-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Photoperiodism: Mechanism, Photoperiodism in Chrysanthemum, Photoperiodic perception, Photoperiodic induction, Types of plants based on photoperiods, Practice Problems and FAQs
You all like flowers. They bloom at different periods. This you might have observed in your garden. You might have observed that some plants only flower at certain times of the year. Have you ever wondered why this happens?
Yes, you are correct. This is because of a phenomenon called photoperiodism. Now you are eager to know what it is? You know the total length of a day is 24 hours which include day and night periods. The effect of photoperiods or daily duration of light periods on the growth and development plants, especially the flowering plants is called photoperiodism. Now you understand that like we detect the time with the help of a clock plants also respond to time.
Depending on the day length and night length, plants undergo their reproductive phase and bloom. Let us discuss more about the phenomenon of photoperiodism in this article.

Table of contents
- Photoperiodism
- Mechanism of photoperiodism
- Photoperiodism in Chrysanthemum
- Photoperiodic perception
- Photoperiodic induction
- Types of plants based on photoperiods
- Difference between short day plants and long day plants
- Practice Problems
- FAQs
Photoperiodism
Photoperiodism is the phenomenon of the response of plants to the relative length of day and night. It was first studied by Allard and Garner and in 1920 using the ‘Maryland mammoth’ variety of tobacco plants
Let us consider the timeline of an entire day i.e of 24 hours. A part of the day that would experience light is known as the light period or photoperiod. The remaining part of the day would experience a dark period or skotoperiod.

Mechanism of photoperiodism
During photoperiod some sort of stimulus moves from the light exposed leaves to the shoot to induce flowering. This stimulus is identified as florigen. Along with florigen a number of growth hormones or their precursors are also involved in this process. This photoperiodic response is also under the influence of genes. So manipulation of genes also can result in flowering.
Critical photoperiod
Critical photoperiod is the definite period of light exposure required for a plant. Above or below this period the plant does not flower. Critical photoperiod is different for different plants. For example photoperiodism in Chrysanthemum.
Photoperiodism in Chrysanthemum
In Chrysanthemum, flowering occurs only if the photoperiod is shorter than the critical period.

This type of response to the relative length of day and light is termed as photoperiodism. Flowering response is initiated only if the optimum condition is met for several days, weeks, or even months. This duration varies from species to species.
Experiment in Chrysanthemum
This experiment is performed to see what actually happens in the Chrysanthemum when it is exposed to different periods of light.
Case I - Length of day exceeds the critical photoperiod
If you observe the day-night graph below, you can see that the length of day exceeds the critical photoperiod. As we said, Chrysanthemum requires a photoperiod lower than the critical photoperiod to bloom and hence, under these conditions, the flower will not bloom.

Case II - Length of day is below the critical photoperiod
But when the duration of light reduces below the critical photoperiod, the plant starts to bloom.
This is kind of a response to the relative length of day and night is exactly what is known as photoperiodism. It is important to remember that here we are talking only about a 24 - hour day. But the flowering response is initiated only if this condition is met for several days, weeks or event months and this duration varies from species to species.

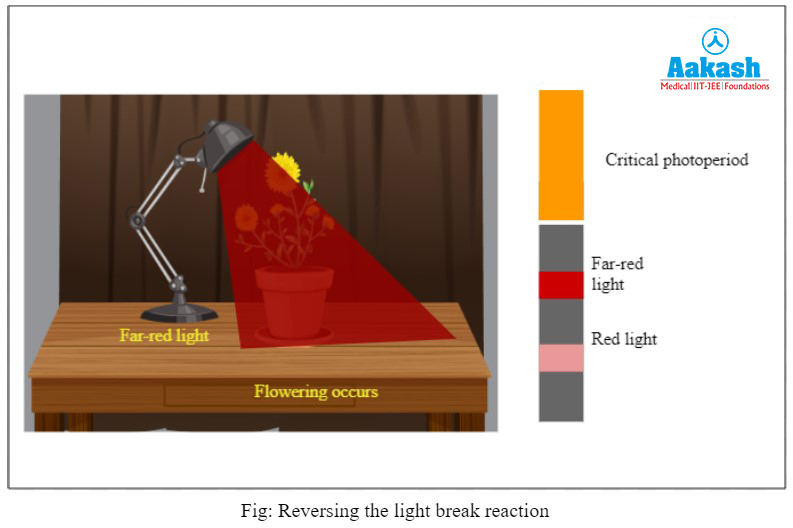
Case III - Reversing the light break reaction
If a flash of red light, having a wavelength of 660 nm, is given to the plant, then the plant does not bloom. This condition persists even if the light period is below the critical photoperiod. This is commonly known as the light break reaction. However, this condition can be reversed. After the exposure of red light, if the plant is exposed to far-red light, which has a wavelength of approximately 730 nm, then the plant successfully blooms.
Photoperiodic perception
Leaves are the site that detect photoperiod. In leaves phytochromes are the photoreceptors. The hormones like florigen and molecules responsible for the photoperiodic response normally migrate from leaves to shoot apices for inducing flower formation only when the plants are exposed to the required amount of inductive photoperiod. For example, in Xanthium ( a short day plant) a single leaf or even one eight part of a leaf was sufficient for photoperiodism.

Phytochrome
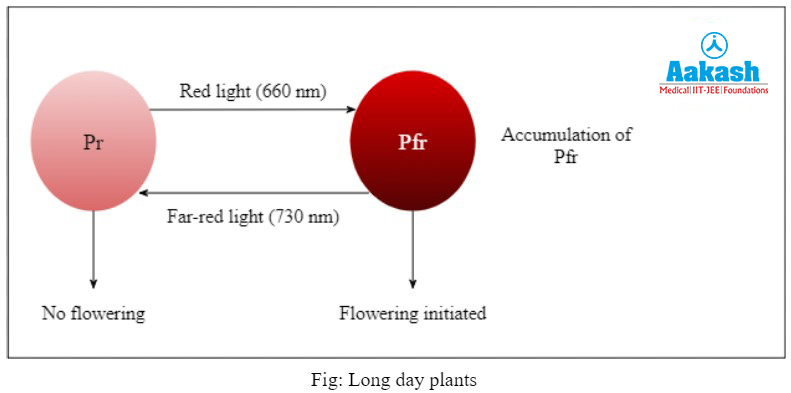
Phytochromes are considered as a group of proteins that are bound to light absorbing pigments in plants. They play a role in initiating the floral and developmental processes when activated by red or far-red radiations. It detects red and far red light and regulates the photoperiodic response. Phytochrome has 2 interconvertible forms as follows:
- Pr - It is considered as a blue form that absorbs red light at 660 nm.
- Pfr - It is considered as a blue-green form that absorbs far-red light at 730 nm.
They both regulate the photoperiodic response. During the day, Pr will absorb red light at 660 nm and will get converted into the Pfr form. On the other hand, during the night time, Pfr absorbs far-red light at 730 nm and gets converted into Pr form.

Photoperiodic induction
The conditions that affect a suitable cycle of light and dark periods can persist in a plant and lead to flowering is called photoperiodic induction. This occurs when the plant achieves certain minimum vegetative growth. For example, an 8 leaves stage of Xanthium. But in some plants photoinduction can be done in their cotyledonary stage also. For example, Chenopodium rubrum.
Types of plants based on photoperiod
On the basis of photoperiod, plants are of three types as follows:
- Short day plants
- Long day plants
- Day neutral plants
Short day plants
Short day plants are considered as long night plants. In these plants flowering is initiated when the day length (photoperiod) becomes shorter than the critical photoperiod. In these types of plants, flowering is inhibited by the accumulation of Pfr. In the dark, slow conversion of Pfr into Pr induces flowering.

Examples of short day plants
Examples of short day plants include Xanthium, sugarcane, Chrysanthemum, tobacco (Maryland Mammoth) and strawberry.

Long day plants
Long day plants are considered as short night plants. They flower when exposed to a long photoperiod above the critical photoperiod. Flowering is initiated by the accumulation of Pfr. In the dark, slow conversion of Pfr to Pr inhibits flowering in them.
Examples of long day plants
Examples of long day plants include oats, radish, wheat, lettuce and barley.

Day neutral plants
These plants do not show any dependence on light and dark periods. They blossom throughout the year. They flower normally after a period of vegetative growth.
Examples of day neutral plants
Examples of day neutral plants include tomatoes, sunflowers, cotton and cucumbers.

Difference between short day plants and long day plants
|
Short day plants |
Long day plants |
|
Flowers when the photoperiod is less than critical value |
Flowers when the photoperiod is more than the critical value |
|
Accumulation of Pfr inhibits flowering |
Accumulation of Pfr stimulates flowering |
|
Pfr/Pr <1 |
Pfr/Pr >1 |
|
They are also called long night plants |
They are also called short night plants |
|
Plants can flower in complete darkness under the supply of nutrients |
Plants cannot flower in complete darkness under the supply of nutrients |
|
Plants will not flower if the long dark period is interrupted by a flash of light |
Flowering is stimulated if dark period is interrupted by light |
|
They flower in autumn season and early spring periods |
They flower in late spring and summer periods |
|
Examples include Chrysanthemum, sugarcane, strawberry, soybean etc. |
Examples include radish, spinach, wheat, lettuce etc. |
Significance of photoperiodism
The following are the major significances of photoperiodism in plants:
- Knowledge of photoperiodism is useful in plants kept in glass houses to adjust the temperature and light conditions.
- It is used to retard or induce flowering in plants.
- It can be applied efficiently in agriculture for good yield.
- It is useful for commercial flower growers.
Youtube link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OuNuSo547-g
Practice Problems
Q 1. For two flowering plants, X and Y, the critical photoperiod is 10 hours. Plant X flowers with 14 hours of light every day, whereas Y has no flowers. Could you classify the two plants based on their photoperiodic responses?
a. X - Short day plant, Y - Long day plant
b. X - Long day plant, Y - Short day plant
c. X - Short day plant, Y - Day neutral plant
d. X - Long day plant, Y - Day neutral plant
Answer: Photoperiodism is the phenomenon of the response of plants to the relative length of day and night or photoperiod. A part of the day that would experience light is known as the light period or photoperiod. The remaining part of the day would experience a dark period or skotoperiod. On the basis of photoperiod, plants are of three types as follows:
- Short day
- Long day
- Day neutral
The critical photoperiod for Plant X is 10 hours. It bloomed after being exposed to light for 14 hours. Hence it is a long day plant. Examples include radish. The critical photoperiod for plant Y is 10 hours. It was unable to flower after being exposed to light for 14 hours. Hence it is a short day plant. Examples include sugarcane. Hence, the correct option is b.
Q 2. From the given plants, identify the short day plants?
Strawberry, Oats, Xanthium, Tomato
a. Oats and tomato
b. Oats and strawberry
c. Strawberry and Xanthium
d. Xanthium and oats
Answer: Short day plants are also known as long night plants. In these types of plants, flowering is inhibited by the accumulation of Pfr. In the dark, slow conversion of Pfr into Pr induces flowering. Examples include Xanthium and strawberry. Hence, the correct option is c.
Q 3. Determine the incorrect statement regarding long day plants.
Statement I : Long day plants are also known as short night plants.
Statement II : In the dark, slow conversion of Pfr into Pr induces flowering.
Statement III : Long day plants flower during a long photoperiod above the critical length.
Statement IV : Flowering is initiated by the accumulation of Pfr.
a. Statement II only
b. Statement I and III
c. Statement III and IV
d. Statement IV only
Answer: Long day plants are also known as short night plants. They flower during a long photoperiod above the critical length. Flowering is initiated by the accumulation of Pfr. In the dark, slow conversion of Pfr to Pr inhibits flowering. Hence, the correct option is a.
Q 4. How does phytochrome regulate photoperiodic response in plants?
Answer: Phytochromes are considered as a group of proteins that are bound to light absorbing pigments in plants. They play a role in initiating the floral and developmental processes when activated by red or far-red radiations. It detects red and far red light and regulates the photoperiodic response. Phytochrome has 2 interconvertible forms as follows:
- Pr - It is considered as a blue form that absorbs red light at 660 nm.
- Pfr - It is considered as a blue-green form that absorbs far-red light at 730 nm
They both regulate the photoperiodic response. During the day time, Pr will absorb red light at 660 nm and will get converted into the Pfr form. On the other hand, during the night time, Pfr absorbs far-red light at 730 nm and gets converted into Pr form.
FAQs
Q 1. Are the phenomena of phototropism and photoperiodism the same?
Answer: Phototropism and photoperiodism are two different phenomena. Phototropism is defined as the bending of plants towards the light. On the contrary, photoperiodism is the phenomenon of the response of plants to the relative length of day and night or photoperiod.
Q 2. Why is photoperiodism an essential phenomenon for plant life cycle?
Answer: Photoperiodism is the phenomenon of the response of plants to the relative length of day and night. In some plants, photoperiodism induces flowering and allows the plant to enter the reproductive mode in certain periods of the year.
Q 3. Give some examples of photoperiodism in animals?
Answer: Photoperiodism in animals is not so prominent as in plants. But, there are certain examples in animals, such as seasonal breeding in some animals, birds singing during longer days and diapause in some insects.
Q 4. Which part of the plant detects photoperiod?
Answer: The leaves of the plant usually detect photoperiod or length of day and night. The hormones and other molecules responsible for the photoperiodic response normally migrate from leaves to shoot tips for the induction of flowering. This happens only when the plants are exposed to the required amount of inductive photoperiod.
Related Topics
|
Ethylene: Discovery and Physiological effects, Practice Problems and FAQs |
|
Auxin: Discovery and Functions, Cholodny Went Theory, Practice Problems and FAQs |
|
Gibberellin: Discovery, Functions and Uses, Practice Problems and FAQs |
|
Cytokinin: Discovery and Functions, Morphogenesis, Practice Problems and FAQs |


