-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Glycogen- Carbohydrate Type, Significance, Structure, Similarities and Differences between Glycogen and Starch, Practice Problems, FAQs
You know that motor vehicles need the fuel petrol or diesel to burn and produce the energy for running. The fuel is also to be securely stored in a tank and consumed only as and when required. Again the fuel is not directly available and has to be prepared or produced from multiple sources and by different technologies.

The same is the case with biotic species also. All animals and plants need energy for their functioning and living. The energy-producing fuel for them is glucose. This glucose is not readily available as such. Glucose is prepared from the consumed food by animals and from starch formed by photosynthesis by plants. Glucose isolated from food is not freely available as such in the body but is stored as glycogen in animals.
In the case of animals, the glycogen is stored in the liver. Remembering the body functions even while resting or sleeping, there is a continuous requirement of energy and hence a need for glucose- the energy producer. When the energy is required by the body or during fasting or starvation, glycogen present in the body gets converted into glucose by a process known as glycogenolysis. This aids in the maintenance of blood glucose levels by replenishing the body's decreased glucose levels.
Let's have a tour with this article to understand more information related to glycogen.
Table of content
- Glycogen
- Structure of glycogen
- Significance and importance of glycogen
- Difference between glycogen and starch
- Practice problems
- FAQs
Glycogen
Glycogen is a polymer molecule made from the glucose monomer. This polysaccharide is
stored as a source of glucose for microorganisms and animals. The glucose polysaccharide structure demonstrates the primary form of storing glucose in the body. Glycogen is produced and stored in liver and muscle cells that are hydrated with four parts of water. It serves as a secondary long-term energy storage system. Muscle glycogen is rapidly converted into glucose by muscle cells, and liver glycogen is quickly converted into glucose for use throughout the body, including the central nervous system.
Glycogen accounts for about 5-6 per cent of the fresh weight of the liver; it is present in skeletal muscle at low concentrations of about (1-2) per cent. Glycogen is also found in trace amounts in red blood cells, white blood cells, glial cells, and the kidneys. In fact, the uterus contains some glycogen that is stored and contributes to the embryo's growth. It is found in the cytoplasm of various cell types as dark granules of 10-40nm and plays an important role in the glucose cycle. It creates an energy reserve that can be quickly mobilised to meet sudden glucose needs.
It is similar to starch, which is found in plants. Animals have two types of energy stores: glycogen and triglycerides.
Structure of glycogen
Glycogen is a polymer made by the condensation of glucose molecules after the elimination of water. As it is found in biotic species, it is called a biopolymer. It is a branched polymer. With a linear chain formation linked by 1,4 hydroxyl groups of two glucose units and branches occurring by condensation between 1,6 hydroxyl groups. Each chain linear or branch has about 8 to 12 glucose monomers. There will be many such branches resulting in a macromolecule containing anywhere between 2000 to 60000 glucose units per molecule of glycogen
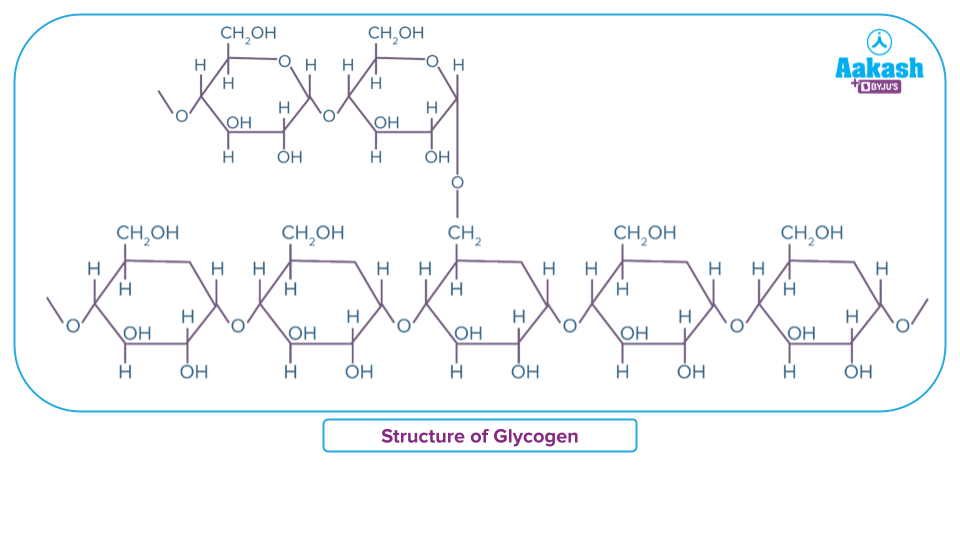
The structure is similar to amylopectin and is a highly branched polymer and more compact than starch. ..
Significance of glycogen
- Glycogen is primarily synthesised in the liver when excess glucose consumed is left unused; the glucose molecules then go through a glycogenesis process in the body to produce glycogen with the help of the enzyme glycogen synthase. These formed glycogen molecules are stored in the liver.
- When blood glucose levels fall below a certain level, the pancreatic Islets of Langerhans secrete the hormone glucagon. This glucagon stimulates the enzymes required for glycogenolysis or the breakdown of glycogen. Now the glucose is released into the bloodstream, reviving the blood glucose level. In addition to glucagon, hormones such as cortisol and epinephrine stimulate glycogen breakdown.
- Microorganisms such as yeast, for example, produce glycogen in response to an excess of carbon available.
- Glycogen reserves in the uterus ensure proper embryo growth because glycogen is a good source of nutrition. Glycogen begins to accumulate in foetal cells around 26 weeks of pregnancy and aids in the synthesis of pulmonary surfactants.
- Muscle cells lack the enzyme required for a complete breakdown of glycogen into glucose. As a result of glycogenolysis in muscle, the end product is glucose-1-phosphate, which is converted to glucose-6-phosphate with the help of the phosphoglucomutase enzyme for energy. Glycogen in skeletal muscles provides energy only for muscle function, not for the entire body.
Comparison of glycogen and starch
Similarities between glycogen and starch
Glycogen and starch are biopolymers. Both are polysaccharides composed of smaller glucose units. Both are branched polymers. These branched polymers glycogen and starch function as an energy stores in mammals and plants respectively. When dried, glycogen and starch are both white powders. Both are hydrolysed by enzymes and strong acids to the monosaccharide glucose. Furthermore, glycogen and starch are only marginally soluble in water at room temperature.
Differences between glycogen and starch
A few important differences between glycogen and starch are:
|
Parameter |
Glycogen |
Starch |
|
Definition |
Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide that acts as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals |
Starch is a long chain sugar molecule that primarily act as energy storage in plants. |
|
Structure |
Glycogen is a branched biopolymer with chains of glucose units that are joined together with a 1,4 and 1,6 alpha acetal linkage. |
Starch is composed of two types of polymers made of glucose monomers. The most basic and smaller form of starch is amylose, a linear polymer, while amylopectin is a branched polymer. |
|
Storage |
Glycogen accounts for about 5-6 per cent of the fresh weight of the liver; it is present in skeletal muscle at low concentrations of about (1-2) per cent. Glycogen is also found in trace amounts in red blood cells, white blood cells, glial cells, and the kidneys. |
Some plants, including potatoes and other tubers, as well as fruits such as bananas and breadfruit, store starch. Amyloplasts are special organelles or cell subunits that store starch. |
|
Size |
Glycogen is found in the cells as dark granules. |
Starch is found as grains in the cell |
|
Commercial importance |
Glycogen is not important commercially as it is not used at the industrial level. |
Starch is important commercially and is used on a large scale in the pharmaceutical industry, and in the food industry where it is used as a thickener in products like- noodles, pasta etc. |
|
Molecular mass |
The glycogen molecule has the approximate molar mass of 666.577 g/mol. |
Starch is a carbohydrate polymer made up of two macromolecules: amylose, a linear polysaccharide polymer with an approximate molecular mass of 105 gmol-1, and amylopectin, a branching polysaccharide polymer with an approximate molecular mass of 106 -107 gmol-1. |
Practice problems
Q1 Which of the given statement is correct with respect to the glycogen?
A. Glycogen is the form of energy which is stored in plant in the special organelles or cell subunits called Amyloplasts.
B. Glycogen is used as a thickener in the food industry.
C. Glycogen polymer is made up of glucose residues linked together by -(1,4)- and -(1,6)- glycosidic bonds
D. Glycogen is stored in kidneys and intestine in animals which is the primary source of energy
Answer: (C)
Solution: Starch is the form of energy which is stored in plant in the special organelles or cell subunits called Amyloplasts. Starch is used as a thickener in the food industry.
Glycogen polymer is made up of glucose residues linked together by -(1,4)- and -(1,6)- glycosidic bonds. Glycogen accounts for about 5-6 per cent of the fresh weight of the liver; it is present in skeletal muscle at low concentrations of about (1-2) per cent. Glycogen is also found in trace amounts in red blood cells, white blood cells, glial cells, and the kidneys. Therefore option(C) is correct.
Q2. Which of the following statement is correct with respect to the structure of glycogen?
A. Glycogen is formed by combining two macromolecules amylose, a linear polysaccharide polymer and amylopectin, a branching polysaccharide polymer.
B. Glycogen is made up of long polymer chains of glucose units that are joined together with an alpha acetal linkage which is formed by combining carbonyl and alcoholic groups.
C. Glycogen is formed by the combination of amino acids through peptide bonds
D. Glycogen is a polymer of glucose and fructose molecule.
Answer:(B)
Solution: Starch is formed by combining two macromolecules amylose, a linear polysaccharide polymer and amylopectin, a branching polysaccharide polymer.
Protein is formed by the combination of amino acids through a peptide bond.
It has a structure similar to amylopectin, a component of starch, but it is more extensively branched and compact than starch. This polymer is made up of glucose residues linked together by -(1,4)- and -(1,6)- glycosidic bonds. There are joined together with an alpha acetal linkage which is formed by combining carbonyl and alcoholic groups. Therefore option(B) is correct.
Q3. In the glycogen polymer, the monomer present will be ________.
A. Fructose
B. Glucose
C. Both glucose and fructose
D. Glucose and galactose
Answer:(B)
Solution: Glycogen is the polymer of glucose monomer. Insulin polymer is formed from fructose monomer. Glucose is linked with galactose to form lactose polymer. Therefore option(B) is correct.
Q4. Select the correct option which does not represent the use of galactose polymer.
A. Glycogen reserves in the uterus ensure proper embryo growth because glycogen is a good source of nutrition.
B. Glycogen in skeletal muscles provides energy only for muscle function, not for the entire body.
C. In foods such as sauces, puddings, gravies, custards, soups and salad dressings, glycogen is commonly used as a thickener and stabiliser.
D. Glycogen is the primary source of energy in bacteria and fungi
Answer: (C)
Solution: Some important use of galactose include:
- Glycogen reserves in the uterus ensure proper embryo growth because glycogen is a good source of nutrition. Glycogen begins to accumulate in foetal cells around 26 weeks of pregnancy and aids in the synthesis of pulmonary surfactants.
- Glycogen is the primary source of energy in bacteria and fungi. Microorganisms such as yeast, for example, produce glycogen in response to an excess of carbon available.
- Muscle cells lack the enzyme required for a complete breakdown of glycogen into glucose. As a result of glycogenolysis in muscle, the end product is glucose-1-phosphate, which is converted to glucose-6-phosphate with the help of the phosphoglucomutase enzyme for energy. Glycogen in skeletal muscles provides energy only for muscle function, not for the entire body
Therefore, option(C) is incorrect.
Frequently asked questions-FAQs
Q1. When does the glycogen turn into fat?
Answer: The amount of glycogen that your body can store is approximately 600 grams. Once the maximum amount of glycogen is stored in the body, the remaining glycogen is converted into triglycerides, a type of fat. Triglycerides can enter the bloodstream directly for energy or be stored in your body fat.
Q2. Why glycogen storage is important for newborns?
Answer: Glycogen is important in newborns as it is the source of the energy and is required to maintain physiological blood glucose concentration in the body.
Q3. Why glycogen is also called animal starch?
Answer: . It is similar to starch, which is found in plants, Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide that acts as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals. When the glucose level of the body decreases, glycogen is converted into glucose with the help of the glucagon enzyme which increases the blood sugar level in the body.
Q4. What is the difference between glycogenolysis and glycogenesis?
Answer: Glycogenolysis is the process in which glycogen is converted into glucose with the help of the glucagon enzyme which increases the blood sugar level in the body. Whereas glycogenesis is the process in which the synthesis of glycogen takes place from the extra glucose present in the body with the help of an enzyme known as glycogen synthase. The glycogen formed is generally stored in the liver.


