-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Applications of Redox Reactions - Redox Reactions and their Applications, Practice Problems and FAQ
Smartphones play a vital role in our daily lives. They have become a part of our lives of late. In reality, you could find people without a wristwatch but not without a smartphone, right?
Just imagine. Your smartphone’s battery runs dry and you’ll have to charge it for an hour. I suppose only then will you realise that there are people around you to interact with.
Just kidding!
Let’s get back to the topic. Where did we leave? Yeah, charging your smartphone!
Have you ever pondered the process involved in charging a smartphone? Have you ever thought of the chemistry involved?
Redox-based electrochemistry is the process involved in charging a smartphone.
Want to learn more about redox processes?
Let's get going.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is Redox Reaction?
- Redox Reactions - Applications
- Uses of Redox Reactions in Daily Life
- Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions - FAQ
What is Redox Reaction?
A redox reaction is defined as a reaction in which two separate reactants participate and electrons are transferred between them. A reaction which involves both oxidation and reduction is known as a redox reaction. When a species reacts, distinct conversions in the oxidation states can be used to identify the transport of electrons. The graphic below illustrates in great detail how an electron is transferred between two reactants during a redox reaction.
Oxidation is the process of losing electrons and causing a given reactant to become more oxidised as a result.
Reduction is the process of gaining electrons and resulting in a drop in the oxidation state of a reactant.
Oxidising agents are electron-accepting species that experience a decrease in the oxidation state in a redox reaction. Reducing agents are electron-donating species that experience an increase in the oxidation state in a redox reaction. Reducing agents are oxidised and oxidising agents are reduced in redox reactions.

Any redox reaction can be split into two half-reactions namely, the oxidation half-reaction and the reduction half-reaction.
Each of these half-reactions must be balanced when written independently in order for the number of electrons in each to be equal.

Redox Reactions - Applications
1. Applications of Redox Reaction in Electrochemistry
The redox reaction mechanism is used to release electrical energy from a battery that generates a direct current. Our daily lives, which rely on redox processes, use batteries, also referred to as electrochemical cells. For instance, the most simple example is the button cells or dry cells which are used in our remote controls, clocks and watches.

Daniell cell is an example of a galvanic cell or electrochemical cell, which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. Copper ions are reduced at the cathode and zinc ions are oxidised at the anode in the Daniell cell.
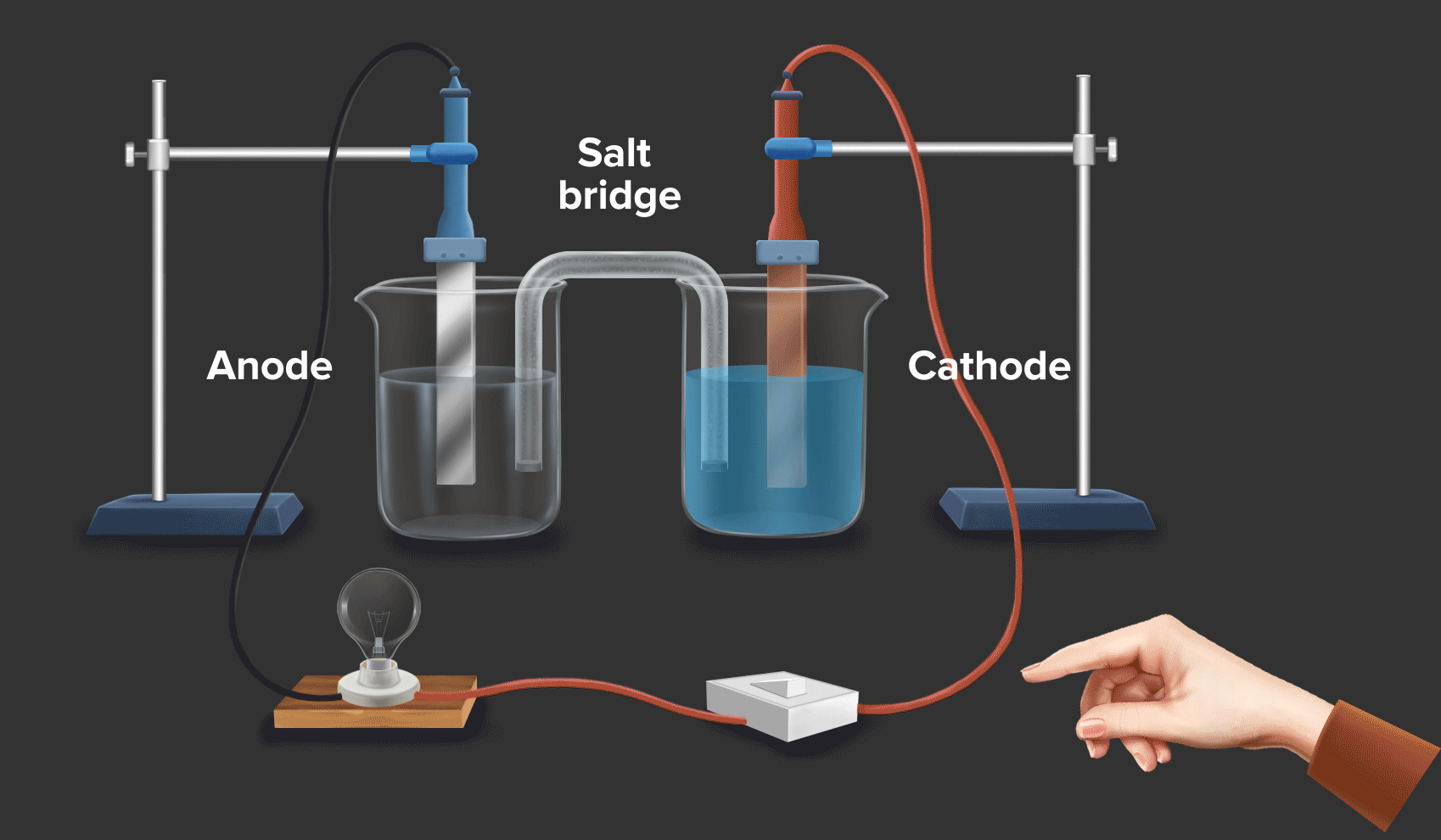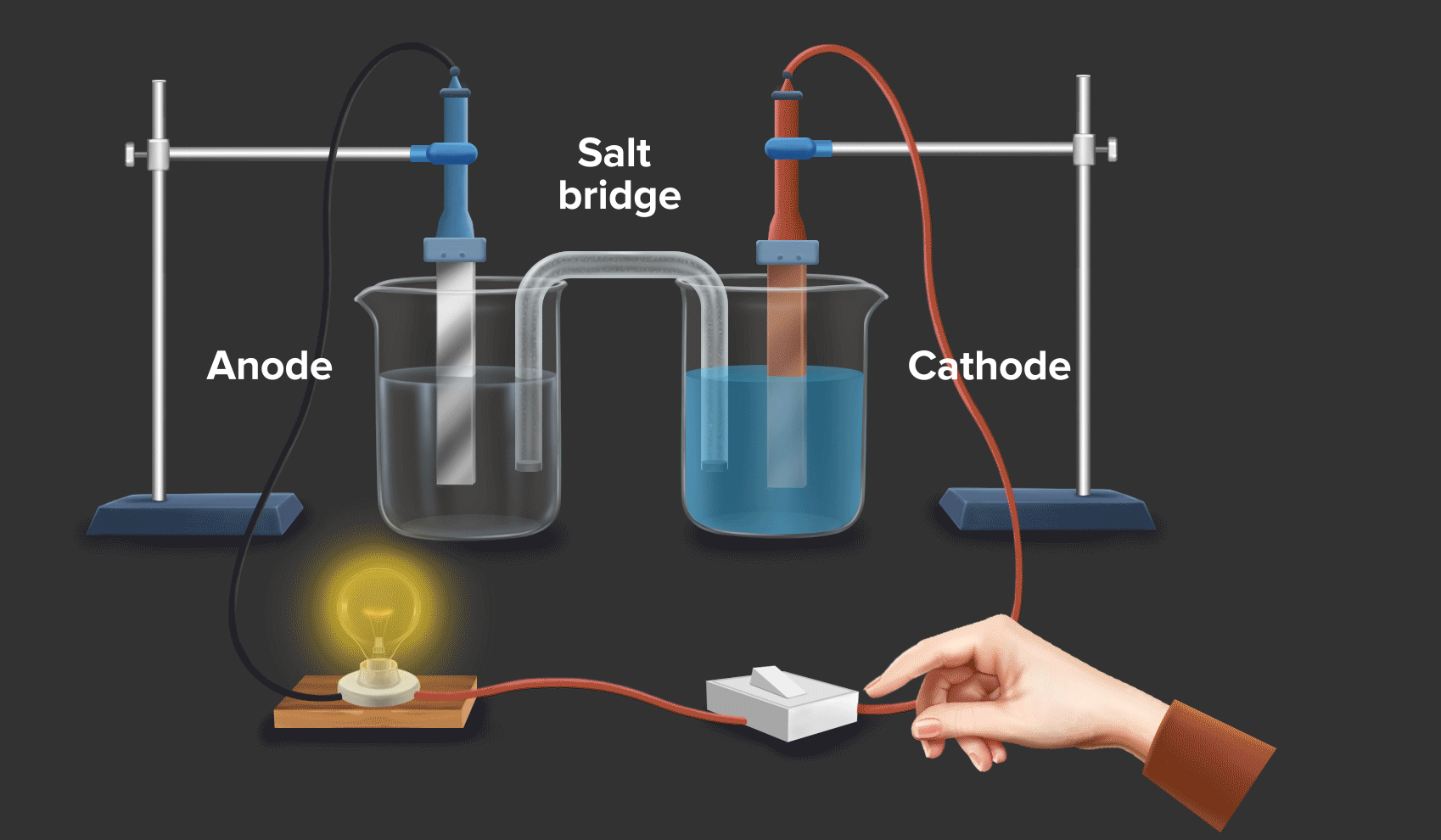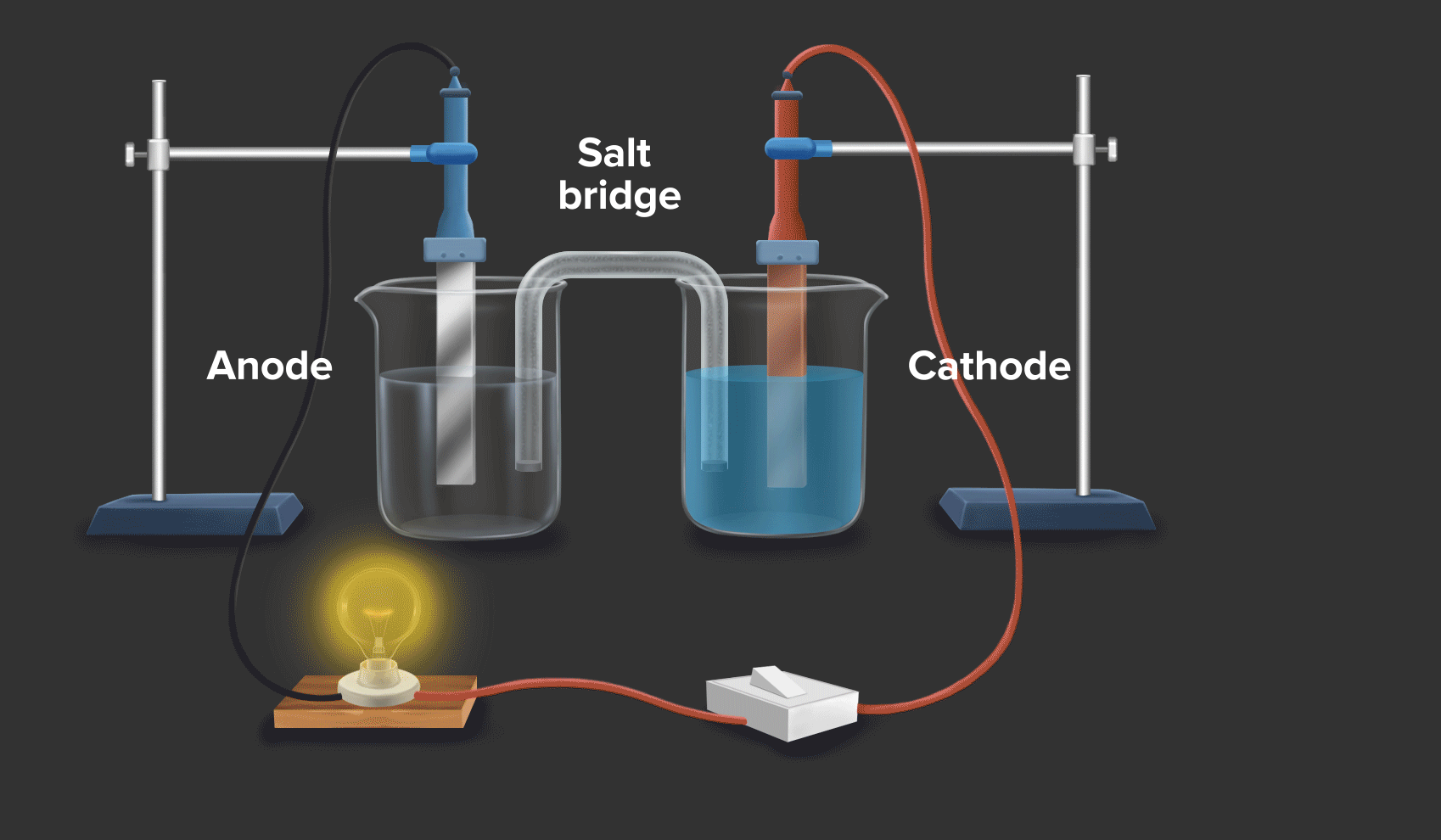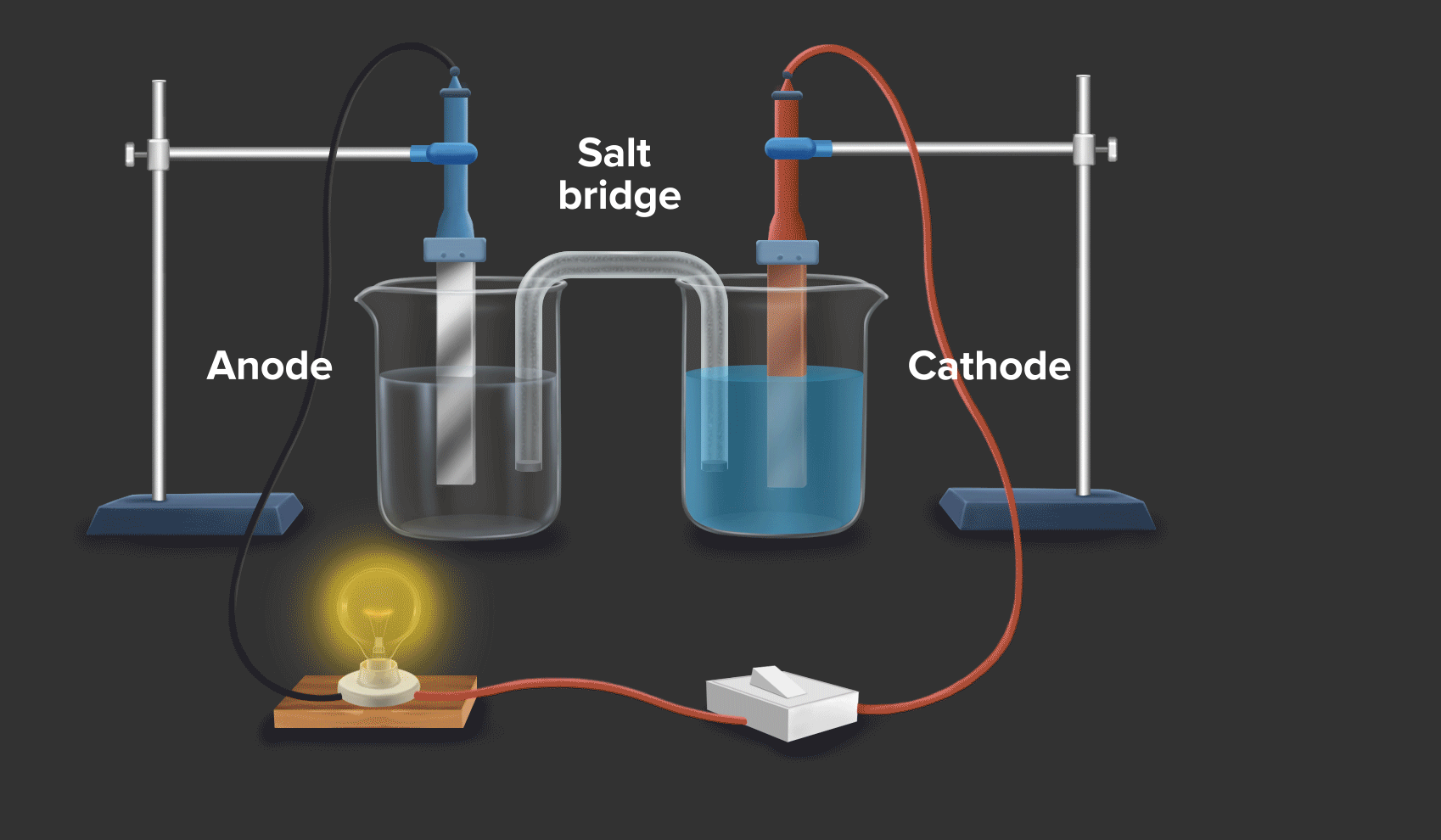
Half-cell reaction at the anode: Zn(s) --> Zn2+(aq) + 2e- |
As zinc loses the electron, hence at the anode, oxidation occurs.

Half-cell reaction at the cathode: Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- Cu(s)
As Copper gains the electron, hence at the cathode, reduction occurs.

Half-cell reaction at the anode: Zn(s) --> Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
Half-cell reaction at the cathode: Cu2+(aq) + 2e- --> Cu(s)
Overall reaction: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) --> Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
When a zinc rod is dipped in copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution, we can see that after some time solid copper gets deposited over the zinc rod and the zinc from the zinc rod gets converted into zinc sulphate (ZnSO4). This is indicated by the change in colour of the solution from blue to transparent.

The aforementioned reaction can be represented as

2. Application of Redox Reaction in Combustion
Combustion falls within the category of an oxidation-reduction reaction, making it a redox reaction. An explosion is a form of combustion and is typically classified as a redox reaction. Space rockets use redox reactions as their internal mechanism. An oxidation-reduction reaction results from the mixture of ammonium perchlorate and powdered aluminium inside the rocket boosters. The aluminium powder acts as the fuel and ammonium perchlorate acts as the oxidiser.
For example, the combustion of methane can be expressed using the chemical equation given below.
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) --> CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Oxygen (O2) is reduced and the other elements carbon and hydrogen are oxidised during combustions. O2 is the most common oxidising agent on Earth due to its abundance in the atmosphere.
3. Redox Reaction in Photosynthesis applications
Photosynthesis is the conversion of water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates in green plants.
The reaction involved is

In the aforementioned reaction, it can be seen that the water molecules are oxidised to oxygen while the carbon dioxide is brought down to carbohydrates, forming a redox reaction. Sunlight provides the necessary heat energy for this reaction to take place. An important source of nourishment for both plants and animals is provided by this reaction.
4. Redox Reaction in Photographic Films
Silver bromide is used in photography as a component of an emulsion that aids in the development of a photographic image. Because the grains of silver bromide are light-sensitive and suspended in gelatin, they can be used to make photographic emulsions. Silver bromide breaks down when exposed to light, which helps to preserve photographs.

Uses of Redox Reactions in Daily Life
1. Redox reactions are used in the electroplating process to apply a thin layer of a substance to an item. Gold-plated jewellery is made using an electroplating process.

2. Electrolysis, which is dependent on redox processes, is used to purify metals.

3. Additionally, oxidation-reduction reactions are used to sanitize water and bleach materials.
4. Redox reactions are used in the production of many chemicals, including chlorine and caustic soda.

5. By attaching them to sacrificial anodes, which go through corrosion instead, many metal surfaces can be shielded against corrosion. The galvanization of steel is a typical illustration of this method.

6. In order to produce cleaning goods, enterprises use the oxidation process.
7. The oxidation reaction of ammonia results in the production of nitric acid, which is a component of many fertilisers.

8. Alcohol absorption into the bloodstream is correlated with alcohol concentration in alveolar air. The oxidising agents in the gadget oxidise the ethanol present in the breath when the user breathes into it.

The reaction involved is given as follows

Practice Problems
Q1. Pick out the redox reaction among the given reactions?
- NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) --> NaCl(s) + H2O(aq)
- AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) --> AgCl(|) + NaNO3(aq)
- 2NaCN(aq) + H2SO4(aq) --> 2HCN(aq) + Na2SO4(aq)
- Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) --> ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Answer: D)
Solution: A chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a participating chemical species changes is referred to as an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox reaction.
In option A, there is no change in the oxidation state of any element, indicating that no oxidation or reduction is occurring here. This indicates that this is not a redox reaction.Na(+1 ), H(+1), Cl(-1), O(-2) remains the same after the reaction.
In option B, no element's oxidation state changes, indicating that no oxidation or reduction is taking place. This indicates that the reaction is not redox in nature.
Ag(+1 ), H(+1), Cl(-1), O(-2), N(+5) remains the same after the reaction.
In option C, no element's oxidation state alters, proving that neither oxidation nor reduction is occurring. This suggests that the reaction is not a redox reaction.
Ag(+1 ), H(+1), Cl(-1), O(-2), S(+6) that remains the same after the reaction.
In option D, there is clearly a change in the oxidation states of Zn and Cu which involve oxidation and reduction simultaneously. Hence, this given reaction is a redox reaction.

So, option D) is the correct answer.
Q2. Pick out the non-redox reaction among the given reactions?\
- CuO(s) + H2(g) --> Cu(s) + H2O(aq)
- P4 --> PH3 + H2PO2-
- HNO3(aq) + CuO(s) --> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(aq)
- FeCl3(aq) + HCl(aq) --> HFeCl4(aq)
- 1) and 3)
- 1) and 2)
- 2) and 4)
- 3) and 4)
Answer: D)
Solution: A chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a participating chemical species changes is referred to as an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox reaction.
In reaction 1), there is clearly a change in oxidation states of H and Cu which involve oxidation and reduction simultaneously. Hence, the given reaction is a redox reaction.
Reduction: CuO (2+2) --> Cu (0);
Oxidation: H2(0) --> H2O (+1)
In reaction 2), there is clearly a change in the oxidation states of P, which involve both oxidation and reduction. As a result, the given reaction is a redox reaction.
Reduction: P4(0) --> PH3(-3);
Oxidation: P4(0) --> H2PO2- (+1)
In reaction 3), no element's oxidation state changes, indicating that no oxidation or reduction is taking place. This indicates that the reaction is not redox in nature.
The oxidation states of the elements [ H(+1), Cu(+2), O(-2), N(+5)] remains the same after the reaction.
In reaction 4), no element's oxidation state alters, proving that neither oxidation nor reduction is occurring. This suggests that the reaction is not a redox reaction
The oxidation states of the elements [ H(+1), Cl(-1), Fe(+3)] remains the same after the reactions.
Hence, options 3) and 4) are non-redox reactions.
So, option D) is the correct answer.
Q3. Which of the following is an only oxidising agent?
- H2SO4
- H2S
- SO2
- Both (A) and (C)
Answer: A)
Solution:
In option (A), S in H2SO4 is in the highest oxidation state (+6). So, S can accept electrons and exist in lower oxidation states (+4, +2, -2). Hence, it behaves as an oxidising agent.
In option (B), S in H2S is in the lowest oxidation state (-2). So, S can donate electrons and exist in higher oxidation states (+4, +2, +6). Hence, it behaves as a reducing agent.
In option (C), S in SO2 is in an intermediate oxidation state (+4). So, S can either donte electrons and exist in a higher oxidation state (+6) or can accept electrons and exist in lower oxidation states (+2, -2). Hence, it behaves either as a reducing agent or as an oxidising agent.
So, option A) is the correct answer.
Q4. Which of the following statements is correct about redox reactions?
- In redox processes, reducing agents are electron-accepting species that experience a decrease in oxidation state.
- The electroplating of various metals on jewellery is a redox reaction application.
- In redox processes, oxidising agents are electron-donating substances that donate excess electrons and experience an increase in oxidation state.
- All of these
Answer: A)
Solution: Statement B is true as electroplating by the electrolytic cell is an application of redox reactions.
Electron-accepting species that experience a decrease in oxidation state are called oxidising agents. Electron-donating substances that donate excess electrons and experience an increase in oxidation state are called reducing agents. Hence, statements A and C are incorrect.
So, option B) is the correct answer.
Frequently Asked Questions - FAQ
Question 1. Is cellular respiration a reduction or an oxidation reaction?
Answer. Cellular respiration is a redox reaction. Respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that involve both electron loss and gain. As a result, it is known as an oxidation-reduction or redox reaction. In this context, oxidation refers to electron loss, while reduction refers to electron gain.
Question 2. Is it true that every chemical reaction is a redox reaction?
Answer. No, not all chemical reactions are redox in nature. Non-redox reactions include acid-base neutralisation reactions, double decompositions, and precipitation reactions.
Question 3. Why is redox important to understand?
Answer. Redox reactions lead us down a crucial conceptual path in chemistry. Our understanding of redox begins with oxygen gain and loss and develops into hydrogen gain and loss. This paves the way for understanding all chemical reactions as electron rearrangements.
Question 4. What happens if oxidation does not occur in nature?
Answer. There will be no life if there is no oxidation because it affects all metabolic reactions that occur in nature. The process of reacting to different substances with oxygen is known as oxidation.
Related Topics
|
Iodometric Titrations |
Titration Methods |
|
Non Aqueous Titration |
Iodometric and Iodimetric Titrations |
|
Oxidising and Reducing Agents |
Difference Between Endpoint and Equivalence Point |


