-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Differences Between Vertebrates and Invertebrates, Practice Problems and FAQs
Earthworms and snakes are two crawling animals which we can find in our nearby backyards. What is the difference you can find between these animals? Both look somewhat similar!! But earthworms and snakes have extremely different evolutionary histories. Both crawl because they lack limbs. But the major difference between them is that the earthworms are limbless invertebrates and snakes are limbless vertebrates.


GIF: Earthworm GIF: Snake
So what makes these differences? Yes, it is the presence and absence of the vertebral column. If you observe an earthworm, their body is more flexible than the snakes. Even Though the snakes can also pass easily through small holes and make them roll up over the trees, there is one structure inside them called the vertebral column, which will make them unable to move if it gets injured. Other animals which have vertebral columns include, the fishes, humans, amphibians etc. So what are the animals that lack a vertebral column? We can call them invertebrates. There are many differences between vertebrates and invertebrates. So in this article we are going to discuss more about this.
Table of contents
Invertebrates
Those animals that lack a vertebral column or backbone that are derived from the notochord are called invertebrates. Most of the animal species except the vertebrates can be included under invertebrates.


GIF: Leech (Invertebrate) GIF: Cyanide millipede (Invertebrate)
Invertebrate phyla
The invertebrates are included under the following phyla:
- Porifera (Sponges)
- Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
- Ctenophora (Sea walnuts)
- Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
- Aschelminthes (Roundworms)
- Annelida (Segmented worms)
- Arthropoda (Animals with jointed legs)
- Mollusca (Soft bodied animals)
- Echinodermata ( Spiny skinned animals)
- Hemichordata (Half chordates)
- Some members of Chordata

Fig: Invertebrates
Notochord
Animals which possess a notochord are called chordates. Notochord is a flexible rod-like structure situated on the mid dorsal side between the central nervous system and the alimentary canal. It supports the body. This structure persists throughout life in lower chordates. In phylum chordata there are three subphylum and they are as follows:
- Urochordata or Tunicata
- Cephalochordata
- Vertebrata
Urochordata
These chordates possess the notochord only in the larval tail. In adults the notochord is replaced by a dorsal ganglion. Hence their development is called retrogressive metamorphosis as they change from a better developed larva to a less developed adult. They are called invertebrate chordates. Examples of Urochordata include Doliolum, Ascidia, Salpa, Herdmania, etc.

Fig: Examples of urochordates
Cephalochordata
They possess notochord from the head to the tail region and it persists throughout life. Their development is called progressive metamorphosis, as the less developed larva changes to a better developed adult. An example of cephalochordata is Branchiostoma (Sea lancelet or amphioxus).

Fig: Example of Cephalochordata - Branchiostoma
Distinction between lower invertebrates, higher invertebrates and vertebrates
Both urochordates and cephalochordates are considered as invertebrate chordates. The invertebrates like the members of the phylum, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata and Hemichordata are included under higher invertebrates as they lack backbone but possess coelomic cavity. The lower invertebrates include the phylum Porifera, Cnidaria, Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes and Aschelminthes as they lack backbone and coelom or true body cavity. The third subphylum of Chordata has a notochord which is developed into a vertebral column in adults and they are called vertebrates.
Vertebrates
The chordates having a single notochord during the embryonic stage of their life, and it eventually develops into a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult form, are called vertebrates. Vertebrates are also called craniata, because the anterior notochord segment is replaced with a skull or cranium to protect the brain in them.

Fig: Development of notochord into a vertebral column in vertebrates
Classification of vertebrates
On the basis of presence or absence of jaws, the subphylum Vertebrata can be classified into two divisions as follows:
- Agnatha - Vertebrates that lack jaws.
- Gnathostomata - Vertebrates that bear jaws.

Fig: Classification of vertebrates
Classification of Agnatha
Cyclostomata is the only one class present in the division Agnatha. The major characteristic of this class is the presence of a suctorial mouth. Examples include lamprey (Petromyzon) and hagfish (Myxine).

Fig: Members of class Cyclostomata
Classification of Gnathostomata
On the basis of the organ which helps them for the movement, there are two super classes under the division Gnathostomata and are as follows:
Super class Pisces
They bear fins. Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) and Osteichthyes (bony fishes) are the two classes of Pisces.

Fig: Super class Pisces
Superclass Tetrapoda
They bear limbs. There are four classes in the superclass Tetrapoda and are as follows:
- Class Amphibia
- Class Reptilia
- Class Aves
- Class Mammalia

Fig: Examples of Superclass Tetrapoda
Differences between vertebrates and invertebrates
The major differences between vertebrates and invertebrates are as follows:
Vertebrates |
Invertebrates |
|
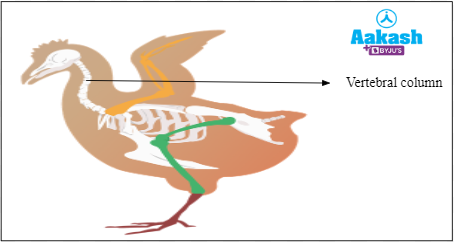
Backbone or vertebral column is present
Fig: Vertebral column |
Backbone or vertebral column is absent |
|
Notochord is present in the mid-dorsal line beneath the nerve cord during the embryonic period
Fig: Notochord |
Do not possesses a notochord (exceptions include the invertebrate chordates like urochordates and cephalochordates) |
|
They are large sized animals mostly |
They are small and slow moving animals |
|
Highly developed animals |
Lesser developed animals |
|
2% of animal species are vertebrates |
98% of the animal species are invertebrates |
|
Pharyngeal gill slits present and it increase the efficiency of breathing
Fig: Pharyngeal gill slits |
Pharyngeal gill slits are absent. Exceptions include hemichordates |
|
Central nervous system is a hollow tube and it is located in the mid-dorsal line
Fig: Central nervous system |
Central nervous system is a solid tube and it is located in the mid-ventral line
Fig: Central nervous system |
|
Endoskeleton is living and is composed of a skull and vertebral column
Fig: Endoskeleton |
Endoskeleton is present some like squids |
|
Internal skeleton is present |
Internal rigid skeleton is absent |
|
Closed circulatory system is present
Fig: Closed circulatory system |
Open circulatory system is present
Fig: Open circulatory system |
|
A chambered heart is present on the ventral side of the body
Fig: Chambered ventral heart |
When heart is present, it is located on the dorsal side
Fig: Dorsal heart |
|
Possess hepatic portal system |
Hepatic portal system is absent |
|
Do not have more than two pairs of limbs
Fig: Limbs |
Many have more than two pairs of limbs
Fig: Limbs |
|
Most are unisexual animals |
Most are hermaphroditic or bisexual animals. Examples include sponges, worms, snails and slugs |
|
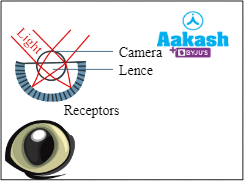
Compound eyes are absent in all animals and possess simple eyes
Fig: Simple eyes |
Animals with compound eyes are also present
Fig: Compound eyes |
|
Blood temperature and outside temperature can be different |
Blood temperature and outside temperature are same |
|
Examples include fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals |
Examples include sponges, jelly fishes, insects, crabs, worms etc. |
|
Fig: Vertebrates |
Fig: Invertebrates |
Practice Problems
1. Which of the following is a vertebrate chordate?
- Ctenophora
- Echinodermata
- Hemichordata
- Cephalochordata
Solution: Those animals that lack a vertebral column or backbone that are derived from the notochord are called invertebrates. Most of the animal species except the vertebrates can be included under invertebrates. The lower groups of organisms in the phylum Porifera, Coelenterata, Platyhelminthes, Aschelminthes and Ctenophora, are called lower invertebrates. The invertebrates like the members of the phylum, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata and Hemichordata are included under higher invertebrates as they lack backbone but possess coelomic cavity. Chordates are those animals which possess a notochord. In phylum chordata there are three subphylum and they are Urochordata or Tunicata, Cephalochordata and Vertebrata. The third subphylum of Chordata has a notochord which is developed into a vertebral column in adults and they are called vertebrates. Among these only urochordates and cephalochordates are called invertebrate chordates as they lack vertebral columns. Hence the correct option is d.
2. If chordates have the presence of notochord in the larval tail, then they are called _________________.
- Hemichordata
- Urochordata
- Cephalochordata
- Vertebrata
Solution: Hemichordata has a stomochord in the collar region. If chordates have the presence of notochord in the larval tail, then they are called urochordates. In adults the notochord is absent. If the notochord runs from head to the tail region of an adult, then they are called cephalochordates. They possess notochord from the head to the tail region and it persists throughout life. Their development is called progressive metamorphosis, as the less developed larva changes to a better developed adult. An example of cephalochordata is Branchiostoma (Sea lancelet or amphioxus). The chordates having a single notochord during the embryonic stage of their life, and it eventually develops into a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult form, are called vertebrates. Hence the correct option is b.
3. Assertion: Vertebrates are called craniata.
Reason: Anterior notochord segment is replaced with a skull or cranium to protect the brain in a vertebrate.
- Both the assertion and the reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
- Both the assertion and the reason are false.
Solution: The chordates having a single notochord during the embryonic stage of their life, and it eventually develops into a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult form, are called vertebrates. Vertebrates are also called craniata, because the anterior notochord segment is replaced with a skull or cranium to protect the brain. Hence the correct option is a.
4. Which of the following are included under vertebrates?
- Aves
- Mammals
- Pisces
- All the above
Solution: The chordates having a single notochord during the embryonic stage of their life, and it eventually develops into a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult form, are called vertebrates. On the basis of presence or absence of jaws the subphylum Vertebrata can be classified into two; Agnatha that lacks jaw and Gnathostomata that bears jaw. On the basis of the organ which helps them for the locomotion, there are two super classes; Pisces that bears fins and Tetrapoda that bears limbs. Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) and Osteichthyes (bony fishes) are the two classes of Pisces. There are four classes in the superclass Tetrapoda and are; Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammalia. Hence the correct option is d.
FAQs
1. Which is the largest terrestrial invertebrate in the world?
Answer: The largest terrestrial invertebrate in the world is the coconut crab (Birgus latro). Charles Darwin described it as ‘a monstrous size’. It has a leg span of 1m and weights up to 4kg.

GIF: Giant coconut crab
2. Which is the largest vertebrate?
Answer: The largest vertebrate is the blue whale. It is also the biggest mammal in the world. It is 100 feet long and weighs 200 tons.

Fig: Blue whale
3. What is a sonic hedgehog?
Answer: Sonic hedgehog is a protein secreted from notochord and floor plate. It is a morphogen, which has the ability for organogenesis in embryonic development. It also helps in the signalling of the development of motor neurons.
4. What is notogenesis?
Answer: The development of the notochord by epiblasts (primitive ectoderm) is called notogenesis. The cells migrating from primitive nodes and pit derives the progenitor notochord.