-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Buccal Cavity: Structure and Role in Digestion, Deglutition, Practice Problems and FAQ’s
Once we think about some foods like samosa, kachori or ice cream, the water comes into our mouth.
Have you ever wondered where this water comes from and what exactly this water is?
As we all know that we eat food through our mouth. It forms the first organ of the digestive system.
The watery substance that is secreted in our mouth is called saliva. It comes from the salivary glands that are present in the buccal cavity. Apart from these, we all know that other structures are also present in our buccal cavity.
Now, open your mouth and see in the mirror what structures are present there?

Yes, tongue and teeth are there. These help in the digestion of food. In this topic, let's discuss the digestion of food in the buccal cavity and understand its parts.
Table of Contents
- Buccal Cavity
- Role of Buccal Cavity in Digestion
- Deglutition
- Practice Problems of Buccal Cavity
- Frequently Asked Questions of Buccal Cavity
Buccal Cavity
The first part of the alimentary canal is the mouth. The mouth opens into buccal cavity or oral cavity. The buccal cavity has three parts as follows:
- Palate
- Tongue
- Teeth

Palate
Palate is considered as the roof of the buccal cavity. The rugae are present in the palate that are characterised as ridges. Palate is divided into three parts as follows:
Hard Palate
It is the anterior part of the palate that possesses ridges. It helps in chewing.
Soft Palate
It forms the posterior part of the palate and is smooth and fleshy.
Uvula
It is considered as the extension of the soft palate and is found hanging above the throat. It helps in swallowing the food and prevents food entry into the nasal chamber.

Tongue
Tongue is a freely movable and muscular organ that occupies the floor of the mouth. It is a flat and voluntary organ. The functions of the tongue are sensory and it helps in mastication of food.
Parts of Tongue
Tongue consists of the following parts:
Frenulum
Tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth with the help of lingual frenulum.

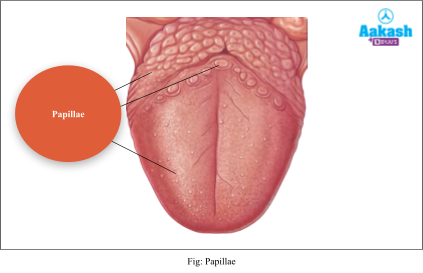
Papillae
Papillae are projections present on the upper surface of the tongue. Some of them bear taste buds.
Types of Papillae
There are four types of papillae on the tongue as follows:
- Foliate papillae - It is normally present in mammals except human beings. They are present on the sides of the bases of the tongue.
- Filiform papillae - They are present near the centre of the tongue. They are small and numerous. They possess tactile or touch receptors.
- Circumvallate papillae - They are the largest papillae. They are arranged in the form of an inverted V-shape. They are present towards the base of the tongue.
- Fungiform papillae - They are spherical in shape and numerous. They present near the tip of the tongue.

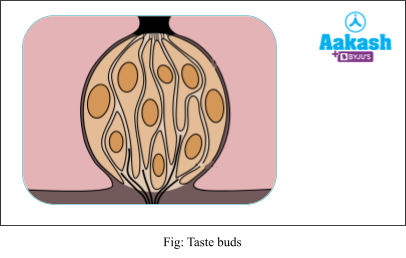
Taste Buds
They are considered as the receptors of taste that are present within some papillae. They sense all four tastes (bitter, sour, salty, and sweet) and send messages to the brain to generate the sensation of taste. An average person has about 10,000 taste buds.
Functions of the Tongue
The tongue performs the following functions:
- It aids in chewing and swallowing the food.
- It is the organ of taste.
- It acts as a brush and helps in cleaning the teeth.
- It plays an important role in speech.
- It helps in lodging the food between the grinding surfaces of teeth.
Teeth
Teeth are hard structures. They are present in two semicircles. They are embedded in the socket of the jaw bone. Teeth are eco-mesodermal in origin. They are of several uses, such as gripping, cutting, gnawing, tearing and crushing.
Parts of Tooth
The tooth is composed of the following parts:
- Crown - The exposed part of the tooth is termed a crown. It projects above the gums.
- Enamel - It is the hardest part of the human body that covers the crown. Enamel is secreted by the ameloblast cells. It is acellular, avascular and non-regenerable. The function of enamel is to masticate the food.
- Neck - It is the middle part of the tooth which is surrounded by the gums.
- Root - It is the basal part of the tooth which is embedded in the jaw bone.
- Dentine - Crown and root of the teeth are made up of dentine.
- Pulp cavity - It is the cavity enclosed by the dentine. It possesses soft, gelatinous connective tissue called pulp. It possesses dentine forming cells called odontoblasts.
- Pulp canal - Through this canal blood supplies and nerves enter the pulp cavity.
- Periodontal membrane - It fixes the root to the jaw bone.

Classifications of Animal Teeth
There are three classifications of animal teeth based on structure and function, placement in jaw and appearance in life.
Classification of Dentition on the Basis of Structure and Function
On the basis of structure and function, teeth are classified into two types as follows:
- Homodont teeth - In this condition only a single type of teeth present in the oral cavity. Examples include the teeth of dolphins.
- Heterodont teeth - In this condition different types of teeth are present in the oral cavity. For example, in human beings and cheetahs.

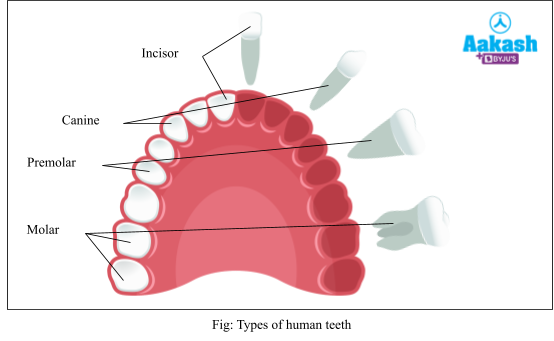
Human Teeth
They are of four types as follows:
- Incisors - They are chisel shaped and have one root. They are eight in number and mainly used for cutting.
- Canines - They are dagger-shaped and have one deep root. They are four in number and used for ripping and shredding.
- Premolars - They are bicuspid teeth, that means they have two cusps at the crown. The premolars of the upper jaw have two roots and the premolars of the lower jaw have one root. They are eight in number and used for chewing and crushing.
- Molars - On the upper jaw they have three roots and the molars of the lower jaw have two roots. They are 12 in number and help in chewing, crushing and grinding.
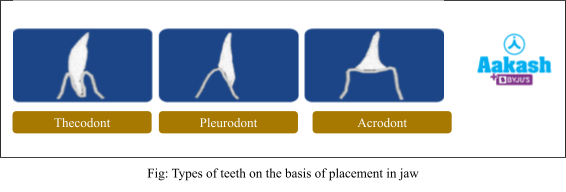
Classification of Dentition on the Basis of Placement in Jaw
On the basis of placement in the jaw, teeth are of three types as follows:
- Thecodont dentition - These types of teeth are present in the bony sockets. They are found in man and crocodile.
- Pleurodont dentition - These types of teeth are present on the lateral side of jaw bone and commonly found in reptiles.
- Acrodont dentition - These types of teeth are present on the terminal part of the jaw bone. These are found in amphibians and fish.
Classification of Dentition on the Basis of Appearance in Life
On the basis of appearance in life, teeth are of three types as follows:
- Monophyodont - These types of teeth appear once in lifetime. Examples include wisdom teeth (third molar) in man which appear once in lifetime.
- Diphyodont - These types of teeth appear twice in lifetime. Examples include incisors, canines and molars.
- Polyphyodont - These types of teeth appear more than twice in lifetime. Examples include teeth in amphibians.
Classification of Human Dentition on the Basis of Appearance in Life
On the basis of appearance in life, human teeth are of two types as follows:
- Temporary Teeth - They are also known as milk or deciduous teeth. They developed fully by the age of two or three years. They are 20 in number. Premolars are absent in temporary teeth. Dental formula of temporary teeth is shown below.

- Permanent Teeth - They replace the temporary teeth. They start forming at the age of six and complete formation by the age of 12. The wisdom teeth or last molar form after the age of 18. They are 32 in number. Once broken, they cannot be replaced naturally. Dental formula of permanent teeth is shown below:

Role of Buccal Cavity in Digestion
Buccal cavity performs two major functions and these are mastication of food and facilitation of swallowing.
Mechanical Digestion or Mastication
It is the chewing of food and mixing of saliva with the help of teeth and tongue in the mouth. Food enters the alimentary canal through the mouth where it is chewed and broken down into smaller pieces. These smaller pieces of food mixed with saliva with the help of tongue. Saliva is the binding agent that holds the food together and forms a bolus.
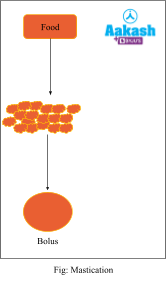
Constituents of Bolus
The constituents of bolus are as follows:
- Water
- Different compounds in food like fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
- Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, chlorine etc.
- Enzymes like salivary amylase and lysozyme
- Bacteria of mouth and food - Lysozyme acts on bacteria and destroys them.
Chemical Digestion
In the buccal cavity, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids are not digested. Only carbohydrates are digested in the buccal cavity. 3-5% of carbohydrates are digested here.
|
Carbohydrates |
Carbohydrates are long chains of sugar molecules (polysaccharides). Saliva contains enzymes like salivary amylase. It is responsible for the breakdown of polysaccharides into simpler forms called disaccharides. Amylase is only able to convert 30% of carbohydrates into monosaccharides. The rest of the carbohydrates remain as polysaccharides.
Salivary amylase is also called ptyalin. 30% of ingested starch is digested as disaccharides in the following way.
Isomaltose is similar to maltose, but with a different structure. |
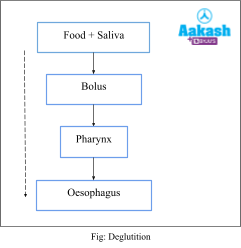
Deglutition
Deglutition is the scientific term of swallowing. The centre for swallowing present in the medulla oblongata initiates the deglutition reflex. It also causes progressive contraction of the pharyngeal muscles which continue to propel the food bolus through the pharynx.

Deglutition helps in the passing of bolus from mouth to the pharynx to the oesophagus in the following way.
Practice Problems of Buccal Cavity
Question 1. Determine the structure which is characterised as the anterior portion of the roof of the buccal cavity?
a. Hard palate
b. Soft palate
c. Rugae and uvula
d. None of the above
Solution: The roof of the buccal cavity is called palate which is divided into two parts: hard palate and soft palate. The anterior and posterior portion of the roof is called hard palate and soft palate respectively. Hard ridge-like structures called rugae are present in the hard palate. Rugae is supported by bones. It holds the food that is under mastication. Hence, the correct option is a.
Question 2. Determine the characteristic features of human teeth?
a. They are thecodont
b. They are heterodont
c. They are diphyodont
d. All of the above
Solution: Human teeth are thecodont. Thecodont detention are the types of teeth that are embedded in sockets. They are heterodont which means they have more than one type of teeth. Different types of teeth present in humans are canines, incisors, premolars, and molars. Human teeth are also diphyodont, that means, two sets of teeth appear during the lifetime. Milk teeth are the first set of teeth. They are temporary and called deciduous teeth. The other set of teeth is permanent which replace the milk teeth. Hence, the correct option is d.
Question 3. Determine the structure which has the small projections on the upper surface of the tongue and some of which have taste buds?
a. Lingual frenulum
b. Papillae
c. Enamel
d. Pulp cavity
Solution: The small projections on the upper surface of the tongue, some of which have taste buds are called papillae. The papillae are of four different types: circumvallate, fungiform, filiform and foliate. Hence, the correct option is b.
Question 4. Label the different parts of a palate in the given figure?

Solution: In the given figure, ‘a’ represents the hard palate, ‘b’ represents the soft palate and ‘c’ represents the uvula. Hard palate is the anterior part. Soft palate is the posterior part. Uvula is the extension of the soft palate.

FAQs of Buccal Cavity
Question 1. The component of food which is digested in the buccal cavity?
Solution: Carbohydrates are commonly digested in the buccal cavity by the enzyme salivary amylase present in the saliva. Amylase converts 30% of carbohydrates into monosaccharides at a pH of around 6.8.
Question 2. Which structures are present in the buccal cavity?
Solution: Buccal cavity contains three prominent structures and these are palate, tongue and teeth. Palate is described as the roof of the buccal cavity. Tongue is a muscular organ that forms the floor of the mouth. Teeth are the hard structures embedded in the sockets of the jaw bone.
Question 3. Write down the role of buccal cavity in the process of digestion of food?
Solution: The digestion of food starts in the mouth when we chew it. Mastication is the process of mixing food with saliva with the help of tongue and teeth. This results in a bolus. The chemical digestion of carbohydrates occurs in the buccal cavity. 30% of carbohydrates are converted into simpler units called monosaccharides via salivary amylase.
Question 4. Which enzyme is responsible for chemical digestion in the buccal cavity?
Solution: Salivary amylase secreted by salivary glands is responsible for chemical digestion in the buccal cavity. The carbohydrates are digested into disaccharides and monosaccharides by amylase.




