-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Viruses: Discovery, Characteristics, Structure and Classification
We have all suffered from cough and cold at some point in our life. Do you know what causes cough and cold? It is caused by infectious agents known as viruses. In fact many common diseases that we know of, such as smallpox, measles, polio, etc are caused due to viruses.
But where do these viruses fall in Whittaker’s Five Kingdom Classification? You will be amazed to know that they are not included in any of the five kingdoms. Do you know why? It’s because viruses possess unique characteristics which cannot be classified into any of the five kingdoms suggested by Whittaker. In fact, viruses are considered to be connecting links between living and non living as they share characteristics of living organisms as well as non living objects. Interesting right? Come let us learn more about these amazing structures. The branch of biology that deals with the study of viruses is called virology.
Table of Contents
- Discovery of viruses
- Characteristics of viruses
- Structure of a virus
- Classification of viruses
- Practice Problems
- FAQs
Discovery of Viruses
The word ‘virus’ means poisonous fluid or venom. Various scientists have contributed to the discovery of viruses as described below:
- Viruses were recognised by Dmitri Ivanowsky in the year 1892 for the very first time as microorganisms which caused tobacco mosaic disease in plants. He found that viruses are smaller than bacteria.

- In 1898, M.W. Beijerinek showed that healthy plants can be infected by the extract of infected tobacco plants. Thus, he called the fluid as Contagium vivum fluidum, i.e., infectious living fluid.

- In 1935, W.M. Stanley crystallised viruses and demonstrated that these virus crystals are mainly made up of proteins. It was also elucidated that the viruses being obligate parasites are not active outside their host cells.

Characteristics of Viruses
Viruses are acellular organisms, i.e, they do not possess a cellular structure. They are non-living (inert) outside the living organism (host) but living inside the living organism. They are obligate intracellular parasites which are smaller in size than bacteria as they can easily pass through bacterial filters. They can replicate themselves only inside the living organism (host) eventually controlling the host machinery and killing host cells. They cause diseases in their specific host.
Structure of a Virus
Viruses have an outer protein coat called capsid inside which the genetic material is present. Thus, a virus is called a nucleoprotein. They do not have enzyme machinery.
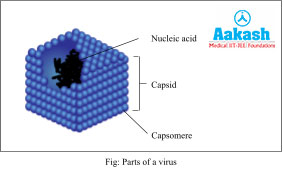
Capsid
The small subunits constituting the capsid are called capsomeres. Arrangement of capsomeres may vary from one virus to another such as helical, geometric or polyhedral. The primary function of capsid is to protect the genetic material of viruses.
Envelope
When a viral particle buds off from the host cell, it gets surrounded by the plasma membrane of the host cell, called envelope. Thus, it is an outer layer present on some viruses. The envelope helps in survival of the viruses and also aids in infecting other host cells. Examples of enveloped viruses are Hepatitis B virus, COVID-19, Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Genetic material
The genetic material of a virus is usually infectious and is injected within the host cell. It can either be single stranded or double stranded DNA or RNA which usually undergoes rapid mutations. Their genetic material can replicate only inside the host by using host replication machinery.
Structure of Some Viruses
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
It is a cylindrical shaped virus containing a capsid made up of 130 helically arranged capsomeres. Genetic material is ssRNA. It causes the mosaic disease in tobacco plants.

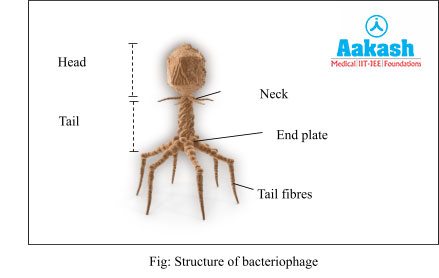
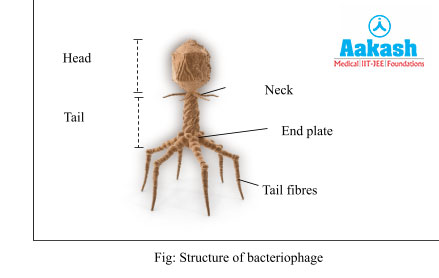
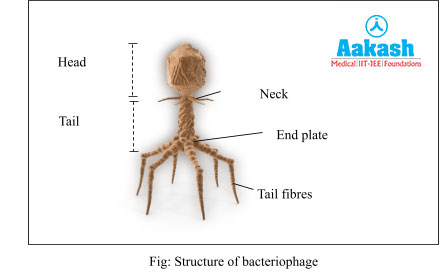
Bacteriophage
These viruses infect bacteria. Bacteriophages have a tadpole-like shape with a hexagonal head and a tail. The head has a protein coat in which double stranded DNA is tightly packed.
The cylindrical tail is made entirely of proteins and has a core tube filled with lysozyme which helps in penetration of the phage DNA into the bacterial host. A narrow neck lies between the head and the tail. The core tube is covered by a contractile sheath and is attached to the head with the help of a collar.
At the base, the tail has an end plate which is hexagonal in shape and has tail fibres emerging from each corner of the hexagon. The end plate and tail fibres help in attachment of the bacteriophage to the host cell.
Viruses: Living or Non-living entity?
Living Characteristics of Viruses
Like living organisms viruses have genetic material (DNA or RNA) and can reproduce in living organisms. They are causative agents of infectious diseases in living organisms. They have a protein coat surrounding their genetic material which can undergo rapid mutation.
Non-living Characteristics of Viruses
Viruses cannot sustain outside the host and are hence called obligate intracellular parasites. They lack an enzyme system and have an acellular structure. Viruses can also be easily crystallised.
Classification of Viruses
Based on shape
Viruses can be classified into the following categories based on their shape:
|
Shape of virus |
Figures |
Example |
|
Spherical |
|
Influenza virus |
|
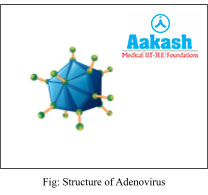
Cuboidal (or polyhedral) |
|
Adenovirus |
|
Rod-shaped |
|
Tobacco Mosaic Virus |
|
Tadpole like/ irregular/ binal (having both helical and cuboidal parts) |
|
Bacteriophage |
Based on host
Viruses can be classified into the following categories based on the host that they infect:
- Phytophage: Viruses that infect plants. Example: Tobacco Mosaic Virus

Fig: Tobacco Mosaic Virus
- Zoophage: Viruses that infect animals (for example, humans).
- Bacteriophage: Viruses that infect bacteria.
Based on nature of genetic material
The viruses have either RNA or DNA as their genetic material. RNA might be present in the form of a single-stranded structure (ssRNA) or a double-stranded structure (dsRNA). DNA in viruses usually exists as a double-stranded structure designated as dsDNA.
|
Nature of genetic material |
Examples of virus |
Possible host |
|
ssRNA |
Tobacco mosaic virus |
Plants |
|
Influenza virus, mumps virus |
Animals |
|
|
dsRNA |
Rotavirus |
Animals |
|
dsDNA |
Pox virus |
Animals |
|
T4 bacteriophage |
Bacteria |
|
|
Cauliflower mosaic virus |
Plants |
Examples of Viral Diseases In plants
Some of the viral diseases in plants are listed below:
- Tobacco mosaic disease
- Cauliflower mosaic disease
- Potato leaf roll
- Papaya leaf curl
- Banana bunchy top etc.
Symptoms of plant diseases caused by viruses
|
Symptoms |
Figures |
|
Leaf rolling |
|
|
Mosaic formation |
|
|
Leaf curling |
|
|
Vein clearing |
|
|
Dwarfing |
|
|
Yellowing of veins |
|
In animals
Some of the viral diseases in animals are listed below:
Animal viral diseases
- Bird flu
- Foot and mouth disease
- Ranikhet disease
Human viral diseases
- Measles
- Chicken pox
- Poliomyelitis
- Hepatitis
- AIDS
- Influenza
- Herpes
Practice Problems of Viruses
Question1. Select the correct statement about viruses.
A. They have only RNA as their genetic material.
B. They are facultative parasites.
C. They have a protein coat which protects the genetic material.
D. They cannot be crystallised.
Answer: Viruses have a protein coat called capsid which protects the genetic material. Viruses are obligate parasites which can have either DNA or RNA as the genetic material. Viruses have an acellular structure and can easily be crystallised. Thus, option c is correct.
Question2. Match the following.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
I. dsDNA |
A. Tobacco Mosaic Virus |
|
II. dsRNA |
B. Pox virus |
|
III. ssRNA |
C. Rotavirus |
- I - C, II - A, III - B
- I - A, II - C, III - B
- I - C, II - B, III - A
- I - B, II - C, III - A
Answer: The correct match is as follows:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
I. dsDNA |
B. Pox virus |
|
II. dsRNA |
C. Rotavirus |
|
III. ssRNA |
A. Tobacco Mosaic Virus |
Hence, option d is correct.
Question3. Explain the structure of a bacteriophage.
Answer: Bacteriophages have a tadpole-like shape with a hexagonal head and a tail. The head has a protein coat in which double stranded DNA is tightly packed.
The cylindrical tail has a core tube filled with lysozyme. The core tube is covered by a contractile sheath and is attached to the head with the help of a collar. A narrow neck lies between the head and the tail.
At the base, the tail has an end plate which is hexagonal in shape . Tail fibres emerge from each corner of the hexagonal plate. The end plate and tail fibres help in attachment of the bacteriophage to the host cell.
Question4. What is the function of capsid in viruses?
Answer: The major role of the capsid is to protect the genetic material present beneath it.
FAQs of Viruses
Question1. Name the virus which causes AIDS.?
Answer: AIDS is caused by a retrovirus named Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). It has two single stranded RNA molecules as its genetic material.
Question2. Can viral diseases be treated with antibiotics?
Answer: Antibiotics are chemicals which are used to kill or stop the growth of microbes. Most antibiotics work against bacteria and kill them by inhibiting cell wall synthesis or protein synthesis. As viruses are acellular in structure and do not possess their own enzyme machinery, they cannot be killed using antibiotics. Thus antibiotics cannot be used to treat viral diseases.
Question3. Can viruses infect bacteria?
Answer: Bacteriophages are viruses which infect bacteria. For example: T4 phage, M13 phage.
Question4. Are viruses living or nonliving?
Answer: Viruses are considered to be connecting links between living and nonliving as they share characteristics of both living organisms and nonliving objects. Like living organisms they have a genetic material and are capable of reproducing within a host. But it behaves like a nonliving object outside the host body as it lacks a cellular structure, does not possess any enzyme machinery and can easily be crystallised.












