-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Have you ever observed some walls of the unused buildings with small green plants growing on them? It is such a beauty to see. Sometimes you might have seen the same kind of plants on the ground during rainy seasons.
Ever wondered what these plants are? If we closely observe these plants, we can see the small leaf-like structures, but it is not as much a plant though!!! Then what are these plants?
They are included under Bryophyta, which is a division under subkingdom Cryptogamae. They are nonvascular land plants which live in moist conditions.

Fig: Mosses
Are you excited to know more about these little beautiful plants?
Let’s take a deep dive into the division Bryophyta.
Table of contents
- Life cycle
- Classification of Bryophyta
- Economic importance of Bryophyta
- Differences between liverworts and mosses
- Practice problems
- FAQs
Life cycle
Life cycle in Bryophyta shows alternation of generation. It possesses gametophyte (n) and sporophyte (2n). Gametes are produced by the gametophyte. The sex organs are multicellular. Male sex organ is called archegonium which produce antherozoids. Antherozoids possess two flagella and are motile. Female sex organ is called archegonium which is flask shaped. It produces only one egg. Antherozoids, once released into water, come in contact with the archegonium.

Fig: Antherozoids
Fusion of egg with a male gamete results in the formation of zygote (2n). Zygote develops into a multicellular embryo which eventually grows into a sporophyte (2n). Thus, bryophytes are considered to be the first embryophytes, i.e, plants that develop embryos. Sporophytes possess foot, seta and capsule. Sporophytes are not independent and depend on the gametophyte for nourishment. Reduction division or meiosis in some cells present within the capsule of the sporophytes produces haploid spores. Germination of spores results in the formation of gametophytes. As both the haploid and diploid generations occur with equal prevalence, the life cycle is said to be a haplo-diplontic in Bryophyta.
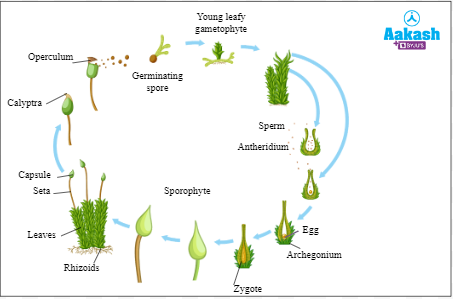
Fig: Life cycle of a bryophyte
Classification of Bryophyta
Division Bryophyta includes three classes as follows:
- Hepaticae (liverworts)
- Anthocerotae (hornworts)
- Musci (mosses)
Common characteristics of Hepaticae or liverworts
The body or thallus is dorsoventrally flattened and dichotomously branched in most liverworts. It looks like a lobed liver, so called as liverworts. They possess unicellular rhizoids. Most liverworts have an undifferentiated plant body but some foliose liverworts have their body differentiated into leaf-like appendages and stem-like structures.
Reproduction in Hepaticae
Reproduction occurs by asexual and sexual methods. Asexual reproduction occurs by fragmentation of thallus or by gemmae. The fusion of gametes results in the sexual reproduction. Male and female sex organs can be present on the same or different thallus. Elaters are present to help in dispersal of spores. They are tube-like structures attached to spores. Examples include Marchantia.
Marchantia
Marchantia is a small dorsiventrally flattened liverwort. They possess unicellular rhizoids. They multiply vegetatively by fragmentation. Asexual reproduction occurs by gemmae. They are unisexual or dioecious, i.e, male and female sex organs are borne on different thalli. Sex organs are present on special stalks called gametophores. Antheridiophore bears antheridium or male sex organ. It produces antherozoids. Archegoniophore possess archegonium or female sex organ.

Fig: Gametophores in Marchantia
Common characteristics of Musci or mosses
Musci possesses a leafy plant body which is a gametophyte. They have multicellular rhizoids for attachment to the substratum. Examples include Funaria.
Sporophyte of mosses
Sporophytes possess three parts as follows:
- Foot - It attaches the sporophyte with the gametophyte.
- Seta - It is a long cylindrical stalk.
- Capsule - It is present on the tip of the stalk. Spores are liberated from the capsule. Peristome is a teeth- like structure which is present on capsules to help in dispersal of spores.
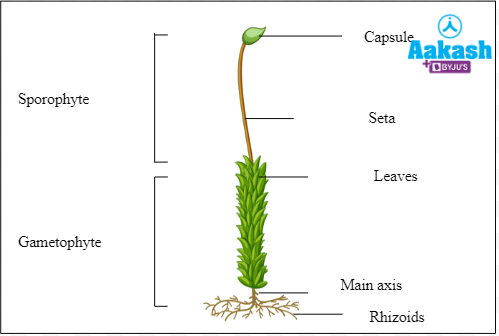
Fig: Moss
Funaria
Funaria grow in moist and shady places and form dense carpets on soil. They are monoecious or bisexual, i.e, both male and female sex organs grow on the same thallus.
Life cycle in Funaria
It shows the alternation of generation. Spores germinate and produce protonema. It is the first stage in the development of the gametophyte. It is a branched filamentous stage. Protonema possesses two branches called the rhizoidal branch and the chloronemal branch. Rhizoidal branch is non-green and helps attach to the substratum. Chloronema possesses buds.

Fig: Protonema
Protonema then develops into a secondary protonema which develops into the second stage called the leafy stage. Leafy stages possess an upright slender axis with spirally arranged leaves. They possess multicellular rhizoids which help in attachment to the substratum. It is an adult plant which bears antheridia and archegonia on separate branches. Fusion of gametes results in the formation of a zygote (2n). It develops into a sporophyte which produces spores.
Common characteristics of Anthocerotae or hornworts
Hornworts have a dorsiventrally flattened body with unicellular rhizoids. The sporophyte is cylindrical like a horn, hence called hornwort. Reproduction occurs by asexual and sexual methods. Asexual reproduction occurs by fragmentation of thallus or by gemmae. The sexual reproduction occurs by the gamete fusion. Examples include Anthoceros.

Fig: Hornwort
Economic importance of Bryophyta
- They prevent soil erosion by forming dense mats on the soil.

Fig: Mat of bryophytes
- They help in primary succession on rock.
- Peat obtained from Sphagnum is used as a fuel.
- Peat is also used as a packing material as it is able to hold water.
- They can be used as food for herbaceous plants.
Differences between liverworts and mosses
|
Liverworts |
Mosses |
|
They possess unicellular rhizoids |
They possess multicellular rhizoids |
|
Filamentous stage is absent |
Filamentous stage called protonema is present |
|
Elaters present |
Elaters absent |
|
Peristome teeth absent |
Peristome teeth present |
|
They are thalloid mainly |
They are mainly foliage with lateral branches |
|
Examples include Marchantia |
Examples include Funaria |
Practice Problems
Q1. In a Bryophyte the cells of X are in haploid and Y are in diploid condition. Now identify X and Y.
A. X - gametophyte, Y - spores
B. X - sporophyte, Y - gametophyte
C. X - gametophyte, Y - sporophyte
D. X - sporophyte, Y - gametes
Solution: Ploidy is the number of sets of chromosomes in a cell or cells of the organism. Gametophyte is the phase which has a haploid number of chromosomes and produces gametes. Sporophyte is the plant body which produces spores. Spores form the gametophyte. Therefore cells of gametophyte are haploid and cells of sporophyte are diploid. Spores and gametes are single celled and they are haploid too. Hence the correct option is c.
Q2. Which of the following options mentions the events when mitosis happens in the life cycle of the bryophytes:
A. I - during the sporophyte formation stage, II - during the gametophyte formation stage
B. I - during the sporophyte formation stage, II - during the spore formation stage
C. I - during the gamete formation stage, II - during the spore formation stage
D. I - during the gametophyte formation stage, II - during syngamy stage
Solution: Mitosis or equational division is the cell division where the number of chromosomes in the offspring remain the same as the parent cell. The zygote undergoes mitosis and forms the sporophyte. Mitosis also takes place to form the multicellular gametophyte. The gametophyte is haploid, independent and photosynthetic. It produces gametes by mitosis. Hence the correct option is a.
Q3. Choose the option with the correct statements with respect to bryophytes:
I. They could play a major role in ecological succession.
II. They were the first land plants.
III. The height of the tallest bryophyte is less than 1 m.
IV. Vascular tissues are present in them.
- Only I and IV
- Only I, II and III
- Only II and III
- Only I and II
Solution: The tallest bryophyte is less than 1 metre. They will not grow taller, since they lack vascular tissues like xylem and phloem. Xylem and phloem are used for long-distance transport of nutrients in tall plants. They also play a major role in ecological succession. They are also included in the first land plants. Hence the correct option is b.
Q4. Rearrange the following life cycle events in Marchantia starting from the formation of the zygote :
I. Formation of sporophyte.
II. Spore germination.
III. Formation of gametophyte.
IV. Gamete formation.
V. Reduction division.
VI. Formation of spores.
VII. Syngamy.
- I→II→III→IV→V→VI→VII
- VII→I→V→VI→II→III→IV
- I→V→VI→II→III→IV→VII
- V→IV→VII→II→I→III→VI
Solution: Marchantia, a bryophyte, has a haplo-diplontic life cycle in which both gametophyte and sporophyte have multicellular, visible structures. The male gamete is called antherozoid (n). The female gamete is called egg (n). They are haploid and fuses to form a diploid zygote. This is known as syngamy. The zygote undergoes mitosis, it will form the sporophyte. The sporophyte is diploid and it is dependent on the gametophyte for nutrition. Sporophyte produces spores by reduction division or meiosis. These spores germinate in a region which has enough moisture. Spores undergo mitosis, then it will form a multicellular gametophyte. The gametophyte is haploid, independent and photosynthetic. It produces gametes by mitosis. The fusion of gamete during syngamy results in the formation of zygote. Hence the correct option is c.
FAQs
Q1. Explain the gametophyte of Bryophyta?
Solution: Bryophyta possesses both gametophyte (n) and sporophyte (2n). Gametes are produced by the gametophyte. The sex organs are multicellular. Male sex organ is called archegonium which produce antherozoids. Antherozoids possess two flagella and are motile. A flask-shaped structure called archegonium is the female sex organ. It produces only one egg.
Q2. Explain the characteristics of liverworts by an example?
Solution: Marchantia is a small dorsiventrally flattened liverwort. They possess unicellular rhizoids. They multiply vegetatively by fragmentation. Asexual reproduction occurs by gemmae. They are unisexual or dioecious, i.e, male and female sex organs are borne on different thalli. Sex organs are present on special stalks called gametophores. Antheridiophore bears antheridium or male sex organ. It produces antherozoids. Archegoniophore possess archegonium or female sex organ.
Q3. Why do bryophytes have a haplo-diplontic life cycle?
Solution: Bryophytes possess gametophyte (n) and sporophyte (2n). Gametes are produced by the gametophyte. The fusion of egg (n) with a male gamete (n) results in the formation of a zygote (2n). Zygote develops into a multicellular embryo which eventually grows into a sporophyte (2n). Germination of spores from sporophytes results in the formation of gametophytes. As both the haploid and diploid generations occur with equal prevalence, the life cycle is said to be a haplo-diplontic.
Q4. Write down the economic importance of bryophytes?
Solution: Bryophytes can prevent soil erosion by forming dense mats on the soil. They help in primary succession on rock. Peat which is obtained from the bryophyte Sphagnum is used as a fuel. Peat is also used as a packing material as it is able to hold water. They can be used as food for herbaceous plants


