-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Viroids, Prions and Lichens: Characteristics, Diseases and Classifications
What is the easiest way to identify an organism? You must be thinking about the system of classification of organisms, right? If we have a group of organisms to identify, classifying them into different groups makes the process of identification easy. For this we consider the organisms with similar characteristics in the same group. You must be familiar with the five kingdom classification by Whittaker. He had used a similar approach in his classification system.
But do you know that there are some organisms which could not fit in any of these five kingdoms? Interesting right? Why do you think this happens? This is because these organisms exhibit some unique characteristics which do match with the ones of any of the known kingdoms. Have you heard of any such organisms? The organisms like viroids, prions and lichens were not included by Whittaker in his classification of organisms because of their unique nature. Want to know more about these unique organisms? Let’s get into it.
Table of Contents:
Viroids
Viroids were first discovered by T. O. Diener in the year 1971. He observed that a new infectious agent smaller than viruses caused potato spindle tuber diseases. The infectious agent was termed viroid.
Characteristics of Viroids
Viroids are smaller in size than viruses. Their structure includes only genetic material, i.e., free RNA of low molecular weight. Protein coat is absent. They are obligate intracellular parasites.
Diseases caused by viroids
Viroids are mostly responsible for several plant diseases such as potato tuber spindle disease, diseases in Chrysanthemum caused by chrysanthemum stunt viroid etc. Hepatitis D is the only animal disease known to be caused by a viroid-like agent.

Prions
Prions stands for proteinaceous infectious particles. These were discovered by Prusiner while investigating transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, including scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
Characteristics of Prions
Prions are small, abnormally folded proteins. They have the ability to convert normal cellular protein to abnormal infectious state. Prions are highly infectious particles and cause untreatable or fatal neurodegenerative disorders.

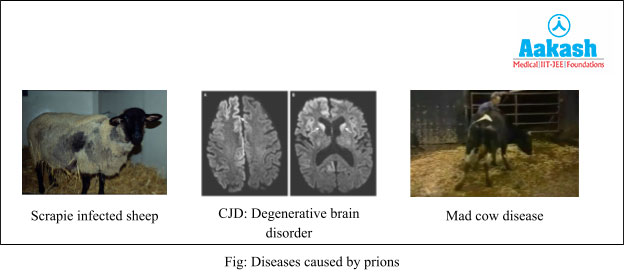
Neurodegenerative Diseases Caused by Prions
- Scrapie in sheep
- Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattles, also called mad cow disease
- Kuru
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) in humans
Lichens
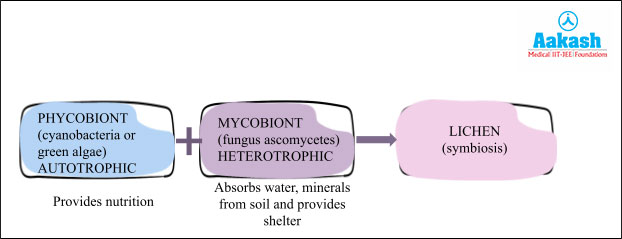
Lichens are formed by symbiotic association between algae or cyanobacteria and fungi in which both the partners are mutually benefited.

Algal partner or cyanobacterial partner is called phycobiont while fungal partner is called mycobiont.
Roles of Phycobiont and Mycobiont
Phycobiont |
Mycobiont |
|
It includes green algae or cyanobacteria that have photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll. Thus, it performs photosynthesis and synthesises food. |
It includes fungi belonging to class Ascomycetes or Basidiomycetes. |
|
The nutrients stored in the algal cells are derived by the fungal partners. Fungi have projections of fungal hyphae called haustoria which penetrate the algal cell wall for this purpose. |
It absorbs water and minerals from soil and provides it to its algal partner, It also protects the algae from high light intensities. |
In this way, both fungi and algae live together and benefit each other.
Classification of Lichens
Lichens are included in the terrestrial group of organisms. Because they are usually seen on rocks, walls, gravestones, on roofs, tree barks, soil, etc. Lichens are of different types. They can be classified based on their growth, habitat, internal structure and also on their fungal partner. Let’s see more about the classification of lichens.
Based on Growth of Lichens
There are three types of lichens based on their growth. These are -
Crustose Lichens: They are flat and thin lichens. Their body has no lobes. They can be found attached over the stones, barks, rocks and even on the trunk of trees. Examples: Haematomma puniceum, Graphic scripta.

Fruticose lichens: They are thin, freely branched, large and attractive. They grow on the branches of trees, foliage and rocks. Examples: Cladonia, Ramalina, Usnea.

Foliose lichens: They are more attractive compared to other types of lichens. They can be seen in different shapes like flat shaped, broad, smooth and leaf-like. Leaf-like lichens resemble crinkled and twisted leaves. Since they are more like leaves, they have a distinct upper and a lower surface. They are found attached to rocks and twigs with the help of the rhizoid. Examples: Cetraria, Cluiudhuria, Parmelia and Xanthoria.

Based on the Habitat of Lichens
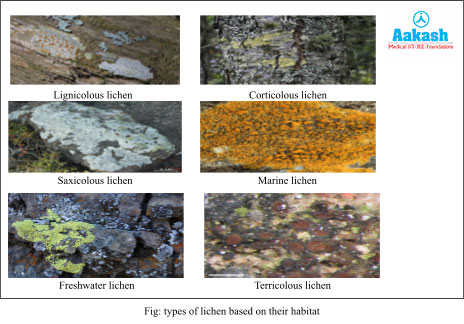
Lichens can be classified into six types based on their habitat. They are Lignicolous, Corticolous, Saxicolous, Marine, Freshwater, and Terricolous.
Lignicolous are the lichens that live in the woods. Corticolous lichens live on the bark of trees. Saxicolous lichens live on stones or rocks. Marine lichens are those just like the name indicates, live on the siliceous rocks, near the shores of the sea. Freshwater lichens can be seen on the siliceous rocks of fresh water. Terricolous lichens are terrestrial lichens that are found on the soil.
Based on the Internal Structure of Lichens
Lichens can be classified into two types based on the internal structure. They are the heteromerous lichens and homoiomerous lichens. If there is a distinct distribution of algal and fungal cells in the lichen, then it is called heteromerous lichen. If the algal cells are evenly distributed in the thallus of the lichen and are more in number, then it is called homoiomerous lichen.

Based on the fungal partner of lichen
Fungal partners are different in different lichens. Based on the variation of fungal partners the lichens can be classified into three types. They are ascolichens, basidiolichens and hymenolichens.
Ascolichens : Fungal component is ascomycetes.
Basidiolichens : Fungal component is basidiomycetes.
Hymenolichens : Fungal component is hymenomycetes.
Importance of Lichens
Lichens are the first organisms to colonise on barren land. Thus, they are the pioneer species during xerarch succession. Lichens are highly sensitive to SO2 and do not grow in a polluted environment. This is due to the presence of insufficient absorption systems which results in accumulation of pollutants restricting their growth. Thus, they are air pollution bioindicators.

Practice Problems of Viroids, Prions and Lichens
Question 1. How many of the organisms given below are not included in Whittaker’s system of classification?
Cyanobacteria, Lichens, Mycoplasma, Slime moulds, Viroids, Prions
a. Four
b. Five
c. Three
d. Two
Solution: Whittaker’s system of classification did not include lichens, viruses, viroids and prions. They all lack cellular structure and hence cannot be classified into any kingdom. As lichens were a combination of two organisms (algae and fungi) living together, it was difficult to assign them into a particular kingdom. Whittaker classified cyanobacteria and mycoplasma within the kingdom Monera, which includes all prokaryotes. Slime moulds are classified in the kingdom Protista which includes all unicellular eukaryotes.
Hence the correct option is c.
Question 2. Which among the following is incorrect?
|
A. |
Viroids |
Infectious free RNA |
Potato spindle tuber disease |
|
B. |
Prions |
Infectious proteins |
Mad cow disease |
|
C. |
Viruses |
Nucleoproteins |
Mumps |
|
D. |
Lichens |
Algae + Bacteria |
Indicators of CO pollution |
a. A, B, D
b. B, D
c. Only A, C
d. Only D
Solution: Lichens are a symbiotic interaction between algae and fungi, that are indicators of sulphur dioxide pollution. Lichens have efficient absorption systems that result in accumulation of sulphur when exposed to high sulphur dioxide concentration. The accumulated sulphur in lichens disrupts photosynthesis by algae and it affects reproduction and spore germination.
Hence the correct option is d.
Question 3. Lichens are formed from organisms belonging to the Kingdoms:
a. Monera and Fungi
b. Mycota and Plantae
c. Plantae and Animalia
d. Both a and b
Solution: Lichens are formed by the symbiotic association of green algae or cyanobacteria with fungi. Cyanobacteria belong to the Kingdom Monera. Green algae (chlorophyceae) belongs to the Kingdom Plantae. Fungi belongs to the Kingdom Fungi, also called Mycota.
Hence the correct option is d.
Question 4. Differentiate between phycobiont and mycobiont.
Answer: Lichens are formed by symbiotic association between algae or cyanobacteria and fungi in which both the partners are mutually benefited. Algal partner or cyanobacterial partner is called phycobiont while fungal partner is called mycobiont. Phycobiont performs photosynthesis and synthesises food. Mycobiont absorbs water and minerals from soil and provides it to the phycobiont. It also protects phycobiont from high light intensities.
FAQs of Viroids, Prions and Lichens
Question 1. How do viroids differ from viruses?
Answer: Viroids differ from viruses in many aspects. Viroids are smaller in size than the viruses. Viroids are RNA particles and viruses are nucleoprotein particles. Viroids have only RNA as a nucleic acid. Viruses have RNA or DNA. Viroids don't have a protein coat like viruses. Viroids mostly infect plants but viruses infect both animals and plants. Hepatitis D is the only animal disease known to be caused by a viroid-like agent.
Question 2. What causes mad cow disease?
Answer: Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattles, also called mad cow disease, is caused by prions. Prions stands for proteinaceous infectious particles. These were discovered by Prusiner while investigating transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Prions are small, abnormally folded proteins. They have the ability to convert normal cellular protein to abnormal infectious state. Prions are highly infectious particles and cause untreatable or fatal neurodegenerative disorders.
Question 3. Why are lichens called the biological pollution indicators?
Answer: Lichens are formed by symbiotic association between algae or cyanobacteria and fungi in which both the partners are mutually benefited. Lichens are highly sensitive to SO2 and do not grow in a polluting environment. Thus, they are air pollution bioindicators.
Question 4. Are lichens poisonous?
Answer: Very lichens which are rich in usnic acid or vulpinic acid can be poisonous.


