-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Elastic collision - Definition, Examples, Practice problems, FAQs
The Newton’s Cradle is a device which demonstrates an important phenomenon called collision. In-order to understand what this is, imagine two billiard balls impinging on each other- they stay in contact for a short time, and then move farther apart. In the case of the Newton’s cradle, a ball located at the extreme end strikes the other balls; and the impulse gets transmitted uniformly till the ball located at the other extremity.

In other words, it is appropriate to say that the kinetic energy from one ball is uniformly transmitted to all the balls. Such an event is called collision; other examples of this would be billiard balls or a golf ball being hit with a bat. But what is the final velocity acquired by each billiard ball after the collision? Also, is energy conserved during the collision?
Table of contents
- Definition of elastic collision
- Derivation of equation for elastic collision
- Coefficient of restitution
- Practice problems
- FAQs
Definition of elastic collision
Collision is an event in which two bodies come into contact with each other for a short period of time. The total momentum and kinetic energy may or may not be conserved. For instance, in an elastic collision, the momentum and kinetic energy before and after the collision are conserved.
Derivation of equation for elastic collision
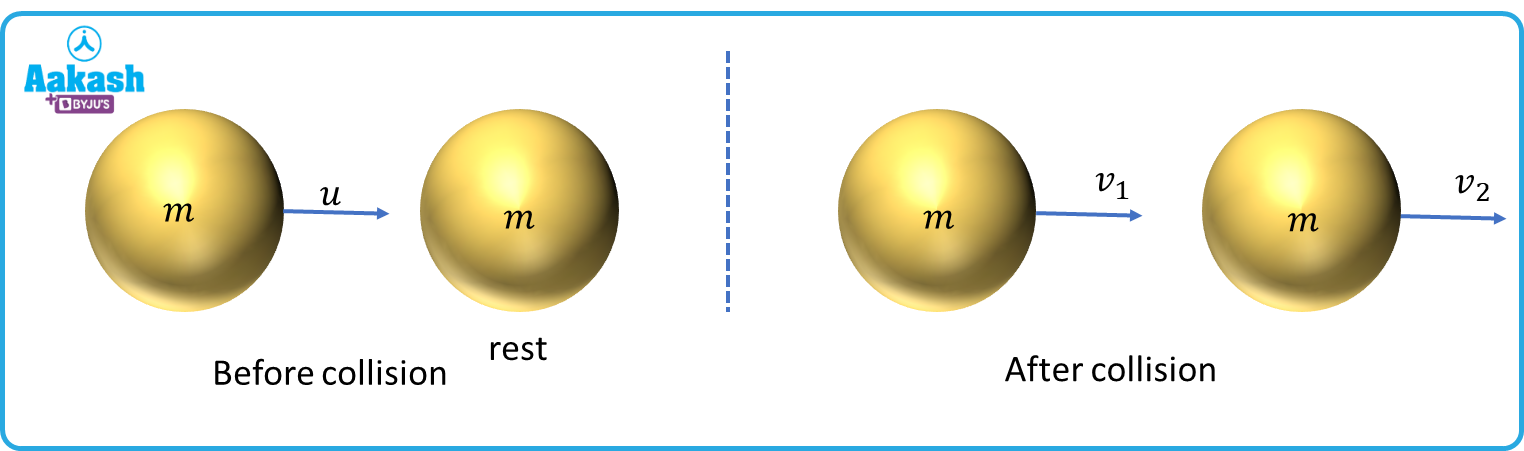
Let us consider two bodies of masses m1 and m2 moving with velocities u1 and u2 (u1>u2). After the collision, their velocities become v1 and v2. Such a condition is called the head on elastic collision. Equating momentum before and after collision, we get

m1u1 +m2u2=m1v1+m2v2--(i) [the direction is assumed as above]
Rearranging the above equation, we get
Also, initial KE =Final KE [ law of conservation of energy]
Dividing equation (v) by (ii),
i.e., in a 1D collision, the relative velocity before collision is equal to the relative velocity after collision. In other words, the velocity of approach is equal to the velocity of separation.
Solving equations (i) and (iv) we get the final velocities as
Special cases of head-on elastic collision
1) If m1=m2, then from equations (vi) and (vii), we get
when two particles having equal masses undergo a head on elastic collision, then their velocities are exchanged.
2) If m1>>m2 and u1=0
Then
Substituting the above two conditions, we get
i.e., if a lighter mass undergoes collision with a heavier mass at rest, the heavier mass remains at rest but the lighter mass rebounds with the same speed.
3) If m2>>m1 and u1=0
Applying
If a heavier mass undergoes collision with a lighter particle at rest, then the lighter mass moves with twice the velocity while the velocity of the heavier mass is unchanged.
Coefficient of restitution
The coefficient of restitution (e) is defined as the ratio of the relative velocities after collision to the relative velocities before collision.
e= v2-v1u1-u2
If e=1, it is a perfectly elastic collision.
If e<1, it is an inelastic collision.
Video explanation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j3F-gP3JASE
Practice problems
Q. An object of mass m moving with speed u undergoes one dimension collision with another identical object at rest. Calculate their velocities after collision, if their coefficient of restitution is e.
A. Applying conservation of momentum, we get
Now coefficient of restitution e
e= v2-v1u1-u2Here u1=u and u2=0
v2-v1=eu--(ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we get
Subtracting equation (ii) from equation (i);
2 v1=(1-e) u
Q. Two particles of masses mA and mB with velocities vA and vB undergo collision. After collision, they interchange their velocities. The ratio of mAmB is?
(a) vAvB (b) vBvA (c) vA+vBvB-vA (d) 1
A. d
Since the collision is elastic, we can apply conserving the momentum,
Thus we get,
Q. Two particles A and B of equal masses traveling along the line joining them with velocities 15 ms-1 and 10 ms-1 undergo perfectly elastic collision. After collision, their velocities would become
(a) 10 ms-1, 10 ms-1 (b) 15 ms-1, 15 ms-1 (c) 10 ms-1, 15 ms-1 (d) 15 ms-1, 10 ms-1
A. c
When two particles of equal masses undergo elastic collision, then their velocities are interchanged.
Q. A sphere of mass m is moving with constant velocity u. It hits another stationary sphere of the same mass. e is the coefficient of restitution in the collision.Calculate the ratio of velocities of the two spheres after collision.
(a)1-e1+e (b)1+e1-e (c)e+1e-1 (d)e-1e+1
A. b
Applying momentum conservation,
mu=mv1+mv2--(i)
From the definition of e,
v1-v2=eu--(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii), we get
∴Ratio of the final velocities
FAQs
Q. Do two bodies stick together after an elastic collision?
A. No. Only in an inelastic collision(e=0), the bodies stick together.
Q. Is the individual momentum/kinetic energy of the bodies conserved after elastic collision?
A. No, only the total momentum and kinetic energy before and after the collision are conserved during an elastic collision. Individual momentum/kinetic energy may change.
Q. Write the unit for the coefficient of restitution(e).
A. The coefficient of restitution, e has no unit and is dimensionless. It is just a ratio between the difference of final velocities to the initial velocities.
Q. Can two objects traveling in the same direction collide and then just stop after the collision?
A. No, only one of the objects can stop after collision. If both objects stop, momentum will become 0, violating the conservation of momentum.


