-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Instruments: Sphygmomanometer, its Parts, Use and ECG
Have you ever seen someone getting their blood pressure checked by a doctor? The doctor ties up a belt above the elbow and then pumps up some air into it. While doing this he looks into the reading of a machine which has measurements marked on it. Do you know what this instrument is called? It is a Sphygmomanometer.
Now tell me, have you ever heard a doctor suggesting someone you know get an ECG done? In case you haven’t, let me tell you that an electrocardiogram or ECG is performed to check the functioning of the heart.
Let’s discuss both the instrumental and functional aspects of these two devices in detail.
Table of contents
Sphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer is an instrument used to measure blood pressure which is the force exerted by blood on the walls of the blood vessels.
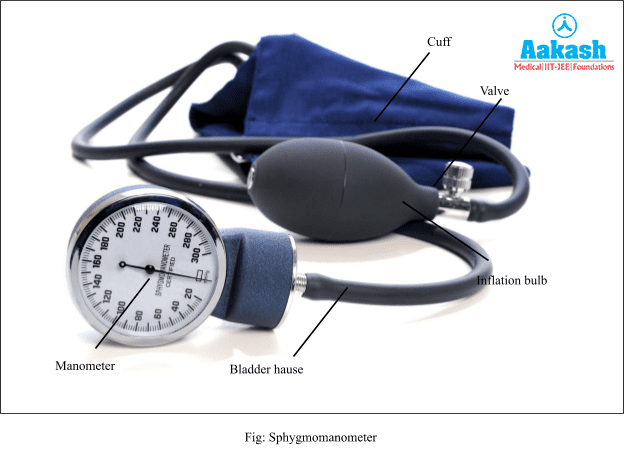
Parts of Sphygmomanometer
- An inflatable bag, known as bladder, is used to compress the arm to block the artery.
- A cuff is designed to hold the bladder around the arm during the measurement.
- A manometer is used to measure the air pressure in mmHg. The manometer measures the air pressure applied to the cuff with a watch-like movement. The gauge uses a sequence of copper or beryllium to expand the diaphragm, and gears convert the linear movement of the diaphragm into mm Hg measurements.
- A deflation valve is used to control the cuff and plays a vital role in getting an accurate measurement.
- Air is pumped into the cuff using a bulb.
How to use a Sphygmomanometer?
To begin with, the length of the cuff bladder should be equal to 80% of the circumference of the upper arm. The cuff is to be wrapped around the upper arm in a way that the lower edge of the cuff is an inch above the antecubital fossa (transitional area between the upper arm and forearm that lies anteriorly at the elbow region). The stethoscope’s (instrument used by doctors to listen to heart sounds) bell is to be pressed lightly over the brachial artery (supplies blood to the upper arm and elbow joint) which lies below the cuff’s edge.
The air from the cuff is to be released at a medium rate to 180mmHg. The first knocking sound is to be monitored by listening with the help of a stethoscope. The mercury reading on the gauge is noted. This should be done for both the arms and the pressure, the position of the subject and the size of the cuff should be recorded. If the pressure is more, then the blood pressure should be measured with few minutes of gaps between the two measurements.
ECG
The graphical representation of all the electrical activities that a heart performs during each cardiac cycle is termed as electrocardiogram or ECG. The instrument used for the recording of these electrical events is called ‘electrocardiograph’.

Method of ECG
To perform ECG, a special gel is applied to the patient;’s upper body,which helps to improve the electrical conduction. Then the patient is connected to the machine with three electrical leads placed on his body at three points - one to each wrist and to the left ankle. These leads continuously monitor the heart activity and record the heart's activities and an electrocardiograph amplifies these signals. The screen then shows a wavy deflection wave known as the ECG.
Transmission of Impulses in the Heart
Before we understand the interpretation of an ECG, let's take a look at how the electrical impulses originate in the heart and are conducted across it.
The SA node or sino-atrial node, known as the pacemaker of the heart, initiates the impulse of contraction for the cardiac muscles by generating an action potential. Action potential is set up due to the depolarisation of the muscle cells which creates a difference in the distribution of charges on either side of the sarcolemma, that is, the cell membrane of the cardiac muscle cell. The action potential set up by the SA node causes the muscles of the atria to contract, resulting in atrial systole.
The action potential is then conducted by the AVN (atrioventricular node) and AV (atrioventricular) to the bundle of His which transmits it through
the entire ventricular musculature causing them to contract (ventricular systole). The atria undergo relaxation (diastole) simultaneously.
As the ventricle muscles, AV node and bundle of His become repolarised, the action potential is lost and the ventricles relax (ventricular diastole). The atria and ventricles remain relaxed simultaneously for 0.40 secs after which the depolarisation of the SA node is repeated.
ECG Waves
A typical human ECG shows five waves or deflections, which are called P wave ,QRS complex and T waves.
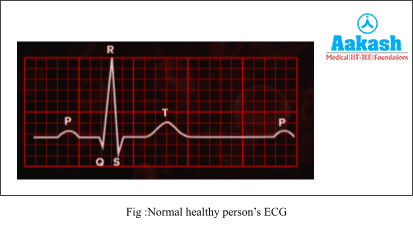
P wave
The P-wave shows atrial depolarisation or atrial systole, leading to the contraction of both the atria. This wave indicates the generation of action potential in the SA node or sino-atrial node.
QRS complex
The QRS complex shows the ventricular depolarisation or ventricular systole, which is due to the depolarisation of the AV node, bundle of His and repolarisation of the SA node.
T wave
The T wave indicates ventricular repolarisation which causes the cardiac muscles of the ventricles to return back to their normal state which results in ventricular relaxation or diastole.
The abnormalities in the functioning of the heart alters the wave pattern of ECG, thus ECG is a great indicator of cardiac diseases.
Practice problems of Instruments
Question1. P wave indicates.?
(a) Depolarization of right ventricle
(b) Depolarization of left ventricle
(c) Depolarization of both atria
(d) Atria to ventricular conduction time
Answer: The P-wave indicates the generation of action potential in the SA node or sino-atrial node. Thus, it shows atrial depolarisation or atrial systole, leading to the contraction of the muscles of both the atria. Thus, the correct option is (c).
Question2. Ventricular muscle depolarization is indicated by.?
(a) PR interval
(b) P wave
(c) U wave
(d) The QRS complex
Answer: The ventricular depolarisation causes contraction of the ventricular muscles leading to ventricular systole. The depolarisation of ventricles occurs due to depolarisation of the AV node and bundle of His as the action potential travels down from the SA node. This simultaneously causes the repolarisation of the SA node. The QRS complex represents the ventricular muscle depolarization.
Question3. How does a sphygmomanometer work?
Answer: To begin with, the length of the cuff bladder should be equal to 80% of the circumference of the upper arm. The cuff is to be wrapped around the upper arm in a way that the lower edge of the cuff is an inch above the antecubital fossa (transitional area between the upper arm and forearm that lies anteriorly at the elbow region). The stethoscope’s (instrument used by doctors to listen to heart sounds) bell is to be pressed lightly over the brachial artery (supplies blood to the upper arm and elbow joint) which lies below the cuff’s edge.
The air from the cuff is to be released at a medium rate to 180mmHg. The first knocking sound is to be monitored by listening with the help of a stethoscope. The mercury reading on the gauge is noted. This should be done for both the arms and the pressure, the position of the subject and the size of the cuff should be recorded. If the pressure is more, then the blood pressure should be measured with few minutes of gaps between the two measurements.
Question4. What is the function of the cuff of a sphygmomanometer?
Answer: in a sphygmomanometer, an inflatable bag, known as bladder, is used to compress the arm to block the artery. A cuff is designed to hold the bladder around the arm during the measurement.
FAQs of Instruments
Question1. Can we place ECG electrode lead on the right ankle as well?
Answer: The ECG electrode which acts as the ground electrode can be placed either on the right or the left ankle without affecting the ECG curve.
Question2. What are the benefits of an ECG?
Answer: An ECG can be used in the detection of following diseases-:
- Cardiac arrhythmias – where the heart beats too slowly, too quickly, or irregularly.
- coronary heart disease – where the heart's blood supply is blocked or interrupted by a build-up of fatty substances.
- heart attacks – where the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked.
- Other heart related issues.
Question3. What does a reading of more than 120/80 mmHg on the sphygmomanometer indicate?
Answer: The upper limit of normal human blood pressure is 120 mmHg which corresponds to the systole phase or contraction of the heart and the lower limit is 80 mmHg which corresponds to the diastole or relaxation phase. Blood pressure recorded beyond this limit is considered to be symptomatic of high blood pressure or hypertension.
Question4. What does an abnormal ECG curve signify?
Answer: An abnormal ECG curve can be a signal to have a heart disease such as cardiac arrhythmia, coronary heart disease or heart attacks. Sometimes an ECG abnormality is a normal variation of a heart's rhythm, which does not affect your health.


