-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Human excretory system: Kidneys, Ureters, Urinary bladder, Urethra, Practice Problems and FAQs
You all know about kidneys, they are our major excretory organs. Did you know, our kidneys filter our blood around 400 times every day! Our kidneys filter the liquid waste from our body in the form of urine.
How do they perform this excretory process? Are there any special units in kidneys for it? Yes. Each kidney has millions of filtering units, called nephrons. You know the colour of our urine can tell us whether we are drinking enough water or not.
It is generally light yellow if we are drinking sufficient water and dark yellow if we are not drinking enough water. Now would you like to know more about our excretory system. The excretory system in humans consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. So let us understand more about the excretory system in this article.
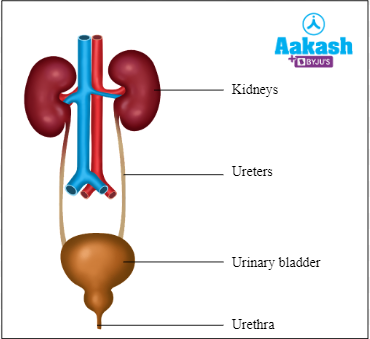
Fig: Human urinary system
Table of contents
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
- Nephrons
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
- Practice Problems
- FAQs
Kidneys
Kidneys are reddish brown, bean-shaped structures located between the levels of the last thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae close to the dorsal inner wall of the abdominal cavity. An adult human kidney measures 10 - 12 cm in length, 5 - 7 cm in width, 2 - 3 cm in thickness. An average weight of a single kidney is 120 - 170 g. In humans, the right kidney is slightly below the left one, due to the presence of liver on the right side. The human kidney is metanephric.
Outer layer
The outermost layer of the kidney is a tough capsule known as the renal capsule. It protects the kidney from infections and injuries. There is a layer of fat around the renal capsule called adipose capsule. The renal fascia or Gerota's capsule or Gerota's fascia is made up of fibrous membrane present outside the adipose capsule. It protects the kidney.
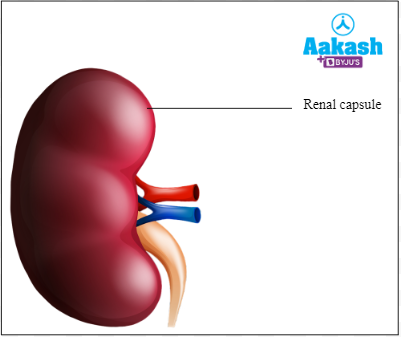
Fig: Outer layer of kidney
Hilum
It is a notch present towards the centre of the inner concave surface of the kidney. It is the entry point of the ureter, blood vessels and nerves.
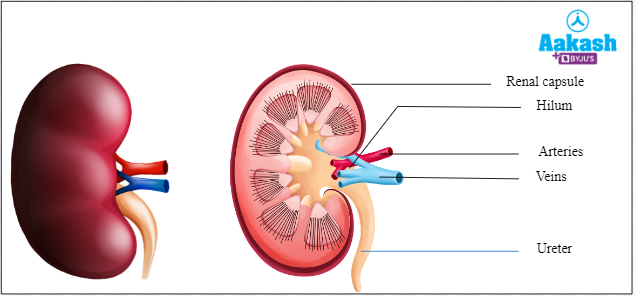
Fig: Structure of kidney
Retroperitoneal arrangement
Organs are said to be retroperitoneal, when they have peritoneum on their anterior side alone. These structures are not suspended normally by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall. For example, kidneys have peritoneal covering present only on the ventral side, fused with the body wall on the dorsal side.
Internal structure of kidney
There are two zones in the inner part of the kidney as follows:
- Medulla (Inner)
- Cortex (Outer)
Cortex
It is the outer zone of the kidneys. It extends in between the medullary pyramids as renal columns called columns of Bertini.
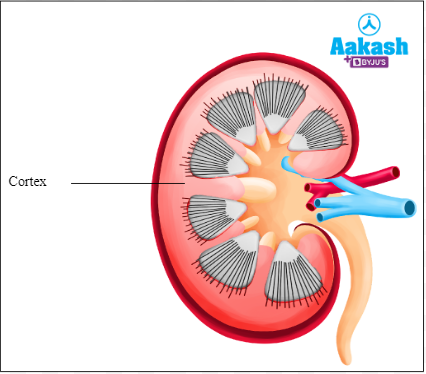
Fig: Cortex
Medulla
It is the inner part of the kidneys. It is divided into a few conical masses known as medullary pyramids. It is 15 - 16 in number. The pyramids project into the next portion of the kidney which is called the minor calyx (plural - calyces). Broad bases of the medullary pyramids face the cortex. Minor calyces lead to major calyces.
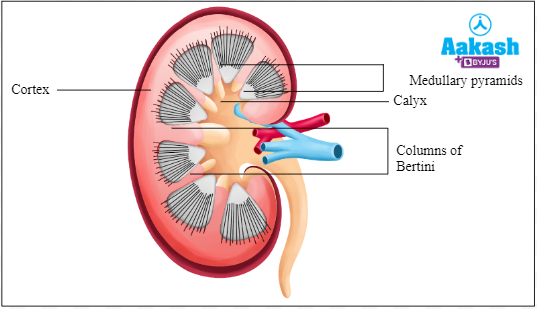
Fig: Medulla
Renal pelvis
The cortical region close to medulla is known as the juxtamedullary area.The calyes open into a funnel shaped region, called the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis opens into the ureter.
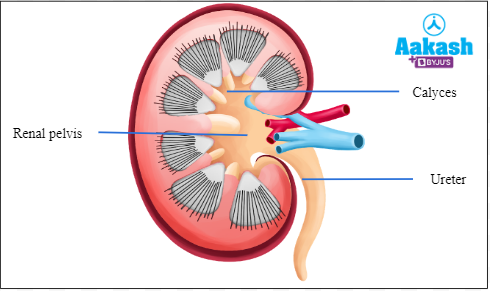
Fig: Renal pelvis
Ureter
They are paired, long thin, whitish tubes made of smooth muscles. Its length is about 25 - 30 cm, and diameter is about 3 mm. It starts from the hilum part of the kidney, descends along the abdominal wall, bends obliquely inwards and upwards to open into the urinary bladder. They are composed of transitional epithelium. They carry urine from kidneys to the urinary bladder.
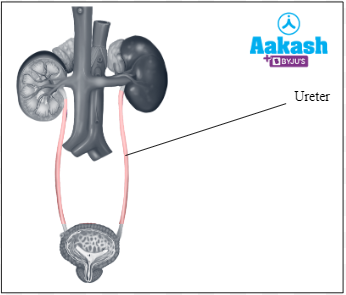
Fig: Ureter
Urinary Bladder
It is a hollow muscular elastic organ, which varies in shape, size, and position, depending upon the amount of urine present in it. The fully distended bladder is ovoid in outline. It is present in the pelvic cavity. It has a thick muscular distensible wall which is lined by the transitional epithelium. This epithelium has the ability to expand to allow the storage of large amounts of urine.
Wall of urinary bladder
The muscles of the wall (detrusor muscles) consists of three layers of smooth muscles as follows:
Inner muscle layer
It is made up of longitudinal fibres.
Middle muscle layer
It is made up of circular fibres
Outer muscle layer
It is made up of longitudinal fibres.
Parts of urinary bladder
Urinary Bladder has four parts as follows:
Apex
It is the anterosuperior part of the urinary bladder that points towards the abdominal wall.
Fundus
It is the postero inferior part of the bladder.
Body
It is the large area situated between the apex and the fundus.
Neck
It is the constricted part of the bladder that leads to the urethra. It has a triangular shaped area called trigone. It has openings for ureters and an internal urethral orifice.
Sphincters
The urinary bladder has two sphincters, involuntary internal and voluntary external sphincters. During the time of micturition, the sphincters normally undergo relaxation, which is directed by the cerebral cortex.
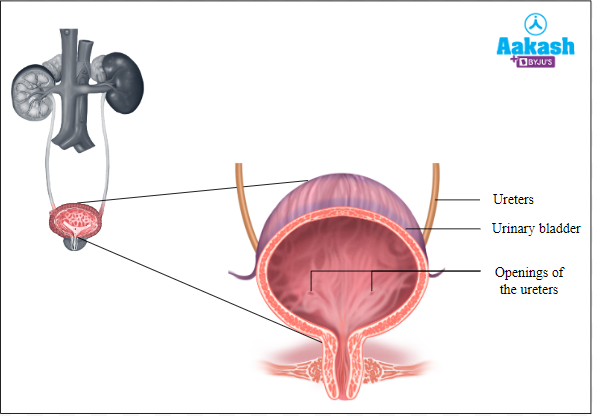
Fig: Urinary bladder
Urethra
It is a thin tube present at the lower end of the urinary bladder,which starts from the neck of the urinary bladder and opens outside the body. It is short in females (2 - 4 cm) and quite long in males (20 cm). It passes urine as well as semen (sperms and the secretions of the accessory glands called seminal plasma) through an aperture called urogenital aperture, which is present at the tip of the penis in men. It passes urine in females.
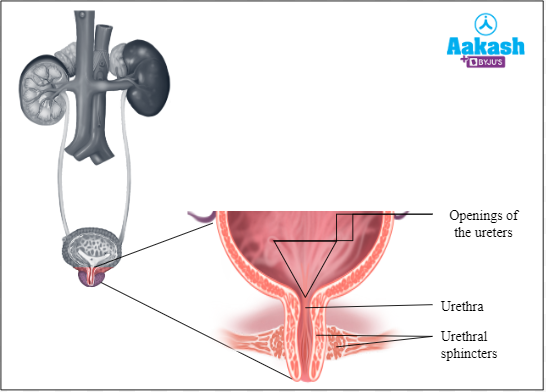
Fig : Urethra
Practice Problems
Q1. The urinary bladder is lined by __________ epithelium.
A. simple columnar epithelium
B. simple squamous epithelium
C. simple cuboidal epithelium
D. transitional epithelium
Solution: The urinary bladder is lined by transitional epithelium. It is a type of stratified epithelium. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed by the urinary bladder.
Q2. What is the position of the kidney with respect to each other?
Answer: The kidney lies in the retroperitoneal region of the abdomen. It is present on either side of the vertebral column. The right kidney is placed slightly lower due to the position of the liver.
Q3. Which duct drains urine out of the urinary bladder ?
Answer: Urethra is a duct that transports urine that is stored in the urinary bladder out of the body. Ureters join the kidneys and the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder receives urine from the ureters.
Q4. Where is trigone found in human beings?
Answer: The trigone is a triangular muscular structure. It is located between the bladder and urethra. It is formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral orifice. The effective connection between the ureters and the trigone is important for the proper functioning of the ureteral valve mechanism
FAQs
Q1. Can a person live with one kidney?
Answer: A person can be born with only one kidney in certain cases. This condition is normally called renal agenesis. In kidney dysplasia, a person is born with two kidneys, but only one of them works properly. The people born with only one working kidney lead normal, healthy lives.
Q2. What will happen if one kidney is removed from a person?
Answer: Nothing will happen to the person if one kidney is removed. The person will survive and remain normal in this case. The remaining kidney will become hypertrophied and perform the function.
Q3. Can a female person donate a kidney to a male?
Answer: Yes, a female can donate a kidney to male. But female donor kidneys do not function as well in men due to their smaller size as per the latest studies.
Q4. Which are the hormones secreted by the kidneys?
Answer: The kidney secretes various hormones like erythropoietin (EPO), calcitriol or 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol and renin.


