-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell, Practice Problems and FAQs
In this twenty-first century everyone has their own electronic gadgets, like mobile phones, laptops, tablets, smart watches etc. Do you know how they work? Every electronic gadget has a chipset which controls all the core set of functions in them. A chipset is an integrated circuit of a motherboard which can combine all the basic components of an electronic system on one chip. There are different types of chipsets for various gadgets according to their type and requirements. So, we can call the chipset the basic unit of an electronic gadget.
Now, we will compare this concept with the biological cell. We know that the cell is the basic unit of life. Just like chipsets differ in different gadgets according to the functions of a gadget, the type of cell differs in structure and function in different groups of organisms.
The major two types of cells present are the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cells. The major difference between a prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell is the presence or absence of a true nucleus. The cell with a true nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane is called a eukaryotic cell and the cell without a true nucleus is called a prokaryotic cell. Animal cells and plant cells are examples of eukaryotic cells and bacterial cells are examples for prokaryotic cells.

Fig: Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
If we consider the structure of a eukaryotic cell, there are many differences present between a plant cell and an animal cell. The variations in the biological functions performed by the plants and animals is the basic reason for the differences in their cells. So in this article we are going to discuss more about the differences between the cells of plants and animals.
Table of contents
- Eukaryotic cell
- Plant cell
- Animal cell
- Difference between plant cell and animal cell
- Practice Problems
- FAQs
Eukaryotic cell
To support and conduct basic life processes, the cell contains certain structures inside it and also performs various functions. Cells have the ability to multiply and divide to form the entire body of living organisms. Not all cells are similar. Nucleus is the cell organelle which is known as the brain of the cell and controls all the functions of a cell.
The type of cell which has a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane is called a eukaryotic cell. The organisms which contain eukaryotic cells are present in the Kingdom Protista, Mycota or Fungi, Plantae or Metaphyta and Animalia or Metazoa.

Fig: Nucleus of the eukaryotic cell
Plant cell
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell with a true nucleus which is membrane bound. It has an additional cell wall, outside the cell membrane which makes it unique from the animal cell. Inside the plant cell, along with the nucleus there are many other cell organelles which play various functions for the sustenance of the cell.
The shape of a plant cell is rectangular. It is larger than the animal cells. But they both have some cell organelles which are common, because both are eukaryotic. But plant cells are quite different from animal cells which can be clearly identified through an electron microscope.

Fig: Structure of a plant cell
Structure of plant cell
The cell organelles are dispersed in the cytoplasm present inside the plant cell. Some organelles are membrane bound and some are not in the plant cell. The cell organelles present in a plant cell are as follows:
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Nucleus
- Plastids
- Central vacuole
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Ribosomes
- Mitochondria
- Cytoskeleton
- Microbodies
Cell wall
It is the outer layer of the plant cell which is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. It protects the plant cell from mechanical stress and also provides a form and structure to the cell.

Fig: Structure of plant cell wall
Cell membrane
The semipermeable membrane made up of lipid bilayer present internal to the cell wall is called cell membrane. It regulates the entry and exit of substances in the cell.

Fig: Structure of the cell membrane
Nucleus
Being eukaryotic, the plant cells have a double membrane bound nucleus which stores the hereditary information in DNA and regulates cell division, metabolism and growth.

Fig: Structure of nucleus
Plastids
The membrane bound organelles which store substances in the plant cell are called plastids. Some plastids provide colour to plants and help in photosynthesis. They have their own DNA and are called semi autonomous organelles. Some of the vital types of plastids are as follows:
- Leucoplasts
- Chloroplasts
- Chromoplasts
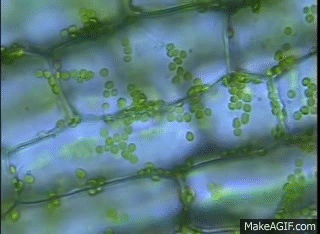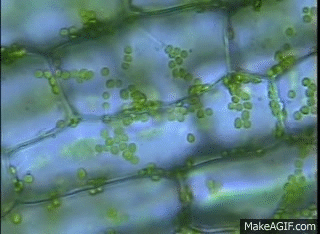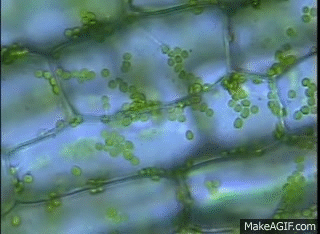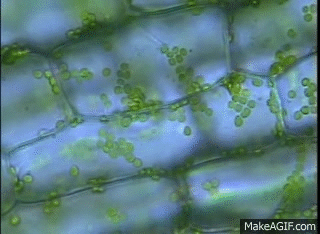
GIF: Chloroplast
Central vacuole
The 30% volume of the plant cell is occupied by a central vacuole, which is covered with a single membrane called tonoplast. The central vacuole helps in storage of water, food, etc. It also helps to maintain turgidity of the cell.

Fig: Structure of vacuole of a typical plant cell
Endoplasmic reticulum
The double-membranous cell organelle which helps in the protein synthesis, calcium storage and lipid metabolism in the cell is called endoplasmic reticulum. If ribosomes are present on the membrane then it is called rough endoplasmic reticulum and if ribosomes are absent, then it is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum.

Fig.: Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
The sac-like organelle, with smooth and flat layers seen near the nucleus is called Golgi apparatus. They are responsible for the modification, packaging and distribution of proteins and fats to different parts of the cell. In plant cells Golgi bodies are referred to as dictyosomes. The Golgi apparatus consists of a stack of flattened sacs called cisternae and vesicles associated with it.

Fig: Structure of Golgi apparatus
Ribosomes
The smallest non-membrane bound organelles made up of RNA and proteins are called ribosomes. Proteins are synthesised in ribosomes. Ribosomes in plant cells are of 80S type and possess a 60S large subunit and a 40S small subunit.

Fig: Structure of ribosome
Mitochondria
It is known as the powerhouse of the cell and has a double membrane made up of inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. The space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane is called the peri mitochondrial space. The foldings present in the inner mitochondrial membrane are called cristae. Mitochondria provide energy in the form of ATP by breaking down carbohydrates and sugar molecules.

Fig: Structure of the mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
Microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate filaments are collectively called the cytoskeleton.
They can contract and are made up of actin which is a protein. Their main function is to maintain the shape of the cell. They also help the cell in the internal organisation, division and movements.

Fig: Structure of cytoskeleton
Microbodies
The membrane bound vesicles containing various enzymes are called microbodies or cytosomes. There are three main types of microbodies that are present in plant cells. They are spherosomes, glyoxysomes and peroxisomes.

Fig: Structure of peroxisomes
Animal cell
An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell with a true nucleus which is double membrane bound. Animal cells are smaller than the plant cells. They have an erratic shape because they lack cell walls. But they have many cell organelles similar to plant cells, because they both originated from the same eukaryotic cells. Animal cells also have a nucleus with a double membrane and many other membrane bound cell organelles. These cell organelles carry out all the functions of an animal cell.

Fig: Structure of animal cell
Structure of animal cell
Animal cells contain the plasma membrane or cell membrane that encloses the cytoplasm inside the cell. Animal cells also have membrane bound cell organelles and non membranous cell organelles. The cell organelles present in animal cell are as follows:
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- Microbodies
- Ribosomes
- Cytoskeleton
- Centrosome
- Cilia and flagella
Membrane bound cell organelles
Among the above given organelles, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, cilia, flagella and microbodies are membrane bound cell organelles. The cell organelles which are present outside the cell membrane are cilia and flagella.
Non membranous cell organelles
The non membranous cell organelles are ribosomes, cytoskeleton and centrioles.
Uniqueness of animal cell
The structure and function of cell organelles like nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosomes, cytoskeleton are similar in animal cells and plant cells. But, the organelles like microbodies are different in plants and animals.
The cell wall, a central vacuole and plastids which are present in plant cells are absent in animal cells. Cell organelles like centrosome, cilia and flagella are unique to animal cells, when compared with plant cells. Centrosomes can be found in some lower plants but they are absent in higher plant cells.
Now we will discuss those organelles which are different in animal cells from plant cells.
Microbodies
The membrane bound vesicles containing various enzymes are called microbodies or cytosomes.
Out of three microbodies, only two are present in animal cells. They are peroxisomes and glyoxysomes.
Centrosomes
The non membrane bound organelles located near the nucleus are called centrosomes. Diplosomes are a pair of centrioles seen in a cell during the non-dividing phase and they are arranged perpendicularly inside the centrospheres or kinoplasm, which is a specialised cytoplasm. So the centriole and centrospheres are together called the centrosome. Centrosomes duplicate during prophase and form spindle fibres that help to pull the chromosomes to both ends of the cells.

Fig: Structure of centrosome
Cilia and Flagella
The hair-like outgrowth arises from the cell membranes which are covered by plasma membranes called cilia and flagella. They are mainly used for locomotion and sensory functions. The major difference between cilia and flagella is that cilia will be more in number and shorter than the flagella.

Fig: Structure of cilia and flagella
Difference between plant cell and animal cell
We have discussed briefly about the plant and animal cells above. Now we will tabularise the major differences between the plant and animal cell.
Plant cell |
Animal cell |
|
The size of the plant cell is 10 to 100 micrometres long |
The size of an animal cell is 10 to 30 micrometres long |
|
Cell wall is the outermost protective layer |
Cell membrane is the outermost protective layer |
|
It cannot change shape |
It can change shape because of the absence of cell wall |
|
Plastids are present in the cell like chloroplast, chromoplast and leucoplast |
Plastids are absent in the animal cell |
|
Photosynthesis occurs with the help of chlorophyll which is present in a plastid called chloroplast |
Photosynthesis can not take place because of the absence of chlorophyll |
|
Number of mitochondria are less |
Number of mitochondria are more |
|
A large central vacuole is present |
Vacuole is absent or very few with smaller size |
|
Due to the presence of vacuole, the nucleus is pushed into one side of the cytoplasm |
Nucleus occupy almost at the centre of the cell |
|
The storage form of carbohydrate or energy is starch |
The storage form of carbohydrate or energy is glycogen |
|
Centrosomes are absent |
Centrosomes are present |
|
Centrioles are usually absent except in motile cells of lower plants |
Centrioles are present |
|
Golgi apparatus consists of a number of distinct or unconnected units called dictyosomes |
Golgi apparatus is either localised or consists of a well connected single complex |
|
Spherosomes are present |
Spherosomes are absent |
|
Plasmodesmata are junctions present in plant cells |
Animal cells possess gap junctions, tight junctions and desmosomes |
|
Plant cell synthesise all twenty one amino acids required for growth |
Animal cells cannot synthesise all the twenty one amino acids |
|
Anastral mitosis is shown by plant cells |
Animal cells shows amphiastral mitosis |
|
Spindle formed during cell division do not possess asters at the poles |
Spindle formed during cell division possess asters at each pole |
|
Examples include cell of an onion peel
Fig: Onion peel cell under microscope |
Examples include human cheek cell
Fig: Human cheek cell under microscope |
Practice Problems
1. Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about the plant cells?
I) Additional cell wall outside the cell membrane makes plant cells unique from animal cells.
II) The shape of a plant cell is rectangular.
III) Plastids perform photosynthesis and give colour to plant cells.
IV) Golgi bodies in plant cells are of 80S type and have a 60S large subunit and a 40S small subunit.
- I and III
- III only
- IV only
- III and IV
Solution: A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell with a true nucleus which is membrane bound. It has an additional cell wall, outside the cell membrane which makes it unique from the animal cell. The shape of a plant cell is rectangular. It is larger than the animal cells. The membrane bound cell organelles which store substances in the plant cell are called plastids. Some plastids like chloroplasts provide colour to plants and help in the process of photosynthesis. The sac-like organelle, with smooth and flat layers seen near the nucleus is called Golgi apparatus. They are responsible for the modification, packaging and distribution of proteins and fats to different parts of the cell. The smallest non-membrane bound organelles made up of RNA and proteins are called ribosomes. Proteins are synthesised in ribosomes. Ribosomes in plant cells are of 80S type and have a 60S large subunit and a 40S small subunit. Hence the correct option is c.
2. Assertion: The nucleus of a plant cell located on one side of the cytoplasm.
Reason: A large central vacuole is present in the plant cell.
Which of the following statements satisfy the above assertion and reason?
- Both the assertion and the reason, are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
- Both the assertion and the reason, are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
- Assertion is true but the reason is false
- Both the assertion and the reason are false
Solution: A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell with a true nucleus which is double membrane bound. It has an additional cell wall, outside the cell membrane which makes it unique from the animal cell. Inside the plant cell, along with the nucleus there are many other cell organelles present which play various functions for the sustenance of the cell. The 30% volume of the plant cell is occupied by central vacuole, which is covered with a single membrane called tonoplast. The central vacuole helps in storage of water, food, etc. It also helps to maintain turgidity of the cell. The presence of a large central vacuole is one thing which makes the plant cell unique from the animal cell. This vacuole pushes the nucleus to one side of the cytoplasm and it is the reason why the nucleus is seen on one side of the plant cell. Therefore the assertion is true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Hence the correct option is a.
3. Which of the following organelles are unique to animal cells when compared with cells of higher plants?
- Cell membrane and cell wall
- Centrioles and centrosome
- Vacuoles
- Microbodies
Solution: Animal cells contain the plasma membrane or cell membrane that encloses the cytoplasm inside the cell and they lack a cell wall. Animal cells also have membrane bound cell organelles and non membranous cell organelles. The structure and function of cell organelles like nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosomes and cytoskeleton are similar in animal cells and plant cells. Even though the organelles like microbodies are present in animals, out of three microbodies, only two are present in them. They are peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. So we cannot say microbodies are unique to animal cells, since they are present in plant cells too. The central vacuole and plastids which are present in plant cells are absent in animal cells. Cell organelles like centrosome, cilia and flagella are those which are unique to animal cells, when compared with higher plant cells. Centrosomes can be found in some lower plants but they are absent in higher plant cells. The non membrane bound organelles located near the nucleus are called centrosomes. Diplosomes are a pair of centrioles seen in a cell during the non-dividing phase and they are arranged perpendicularly inside the centrospheres or kinoplasm, which is a specialised cytoplasm. So the centriole and centrospheres are together called the centrosome. Hence the correct option is b.
4. Explain cilia and flagella with examples?
Answer: The hair-like outgrowths from the cell membrane which are covered by plasma membranes are called cilia and flagella. They are mainly used for locomotion and sensory functions. The major difference between cilia and flagella is that cilia will be more in number and shorter than the flagella. Cilia are present on the epithelial cells of several internal organs like lungs, trachea and digestive system in animals. Sperm is an example for the cell with flagella in animals.

GIF: Sperms with flagella
FAQs
1. Why are centrioles absent in cells of higher groups of plants?
Answer: A pair of centrioles called diplosomes are seen in the non-dividing phase of a cell. They are arranged perpendicularly inside the centrospheres or kinoplasm, which is a specialised cytoplasm. So the centriole and centrospheres are together called the centrosome. The function of centrioles is to pull the chromosomes to both ends of the cell by forming spindle fibres. In plants there are spindle fibres outside the nuclear envelope. Hence they do not need to use centrioles for cell division. As a result centrioles are absent in higher groups of plants, but they can be seen in some lower groups of plants.
2. What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cilia and flagella?
Answer: The hair-like outgrowths from the cell membrane which are covered by plasma membranes are called cilia and flagella. They are mainly used for locomotion and sensory functions. But prokaryotic and eukaryotic cilia and flagella have differences in their movement and structure. The flagella of prokaryotes are smaller and simple, but it is larger,whip-like and complex in eukaryotes. The flagella of eukaryotes are attached through basal bodies to the cell at the cell membrane. The location of prokaryotic flagella is outside the plasma membrane. The movement of flagella is rotatory in prokaryotes, while it is bending in eukaryotes. The prokaryotic flagella is made up of flagellin and eukaryotic flagella is made up of tubulin.


GIF: Movement of flagella and cilia in eukaryotic cells - Euglena and Paramoecium
3. Why is there a lesser number of mitochondria in plants than in animals?
Answer: Mitochondria is known as the powerhouse of a cell, because it provides energy needed for the cell and the organism to survive. Animals need more energy to walk, run and move as they are motile and not sedentary. But plants being stationary they do not need much energy to carry out their metabolic activities. Whatever energy they need, they are getting through the process of photosynthesis, because plants possess chloroplasts. Animals do not possess chloroplasts and energy is generated only by mitochondria in them. These are the reasons why plants possess a lesser number of mitochondria than animal cells.
4. Which is the smallest cell in the biological world?
Answer: The smallest living cell in the biological world is Mycoplasma. The minimal size of Mycoplasma is 0.2 micrometres. Mycoplasma is a genus of bacteria that causes pneumonia in humans. They lack a cell wall around the plasma membrane. Hence the peptidoglycan is also absent, which makes them naturally resistant to antibiotics that will normally target the synthesis of the cell wall.
YOUTUBE LINK: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lq0wyc1wlmw




