-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Gametogenesis: Spermatogenesis, Practice Problems and FAQs
You all know that we came to this beautiful world through our parents. How blessed we are. We are getting a chance to live on this beautiful planet Earth. We all know that humans reproduce sexually. But have you ever wondered how sexual reproduction in humans takes place? We all know that human males and females possess a well developed reproductive system. Both males and females have evolved specific organs and tissues for producing haploid cells or gametes, that means sperms in males, and eggs in females. By fertilisation of male and female gametes, a zygote is formed, which grows into a foetus inside the womb of the mother.

Hence the first thing required for this process is the presence of gametes. Now, where are these gametes formed? They are formed in the male and female reproductive organs, called testis and ovary respectively. But are you aware of the name of the process by which the formation of these gametes takes place? How does this process occur specifically in males?. You are not getting the answer. So let’s take a deep dive into the formation of sperms in males in detail in this article.
Table of contents
- Gametogenesis
- Spermatogenesis
- Stages of spermatogenesis
- Hormonal control
- Practice Problems
- FAQs
Gametogenesis
It is the process of producing male and female sex cells or gametes in the gonads, which are required for the formation of offspring. Diploid or haploid precursor cells divide and differentiate to generate mature haploid gametes during this process. Sperm refers to the male gamete, while egg or ovum refers to the female gamete. In males, it occurs in the testis, while in females, it occurs in the ovary. Now, let us study how it occurs in males in detail.
Types of gametogenesis
It is of two types as follows
Spermatogenesis
It is the formation of sperms in the testis.
Oogenesis
It is the formation of ova in the ovary.
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm generation in males. Male gamete production starts at puberty and takes place in the testis. The testes also produce the male hormone called androgen (testicular hormone). Germinal epithelium lines the seminiferous tubules. The majority of cells here are cuboidal and called primordial germ cells or PGCs. These immature male germ cells undergo successive mitotic and meiotic divisions to produce sperms.
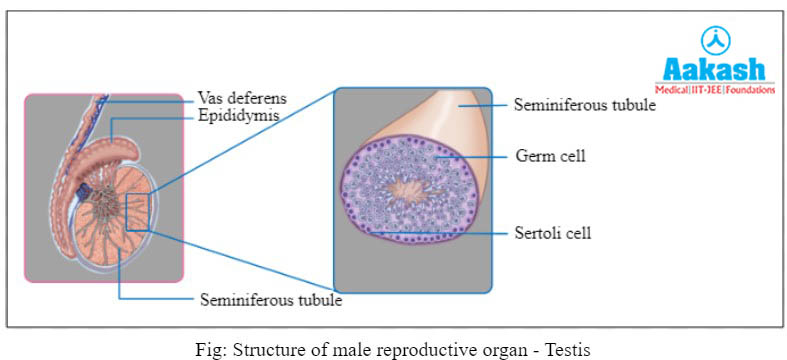
Stages of spermatogenesis
The process of spermatogenesis is divided into several stages:
- Proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonia
- Formation of spermatids
- Spermiogenesis
- Spermiation
Proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonia
The diploid primordial germ cells are present in the lining of the seminiferous tubules of testis. Some cells which are tall and somatic are called Sertoli cells. They help in the nourishment of the developing sperms and are also called nurse cells.
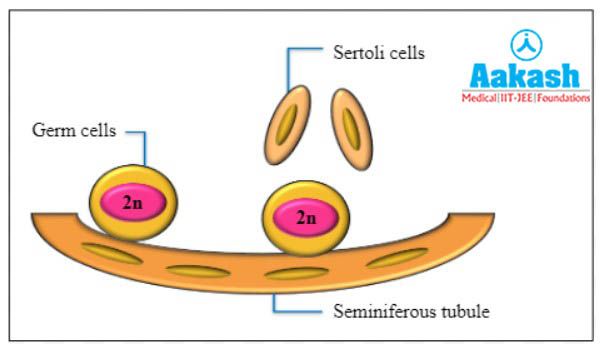
Formation of spermatids
At sexual maturity, the undifferentiated primordial germ cells or PGCs of seminiferous tubules divide several times by mitosis to produce large number of sperm mother cells or spermatogonia. To increase their quantity and cover the interior layer of the seminiferous tubule, spermatogonia also divide mitotically. It involves three phases as follows:
- Multiplication phase
- Growth phase
- Maturation phase
Multiplication phase
Spermatogonia are diploid and possess 46 chromosomes. There are two types of spermatogonia present inside the seminiferous tubules. They are as follows:
Type A spermatogonia
Some of the spermatogonia present in the seminiferous tubules continue as stem cells. They will keep on producing the spermatogonia type A and type B.
Type B spermatogonia
They act as the precursors of the sperms. They will enter into the growth phase.
Growth phase
Some spermatogonia, called type B spermatogonia, grow in size by obtaining nourishment from the nursing cells. It then goes through mitotic division and generates primary spermatocytes.

Maturation phase
Some primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis periodically. Meiosis results in the formation of two haploid cells known as secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte has 23 chromosomes.
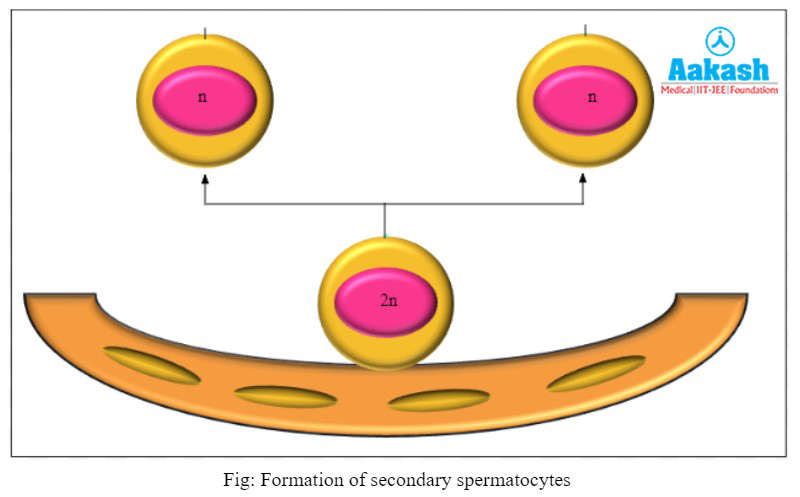
Formation of spermatids
Second meiotic division occurs in secondary spermatocytes, resulting in production of four equal and haploid spermatids.

Spermiogenesis
A nucleus, Golgi apparatus, centriole, and mitochondria are found in the spermatid, which is a more or less circular cell. By the process of spermiogenesis, the spermatids mature to form spermatozoa. The process of spermiogenesis takes place by morphological changes and it does not involve cell division.
The Golgi phase, cap phase, tail phase, and maturation phase are the four primary phases of spermiogenesis. The entire spermatogenesis process, including spermiogenesis, takes place in the coiled tubules of testis known as seminiferous tubules. After spermiogenesis, sperm embeds its head in Sertoli cells.

Spermiation
Spermiation is the release of mature spermatozoa from the lumen of seminiferous tubules. The sperm then moves into the epididymis and the first portion of vasa deferentia, where they undergo maturation and are stored. An adult produces over 1012 to 1013 spermatozoa each day.

Hormonal control of spermatogenesis
The process of spermatogenesis is regulated by several body hormones. The hypothalamus increases the synthesis of a hypothalamic hormone called gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), which initiates spermatogenesis, at puberty.
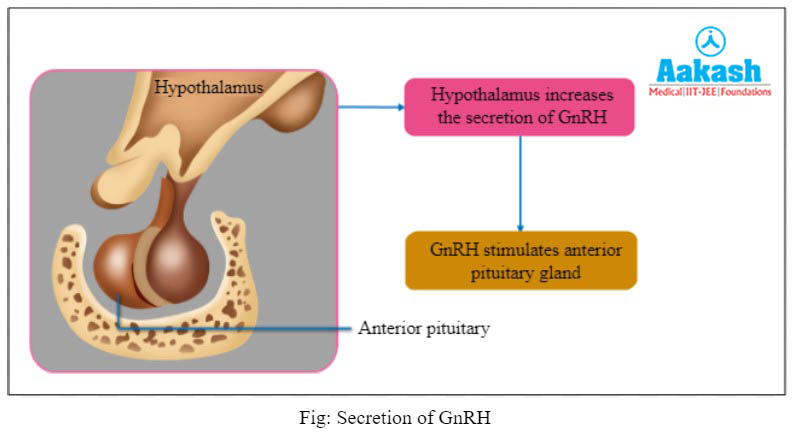
Increased GnRH release activates the anterior pituitary gland, which stimulates the synthesis of two gonadotropic hormones namely, LH (luteinising hormone) and FSH (follicle stimulating hormone).
Luteinising hormone
LH increases androgen production and secretion by acting on the Leydig cells. Testosterone is the main androgen. Androgens (testosterone) stimulate the process of spermatogenesis. It is essential for spermatogenesis.
Follicle stimulating hormone
FSH increases the release of substances that aid in the spermatogenesis process by acting on Sertoli cells. FSH can also directly act on spermatogonia to stimulate sperm production. Sertoli cells produce two main factors as follows:
Androgen binding protein
It helps in the concentration of testosterone in the seminiferous tubules.
Inhibin
It helps in suppressing the FSH synthesis.

Feedback inhibition of GnRH
An increasing level of testosterone suppresses the release of GnRH from the hypothalamus.
Practice Problems
Q 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect about spermatogenesis?
a. It involves mitosis only.
b. It takes place in the seminiferous tubules.
c. Spermatogonia divide by meiosis.
d. It produces four spermatids.
1. I and II
2. II and III
3. I and IV
4. I and III
Answer: The process of formation of sperms from the immature male germ cells (primordial germ cells) is called spermatogenesis. The process of spermatogenesis involves successive mitotic and meiotic divisions. The spermatogonia divide by mitosis in the seminiferous tubules to increase in number. Some of these spermatogonia become primary spermatocytes by increasing in size. They then undergo first meiosis to produce two secondary spermatocytes. Further, the secondary spermatocytes produce four spermatids by second meiotic division. Hence, option d is correct.
Q 2. Which of the following is correctly paired?
a. Spermatogonia - haploid, primary spermatocyte - diploid
b. Primary spermatocyte - haploid, spermatid - diploid
c. Primary spermatocyte - diploid, secondary spermatocyte - haploid
d. Secondary spermatocyte - diploid, spermatid - haploid
Answer: The formation of sperms from spermatogonia is called spermatogenesis. Spermatogonia contains 46 chromosomes and is diploid in nature. Primary spermatocyte is diploid. It undergoes meiosis to produce two equal and haploid secondary spermatocytes. Hence, option c is correct.
Q 3. Match the following:
|
Hormones |
Function |
|
I. Stimulates synthesis of androgens |
|
II. Stimulates secretion of gonadotropins |
|
III. Stimulates factors to help in spermatogenesis |
|
IV. Stimulates the process of spermatogenesis |
a. A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
b. A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
c. A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - I
d. A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Answer: GnRH is a hypothalamic hormone that stimulates the release of two gonadotropic hormones, luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland. LH induces the production and release of androgens such as testosterone, which in turn stimulates the spermatogenesis process. FSH activates the factors that help in the spermatogenesis process through Sertoli cells. Hence, option c is correct.
Q 4. Define the process of spermatogenesis?
Answer: Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperms are produced from the immature germ cell called primordial germ cells. It starts at puberty in males. The male reproductive organ called testis is associated with the formation of male gametes (sperms).
Q 5. Which cells are involved in the process of spermatogenesis?
Answer: Germ cells, also known as primordial germ cells especially spermatogonia and Sertoli cells, are the two main cell types found within the seminiferous tubules that are involved in the process of spermatogenesis. Germ cells will mature into sperm, and Sertoli cells, which are nurse cells, will nourish the germ cells throughout their development.
Q 6. Name the different stages of cells in spermatogenesis?
Answer: During spermatogenesis, germ cell development follows the below mentioned five stages:
1. Spermatogonia
2. Primary spermatocytes
3. Secondary spermatocytes
4. Spermatids
5. Spermatozoa
FAQs
Q 1. In spermatogenesis, how many times does meiosis occur?
Answer: During spermatogenesis, the primary spermatocytes undergo the first meiotic division and produce two haploid secondary spermatocytes. Further, the secondary spermatocytes undergo a second meiotic division resulting in the production of four haploid spermatids. Thus, in spermatogenesis, meiosis occurs twice.
Q 2. Name the hormones that control spermatogenesis?
Answer: The pituitary gonadotropins FSH and LH are required for the development and maintenance of spermatogenesis. The synthesis and secretion of both the hormones is regulated by the gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) released from the hypothalamus.
Q 3. What are the common factors that influence spermatogenesis?
Answer: The process of spermatogenesis is considered sensitive to fluctuations in the environment. It is sensitive particularly to hormones and temperature. Testosterone is the main hormone that is required in large concentrations to maintain the process of spermatogenesis. This is achieved by concentrating testosterone in the seminiferous tubule by binding with androgen binding protein.
Q 4. Do urine and sperm come out together at the same time?
Answer: Both sperm and urine pass through the urethra only. But they will not come out at the same time.
Related Topics
|
The female reproductive system: Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Vagina, Practice Problems and FAQs |
|
Mammary Glands: Structure, Types, Diagram, Function & Breast Cancer, Practice Problems and FAQs |
|
Gametogenesis: Oogenesis, Practice Problems and FAQs |
|
Parts of male reproductive system, Journey of sperms, Practice Problems and FAQs |



