-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Axial Skeletal System: Its Classifications, Skull, Vertebral column, Sternum and Ribs
Have you ever wondered if there were no bones in our body, what would happen?
Yes, without bones the human body is like a semi-empty pack. The human skeleton is a very rigid structure made up of bones. It is primarily involved in providing support for our muscles, skin and our vital organs. If bones are not present in the human body, we won’t be able to do anything. For example, movements, digestion, reproduction etc. This is because our nerves, blood vessels, lungs, brain and visceral organs would be blocked and squeezed.

Table of contents
- Skeletal system
- Axial skeletal system
- Skull
- Types of skull
- Vertebral column
- Vertebrae
- Types of vertebrae
- Sternum
- Ribs
- Types of ribs
- Practice Questions
- FAQs
Skeletal System
Skeletal system or skeleton is the hard, supportive or protective elements of the animal body. In human beings, this system is composed of 206 bones and a few cartilages.

Significance of the Skeletal System
The significance of the skeletal system is enlisted below:
- The skeletal system supports the internal organs.
- This system protects the delicate parts.
- It helps in movement because bones are part of this system.
- It provides attachment sites for muscles.
- It gives the body its shape, look and form.
- The skeletal system helps in the blood cell formation that occurs in the bone marrow.
- It helps in immunity as the immune cells are formed in the bone marrow.
- It helps in facial expression.
- It helps in breathing by regulating the chest volume.
- It supports the uterus during pregnancy.
Classification of Skeletal System
The skeleton of human beings is divided into two parts based on the position of skeletal structures. These are the axial skeletal system and appendicular skeletal system.
Axial Skeletal System
The axial skeleton in human beings is present along the main axis of the body. The axial skeleton involves 80 bones. These 80 bones collectively formed the skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs.

Skull
The skull is made up of four different types of bones. These include the cranium, facial, ear ossicles and hyoid bone.
Cranium
The skeleton of the head is termed as a cranium or brain box. It forms the outer protective covering of the brain.
Bones of Cranium
It is made up of 8 cranial bones that are as follows:
- Parietal bones - It is a pair of flat bones and are present on either side of the head or behind the frontal bone.
- Temporal bones - It is a pair of irregular bones that is present under each of the parietal bones.
- Frontal bone - It is a single flat bone that makes the forehead and upper portion of the eye sockets.
- Ethmoid bone - It is an irregular bone that is situated in front of the sphenoid bone. It forms the nasal cavity.
- Occipital bone - It is a flat bone located at the back of the skull. It has an occipital condyle that allows the connection of the vertebral column with the brain. It has an opening called Foramen magnum; the spinal cord and its accompanying structures pass through this region.
- Sphenoid bone - It is an irregular bone that is situated below the frontal bone. It majorly forms the base of the skull.

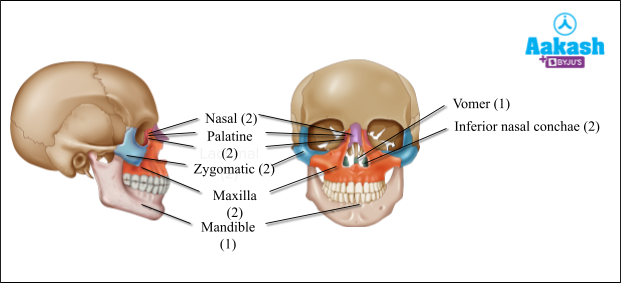
Facial bones
They normally form the front part of the skull. The anatomical name of facial bone is known as Viscerocranium.
Name of the facial bones
It consists of 14 bones that are named below:
- 2 nasal bones
- 2 palatine bones
- 2 lacrimal bones
- 2 zygomatic bones
- 2 maxillae
- 2 inferior nasal conchae
- 1 vomer bone
- 1 mandible
Function of Facial bones
The facial bones perform the following functions:
- The facial bones collectively protect the soft tissues of the face.
- These bones help in breathing, eating, facial expressions and speech.
Ear Ossicles
Ear ossicles are also termed as auditory ossicles. There are normally three bones present in the middle part of each of the human ear. Therefore, there are a total of six ear ossicles. These bones are considered as the smallest bones of the human body.
Name of the Ear Ossicles
The six ear ossicles are named as:
- 2 malleus - They are hammer shaped bones.
- 2 incus - They are anvil shaped bones.
- 2 stapes - They are stirrup shaped bones.

Hyoid Bone
The hyoid bone is situated in the upper part of the throat, above the larynx. It is a U shaped bone. Hyoid bone acts as a point of attachment for certain tongue muscles and the floor of the mouth.

Types of Skull
Skulls are classified into two types on the basis of number of articulations. These bony articulations are described as the projections on the occipital bone and hence, called the occipital condyles. These articulations connect the skull with the vertebral column. The two types of skulls are monocondylic skulls and dicondylic skulls.
Monocondylic Skull
The monocondylic skull has one occipital condyle at the posterior end of the cranium. This type of skull is commonly present in birds and reptiles.

Dicondylic Skull
In this type of skull, two rounded occipital condyles are present at the posterior end of the cranium. These articulations attach with the first vertebrae. The amphibians and mammals possess the dicondylic skull.

Vertebral Column
The vertebral column or the backbone is a curved structure that lies dorsally in the human body. It is composed of 26 serially arranged bones called vertebrae. It extends from the base of the skull and forms the framework of the trunk. The components of the vertebral column are considered as Vertebrae. The vertebral column possesses four slight bends called normal curves when viewed from the side.
Functions of the Vertebral Column
- The major function of the vertebral column is to bear the body weight in a standing position as well as when the body is in motion.
- It also protects the spinal cord
- It supports the head
- It serves as the point of attachment for all ribs like true, false and floating ribs.
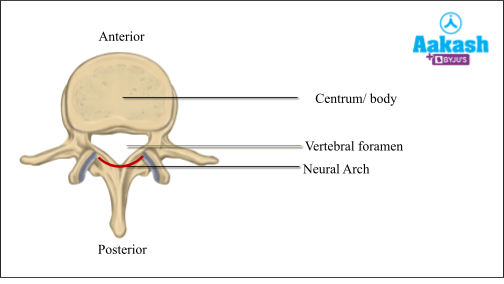
Vertebra
Each vertebra has a typical structure. Large, disc-like flattened body called the centrum or body present at the anterior portion. The posterior portion of the vertebra is known as the neural arch. The neural arch of each vertebra forms a hole called vertebral foramen. The vertebral foramina of 24 vertebrae together form the vertebral canal or neural canal. Through this neural canal, the spinal cord passes.
Intervertebral Discs
Between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae, intervertebral rings are found. These rings are known as Intervertebral discs. They are involved in the following functions:
- Forming strong joints.
- Absorb vertical shock.
- Allows various different types of movements of the vertebral column.
Types of Vertebrae
On the basis of the location, where they are present, vertebrae are classified into five major groups. These are as follows:
Cervical vertebrae
They are located in the neck region. They are seven in number in almost all mammals including human beings. The first cervical vertebra is the atlas which articulates with the occipital condyles. It supports the head. The second vertebra is known as the axis.

Thoracic Vertebrae
They are located in the chest region and are 12 in number. They are larger and stronger as compared to the cervical vertebrae. They articulate with ribs.

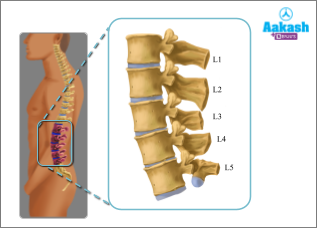
Lumbar Vertebrae
They are present in the lower back region. They are five in number and are the largest and strongest of all the vertebrae. This is because they have to bear the weight of the whole body when the body is in a standing position.
Sacral Vertebrae
There are five sacral vertebrae that are fused and form the Sacrum. These vertebrae are separated in childhood, but start to fuse during adolescence. The sacrum is located between the innominate or hip bones.

Coccygeal Vertebrae
They are four fused vertebrae that form the Coccyx. These are curved triangular bones. The vertebrae are separate during childhood but start to fuse during adolescence. It is considered as the vestigial tail in humans.

Sternum
It is characterised as a flat bone which is located in the center of the anterior thoracic wall. It measures about 15 cm in length. The sternum is also known as a breast bone. It provides the point of attachment for ribs. It protects the organs of the thoracic region like lungs and heart.
Structure of sternum
The sternum is divided into three segments. These segments of the sternum normally fuse around the age of 25. The parts are as follows:
Manubrium or prosternum
It is the superior part of the sternum.
Mesosternum or body
It is the middle and largest part of the sternum.
Xiphoid process or xiphisternum
It is considered as the inferior and smallest part of the sternum.
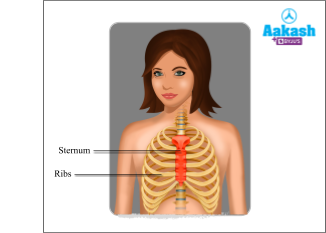
Ribs
In human beings, ribs are present in 12 pairs. They are flat bones and are arranged in the form of a cage and therefore, called the rib cage. The ribs, thoracic vertebrae and sternum together form a ribcage. They protect the internal organs present in the thoracic cavity and the kidneys. Rib cage is essential for the process of breathing and respiration.

Bicephalic ribs
Ribs are bicephalic because they have two articular surfaces. Each rib is articulated dorsally with the vertebral column (thoracic vertebrae) and ventrally with the sternum.

Types of Ribs
Ribs are classified into three types on the basis of their attachment at the ventral side.
- True ribs
- False ribs
- Floating ribs
True Ribs
The first seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs. They are attached to the thoracic vertebrae, dorsally. They are connected to the sternum ventrally with the help of hyaline cartilage, called costal cartilage.

False Ribs
The 8th, 9th and 10th ribs are called False or Vertebrochondral ribs. They do not articulate directly with the sternum but anteriorly they join the seventh rib with the help of hyaline cartilage.
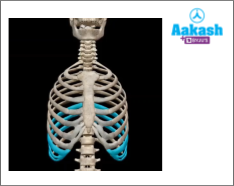
Floating Ribs
The last two pairs of ribs (11th and 12th) are not connected ventrally to the sternum or the cartilage and are therefore called floating ribs.

Practice Problems of Axial Skeleton System
Q1. Determine the structure which is excluded from the axial skeleton.
- Skull
- Sternum
- Vertebral column
- Pelvic girdle
Solution: On the basis of the position of the skeletal structures in the body, the skeleton is divided into two types: axial and appendicular skeletal systems.
- Axial skeletal system - It normally consists of 80 bones that are distributed along the main axis of the body. The skull, sternum, ribs and vertebral column together constitute the axial skeleton.
- Appendicular skeletal system - It is formed along the lateral axis of the body. It consists of a pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, bones of arms and bones of legs. Hence, the correct option is d.
Q2. Determine the function which is incorrect for hyoid bone.
- Swallowing
- Speech
- Movement of the head
- Point of attachment of tongue to the floor of mouth
Solution: The hyoid bone is situated in the upper part of the throat, above the larynx. It is a U shaped bone. Hyoid bone acts as a point of attachment for certain tongue muscles and the floor of the mouth. It aids in swallowing and speech. The movement of the head is possible with the help of neck muscles. Hence, the correct option is c.
Q3. Match the Column A with Column B
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
P. 8th-10th |
|
Q. 11th & 12th |
|
R. First- 7th |
- 1 - R, 2 - P, 3 - Q
- 1 - Q, 2 - R, 3-P
- 1 - P, 2 - Q, 3 - R
- 1 - P, 2 - R, 3 - Q
Solution: The first seven pairs of ribs are true ribs that are directly connected with the sternum. 8th, 9th and 10th pairs of ribs are known as false ribs because they are connected with the 7th pair of ribs with the help of hyaline cartilage. 11th and 12th pairs are floating ribs because they are not connected with the sternum and they hang in the air. Hence, the correct option is a.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
R. First- 7th |
|
P. 8th-10th |
|
Q. 11th & 12th |
Q4. Identify the given image and label the structures.

Answer: The given image represents the structure of a typical vertebra. Label ‘a’ represents the ‘centrum’ which is a large, disc-like flattened body at the anterior portion. Label ‘c’ represents the ‘neural arch’ which is located at the posterior portion of the vertebra. Label ‘b’ represents the ‘vertebral foramen’. The neural arch of each vertebra forms a hole called vertebral foramen.

FAQs of Axial Skeleton System
Question1. Are axial and appendicular skeletons the same?
Answer: The bones in the axial and appendicular skeletons are different. However, they combined to form the structural framework of a human being. The axial skeleton consists of the bones along the main axis. On the other hand, the appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the appendages.
Question2. Is it correct to say that humans possess a tail?
Answer: Humans possess a tail, but it is present only for a short period during the embryonic development. It is present around the 5th to 6th week of intrauterine life. The human embryo has a tail which consists of 10 – 12 vertebrae. Normally by 8 weeks, the human tail disappears. But the coccyx or tailbone remains in human beings which is formed by the fusion of four coccygeal vertebrae.
Question3. Which bone is considered as the smallest bone in human beings?
Answer: Stapes are the smallest bone in the human body. They are two in number, one in each ear. Malleus is considered as the second smallest bone in the human body.
Question4. Which is the only bone in the human skull which is movable?
Answer: Mandible is the only bone in the human skull which is movable. It is also known as the lower jaw. It allows the closing and opening of the mouth. It is the strongest and largest bone in the human skull. It aids in mastication and forms the jaw line.


