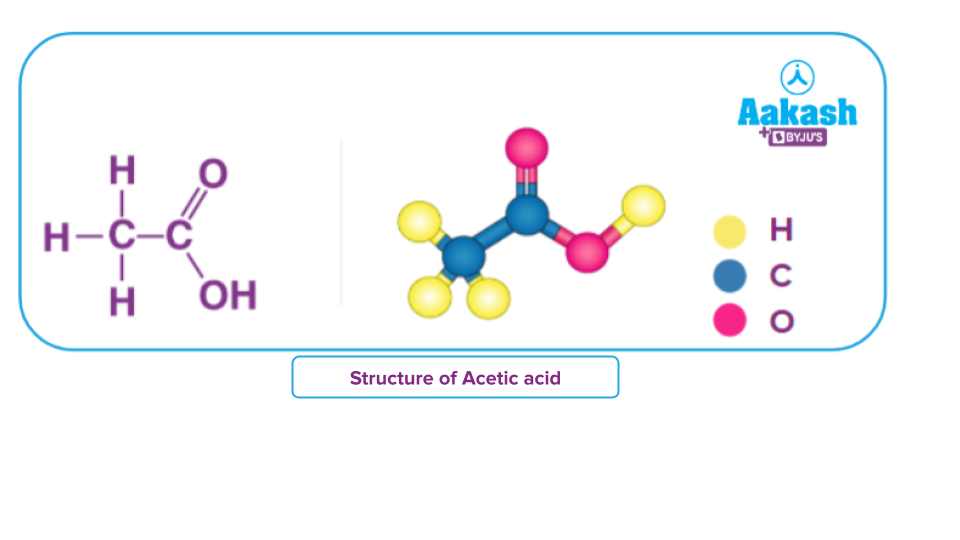
Although acetic acid, CH3COOH is not a carbohydrate but it satisfies the general formula formula of carbohydrate(i.e C2(H2O)2)
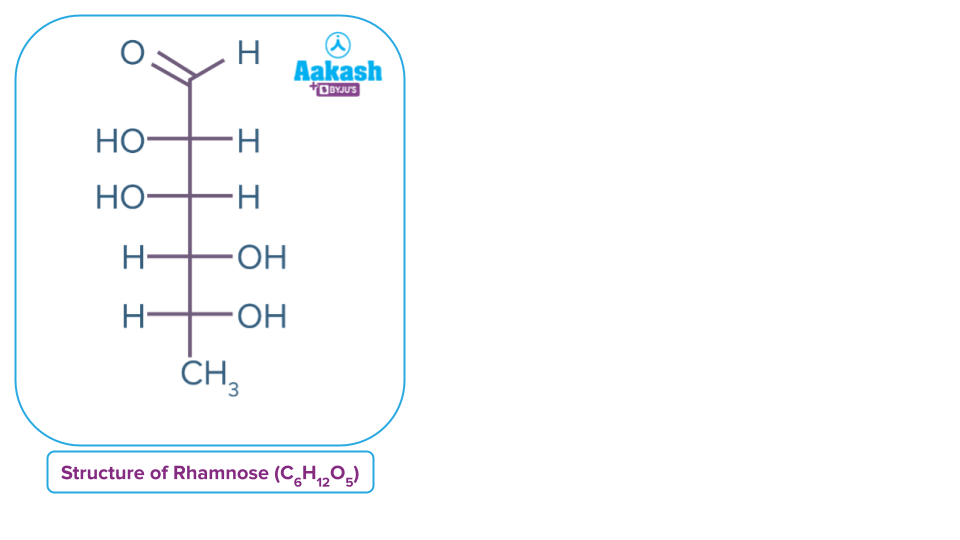
- Carbohydrate can have formula different from this general formula. Rhamnose, C6H12O5, is a carbohydrate but does not satisfy the general formula of carbohydrates.
As a result, we can conclude that carbohydrates cannot be explained solely using this formula.
Carbohydrates can also be defined as optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that hydrolyze to yield polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Almost all carbohydrates are chiral and have optical properties. 1,3-dihydroxypropane is an exception to this rule. Simple carbohydrates are also referred to as saccharides or sugars.
Classification of Carbohydrates and their Structure
Carbohydrates are classified according to three characteristics:
- Based on the product obtained from the hydrolysis of carbohydrates
- Based on their ability to reduce say Tollens and Fehling's solution.
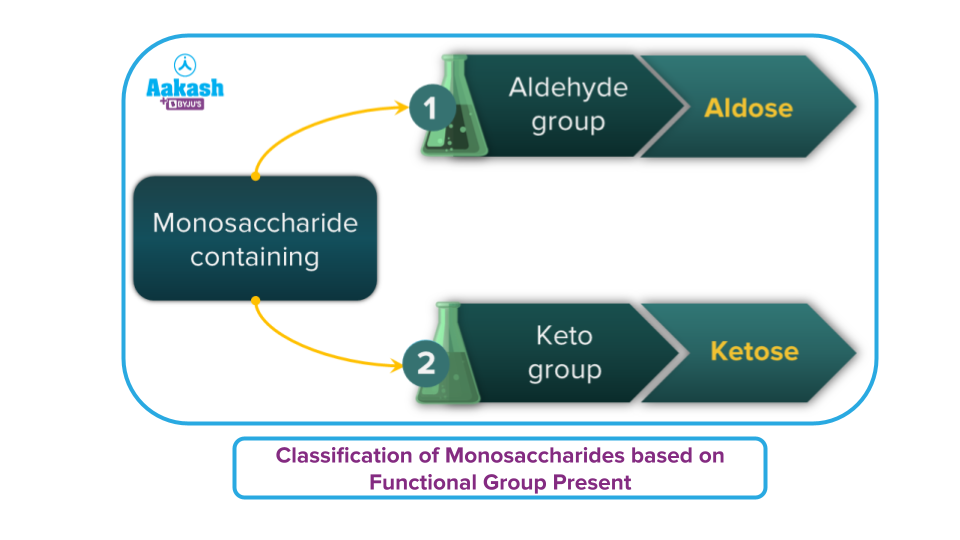
- Based on the functional groups as aldoses or ketosis
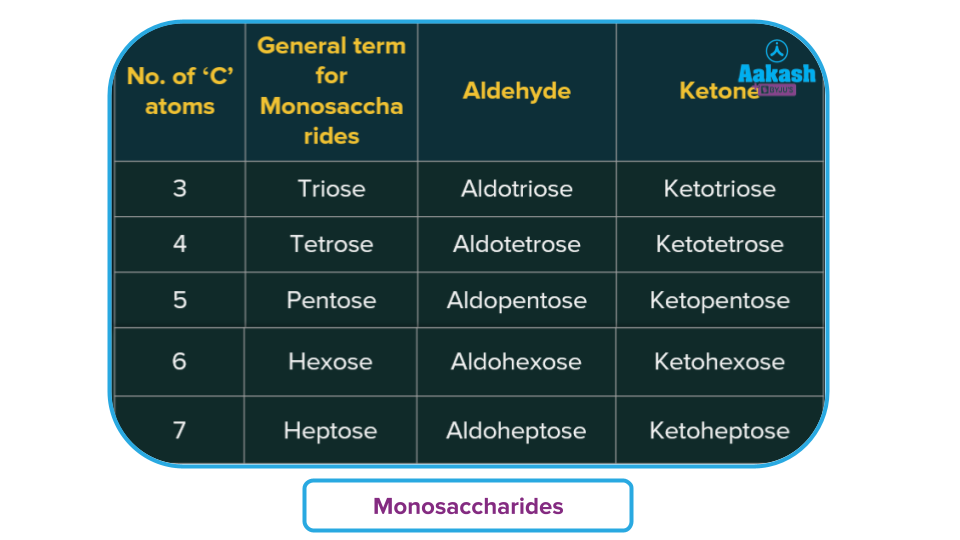
- Based on the carbon chain, as trioses, tetroses, pentoses, etc..
- Based on optical activity / configuration
Carbohydrates Based on Hydrolysis Products:
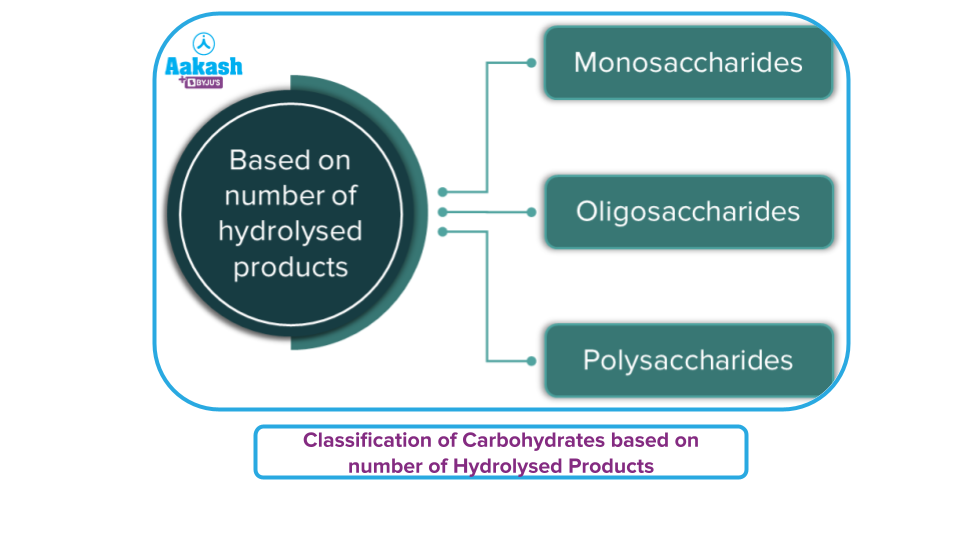
- Monosaccharides: Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates. Some important example of Monosaccharides includes- Glucose, fructose, ribose, etc.
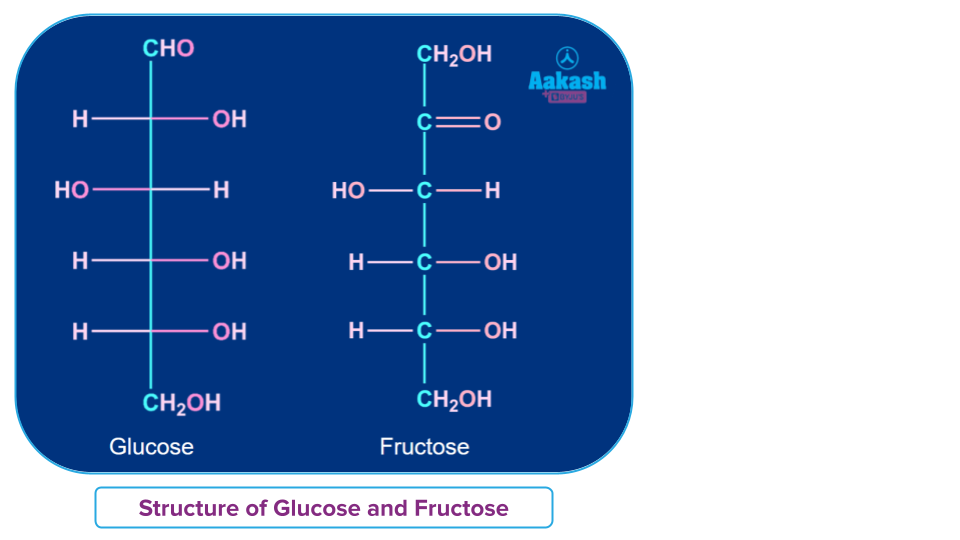
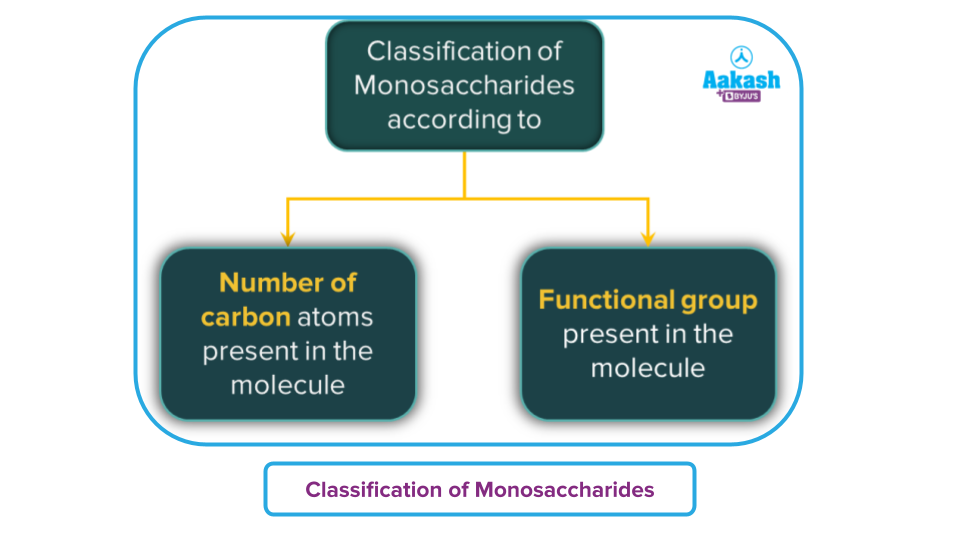
Monosaccharides are further classified into two types based on the number of carbon atoms and functional groups present.
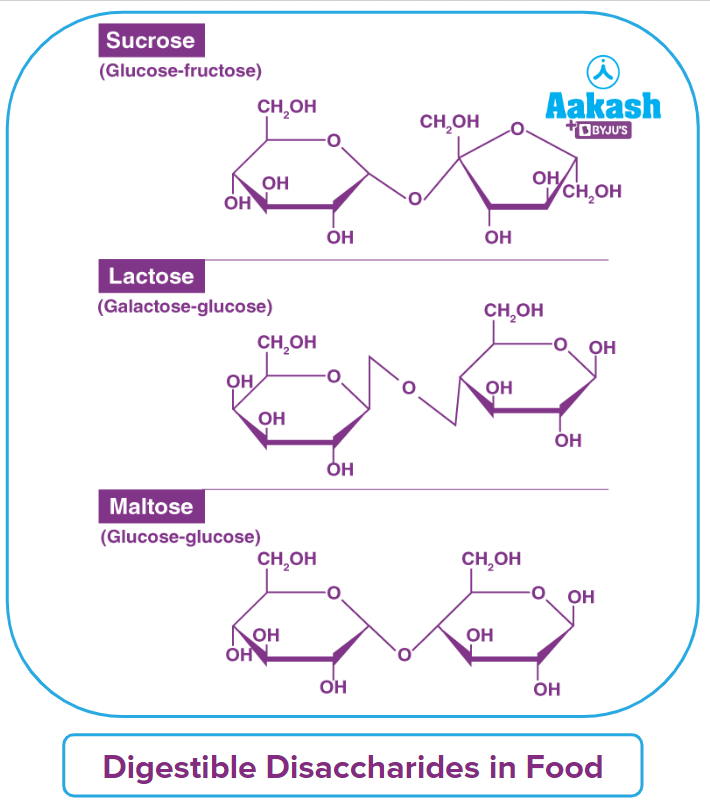
- Oligosaccharides: The condensation of 2-9 monomers produces oligosaccharides, which are carbohydrate molecules. Oligosaccharides are classified as disaccharides, trisaccharides, and so on based on the number of monosaccharide units connected. Polysaccharides are frequently distinguished from oligosaccharides when they contain more than ten sugar residues. Oligosaccharides include trioses, pentoses, and hexoses. Sucrose, Maltose, and Lactose are a few examples.
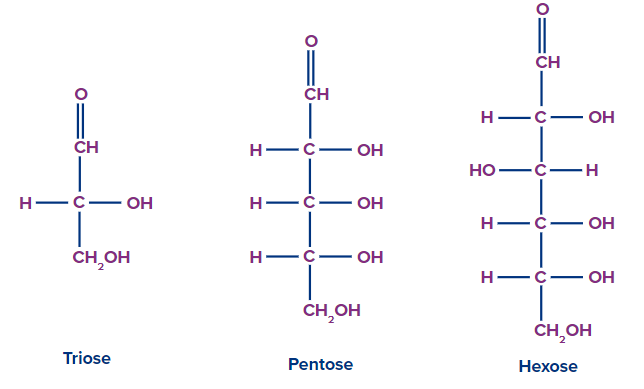
Based on the number of the monomeric unit formed during the hydrolysis Oligosaccharides are classified into disaccharides, trisaccharides, tetrasaccharides etc
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides are joined together or when carbohydrates are hydrolyzed to produce only two molecules of monosaccharides.
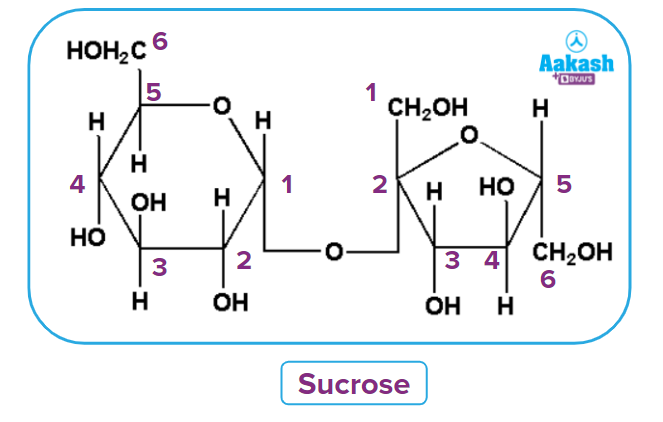
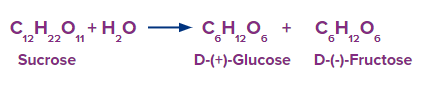
For example, hydrolysis of one molecule of sucrose yields one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose.
Furthermore, when maltose is hydrolyzed, it yields only two molecules of glucose, as shown below.
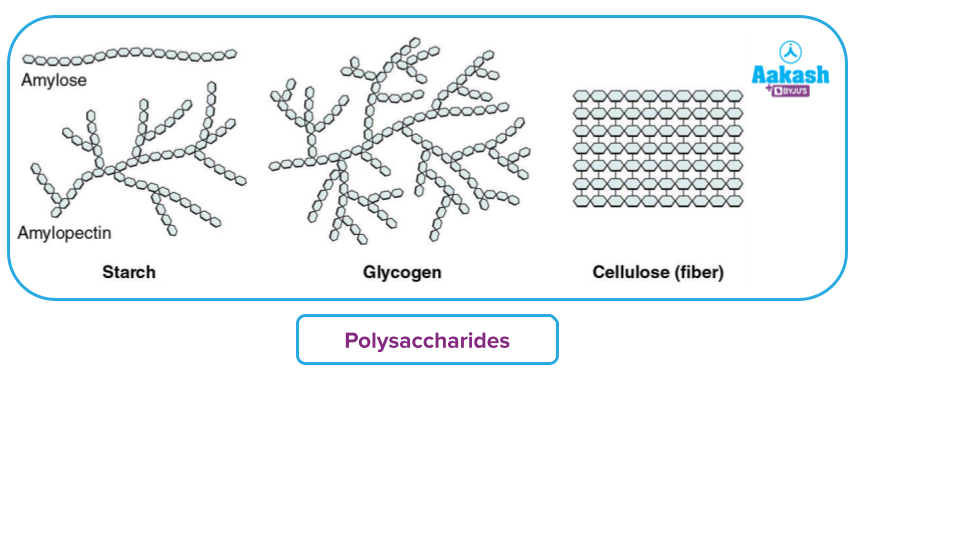
- Polysaccharides: They are carbohydrates that produce a large number of monosaccharide molecules (>10). They are also known as complex carbohydrates because they are made up of several monomers that have been polymerized together. Polysaccharides are carbohydrates that have a lot of branching and are homopolymers, such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose (made up of just glucose units).
Complex carbohydrates are made from more than one sugar molecules. Complex carbohydrates molecules are digested slowly than simple carbohydrates like glucose and sucrose They are abundant in potatoes, wheat, rice, beet root and fruits.
Here are some examples of polysaccharides.
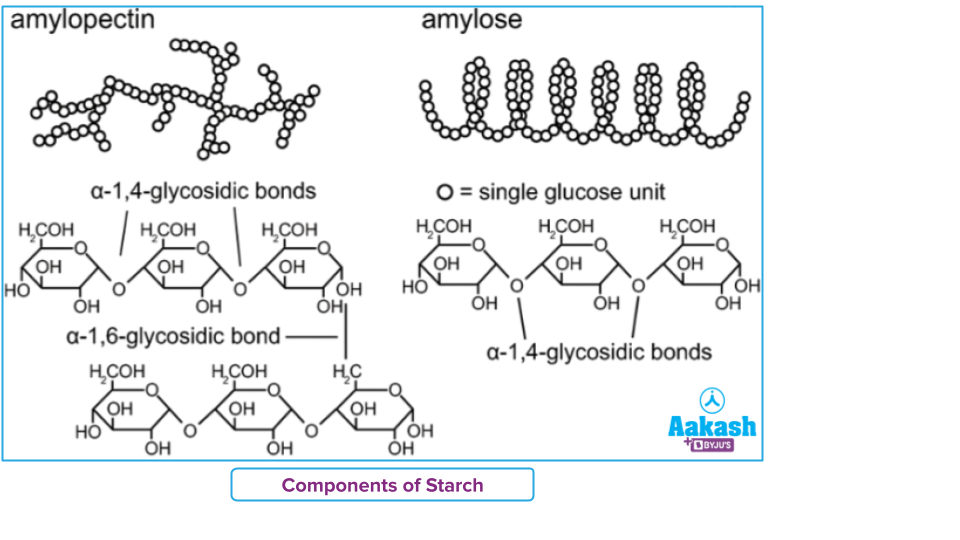
- Starch is a complex molecule of two polymeric saccharides amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a linear chain, whereas amylopectin is a highly branched chain.It is present in plant products.
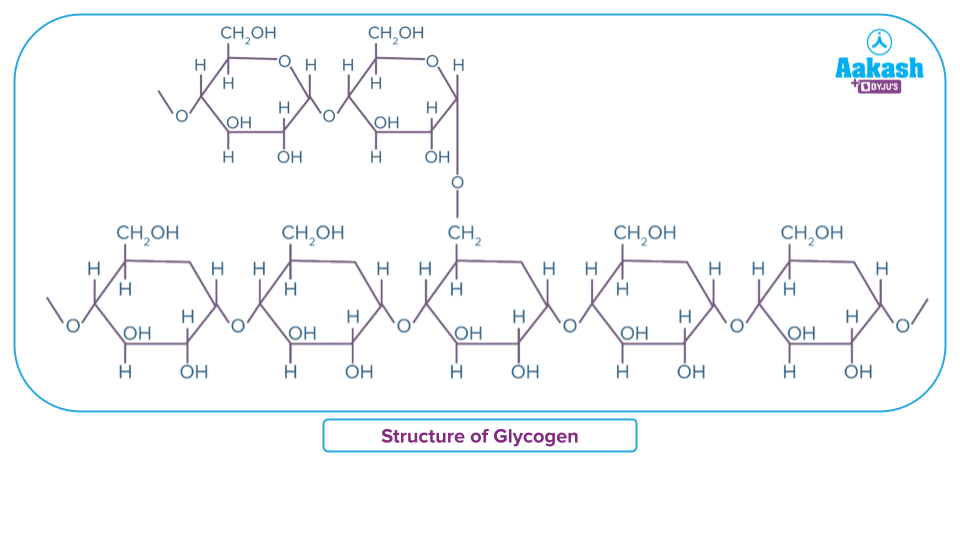
- Glycogen is a polysaccharide present in animals and so called also as animal starch. It has extensive branching.
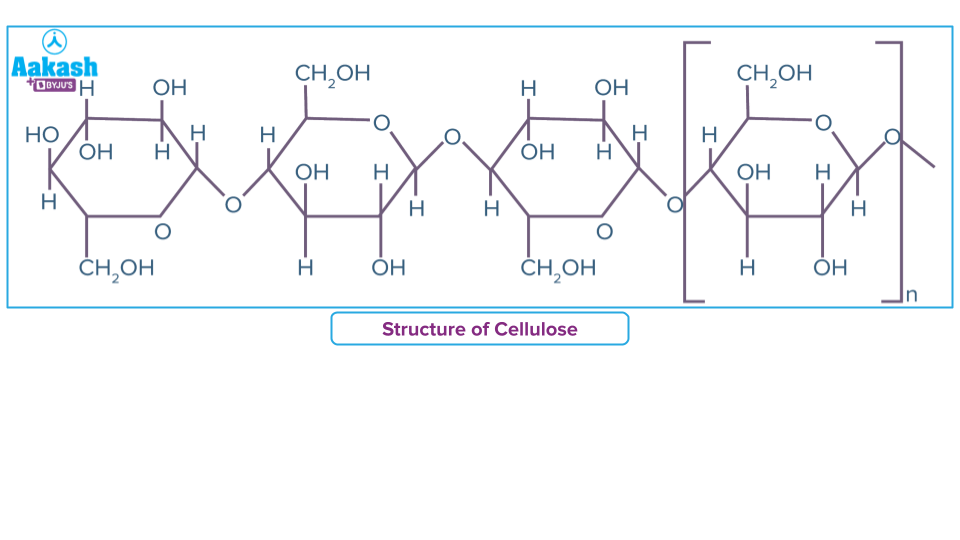
- Cellulose is polysaccharide, useful as a structural component of plants.. It is a a linear polymer of monosaccharides giving a high-tensile-strength fibrous structure..
Classification based on Reducing Nature:
Carbohydrates can also be divided into two types based on their ability to reduce Tollens' and Fehling's reagents as reducing sugar and non-reducing sugar.
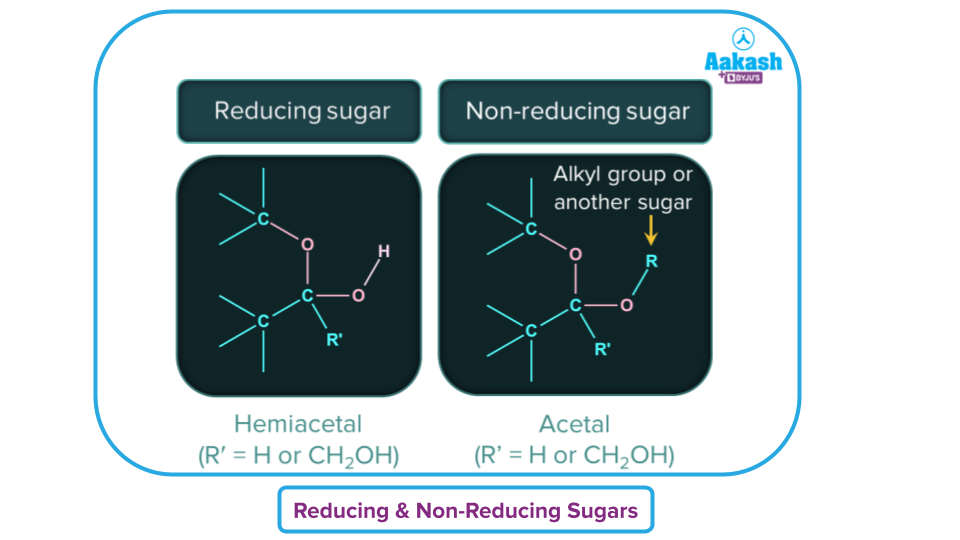
Reducing Sugar: It is a carbohydrate which reduces Tollens' and Fehling's reagent, and they must have at least one hemiacetal or hemiketal functional group.
Non-reducing sugar: Sugars that do not reduce Tollens or Fehling's solutions, should have an acetal linkage.
Note: Except for sucrose, all monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are reducing sugars; all polysaccharides are non-reducing sugars.
Practice Problems
Q1. Which of the following is an example of a monosaccharide?
A. Lactose
B. Starch
C. Cellulose
D. Glucose
Answer: (D)
Solution: Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates. Some important example of Monosaccharides includes- Glucose, fructose, ribose, etc.
Lactose is an example of a disaccharide and cellulose and starch is an examples of a polysaccharide. Therefore option (D) is correct
Q2. Select the correction option which is an example of a non-reducing sugar.
A. Sucrose
B. Glucose
C. Fructose
D. Galactose
Answer: (A)
Solution: Non-reducing sugar: Sugars that do not reduce Tollens or Fehling's solutions, should have an acetal linkage. Except for sucrose, all monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are reducing sugars; all polysaccharides are non-reducing sugars. Therefore option (A) is correct.
Q3. Which of the following option is incorrect with respect to the carbohydrates?
A. Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones or substances that hydrolyze to yield polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.
B. All carbohydrates are represented by the general formula CX(H2O)Y.
C. Sucrose is an example of non -reducing sugar
D. Carbohydrates, which include sugars, fibres, and starches, are essential nutrients.
Answer: (B)
Solution: Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones or substances that hydrolyze to yield polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. Carbohydrates, which include sugars, fibres, and starches, are essential nutrients. It is generally represented by the general formula CX(H2O)Y but there are few molecule like CH3COOH is not a carbohydrate but it satisfies the general formula formula of carbohydrate(i.e C2(H2O)2). Rhamnose, C6H12O5, is a carbohydrate but does not satisfy the general formula of carbohydrates.
Sugars that do not reduce Tollens or Fehling's solutions, should have an acetal linkage are non-reducing sugar. Except for sucrose, all monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are reducing sugar.
Therefore, option (B) is incorrect.
Q4. Select the correct option which represents the example of Polysaccharide.
A. Cellulose
B. Starch
C. Glucose
D. Both A and B are correct
Answer: (D)
Solution: They are carbohydrates that produce a large number of monosaccharide molecules (>10). They are also known as complex carbohydrates because they are made up of several monomers that have been polymerized together. Polysaccharides are carbohydrates that have a lot of branching and are homopolymers, such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose (made up of just glucose units). Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
Q1 . What are the main sources of carbohydrates?
Answer: Carbohydrates can be obtained from a variety of sources. Some of them are detailed below.
- Glucose is the main carbohydrate of fruits..
- Galactose is present in all dairy products.
- Lactose is found in high concentrations in milk and its derived products.
- Maltose is present in cereal, beet root, potatoes, and others.
- Fructose is available natural honey..
Q2. What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Answer: Some important functions of carbohydrates includes:
- Carbohydrates, such as starch in plants and glycogen in animals, are used as stored energy source.
- They supply raw materials to a variety of important industries, including textiles, paper, lacquers, and breweries.
- Carbohydrates coexist with many proteins and lipids in the biosystem.
- Carbohydrates are necessary for both plant and animal life. They make up a significant portion of our diet.
Q3. What are simple and complex carbohydrates?
Answer: The primary distinction between simple and complex carbohydrates is that simple carbohydrates are rapidly digested and absorbed by the body, whereas complex carbohydrates take longer to digest. Simple carbohydrates are small molecules while complex carbohydrates are polymeric in nature.
Q4. How are carbohydrates digested?
Answer: Carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth and ends when the polysaccharides are broken down into single sugars, or monosaccharides, that the body can absorb.
Salivary glands secrete the enzyme salivary amylase, which initiates the breakdown of polysaccharides in carbohydrate food.
The pancreas releases the enzyme pancreatic amylase in response to the presence of chyme in the duodenum, which breaks the polysaccharide down into a disaccharide. The enzymes lactase, sucrase, and maltase are then produced by the small intestine to break down the disaccharides into monosaccharides.
Carbohydrates that were not digested and absorbed by the small intestine reach the colon, where intestinal bacteria break them down partially. Fibre is excreted with faeces or partially digested by intestinal bacteria.


