-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Pregnancy: Embryonic Development, Placenta, Parturition, Lactation, Practice Problems and FAQs
Do you know how long it takes a single fertilised cell to develop into a fully grown foetus? The entire term starting from conception of an embryo till the birth of the foetus is known as gestation of pregnancy. The duration of pregnancy varies from species to species. In humans, pregnancy lasts about 9 months.
You might have heard of granny or elder people telling pregnant women to eat healthy food for the health of the developing baby. But have you ever wondered, how does this food reach from the mother to the developing foetus? Well, the answer is placenta. It is a temporary organ formed during pregnancy and plays an important role by connecting mother and foetus.
Let us study in detail about placenta and pregnancy.
Table of Contents
- Gastrulation
- Embryonic Development
- Placenta
- Parturition
- Lactation
- Practice Problems of Preganancy
- FAQs of Pregnancy
Gastrulation
After fertilisation, the zygote undergoes repeated cell divisions to form a 16-32 celled structure known as a blastocyst which implants itself into the endometrial wall. This blastocyst is a spherical structure consisting of an inner cell mass surrounded by a layer of cells known as the trophoblast.
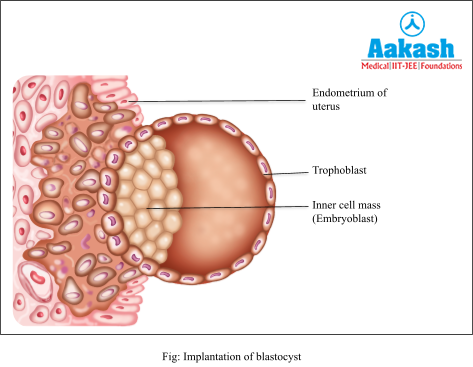
Gastrulation is the process in which embryoblast cells (inner cell mass) forms a structure called gastrula which differentiate to form three germ layers shortly after implantation. The exterior layer is called ectoderm and the innermost layer is called endoderm. Between the ectoderm and the endoderm appears a mesoderm (middle layer). These layers form different tissues and parts of the body.
The cells of the inner cell mass get organised into two layers, upper epiblast and lower hypoblast. The epiblast is composed of two layers of cylindrical cells. A small cavity develops between these two layers and forms the amniotic cavity which eventually gets filled with the amniotic fluid and protects the foetus from shocks and injuries. The epiblast gives rise to the ectoderm and mesoderm and the hypoblast gives rise to the endoderm.
The inner cell mass contains stem cells, called embryonic stem cells. They are pluripotent, that is, they have the ability to give rise to all of the tissues and organs.
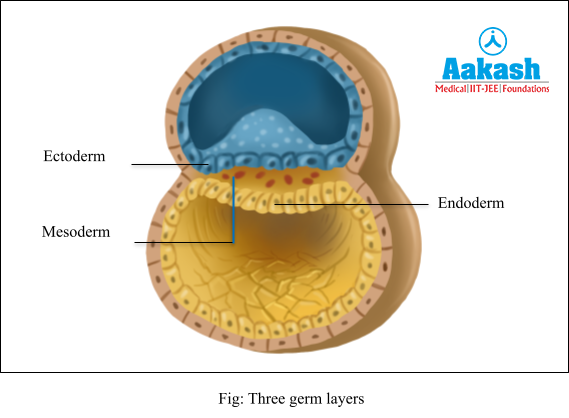
Ectoderm
It is the outermost germ layer of embryo which gives rise to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), the peripheral nervous system, neural tube, the sensory epithelia of the eye, ear and nose, epidermis, mammary gland etc.

Mesoderm
It is the middle germ layer of embryo which gives rise to the connective tissues (bone and cartilage), kidneys, heart walls, spleen etc.

Endoderm
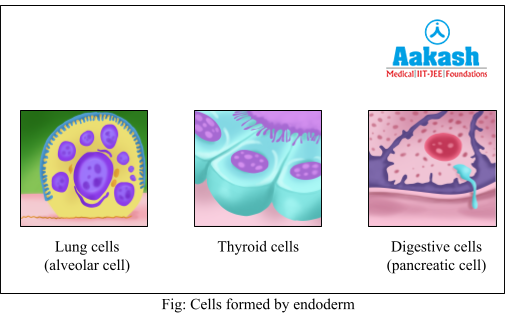
It is the innermost germ layer of embryo which gives rise to the epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tract; urinary bladder and urethra, parenchyma of the thyroid, liver, pancreas etc.
Embryonic Development
In humans, pregnancy lasts around 9 months or 40 weeks approximately. The time period of pregnancy during which a foetus develops within the mother’s womb is also called gestation period. It is divided into 3 trimesters consisting of 3 months each.

Ovulation, fertilisation, implantation, and gastrulation are all part of the first four weeks of pregnancy.
|
Trimester |
Month of pregnancy |
Organs developed |
|
1st |
1 |
Heart forms within the first month. By carefully listening to the heart sound using a stethoscope, the first symptom of a growing foetus can be detected. Major organ systems start developing. |
|
1st |
2 |
Limbs and digits start to form |
|
1st |
3 |
Placenta develops fully, external genitals begin to develop |
|
2nd |
4 |
Ability to hear and taste buds develop |
|
2nd |
5 |
The foetus starts showing movement and hair appears on the head |
|
2nd |
6 |
The eyelids split, the eyelashes form and the body gets covered with fine hair. |
|
3rd |
7 |
Increase in the frequency of eye movements |
|
3rd |
8 |
The sleep-wake cycle is well-controlled. |
|
3rd |
9 |
Foetus moves upside down and is ready for delivery |
During pregnancy, a female body undergoes various changes such as nausea, breast enlargement, weight gain and increase in urinary frequency
Placenta
After implantation of the embryo, the trophoblast develops two types of villi - trophoblastic villi and the chorionic villi. The chorionic villi are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood and become interdigitated to form a structure called the placenta that forms an intimate connection between the developing embryo (foetus) and the mother’s body.
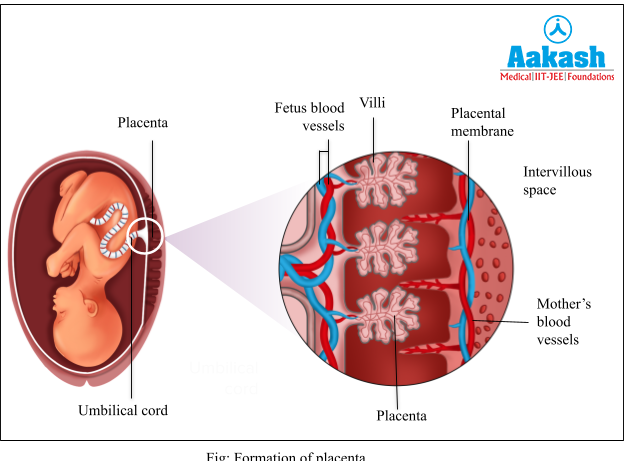
Role of Placenta
The placenta helps the embryo receive oxygen and nutrition from the mother and also removes carbon dioxide and excretory/waste products produced by the embryo by allowing these to diffuse into the mother’s blood. An umbilical cord connects the placenta to the embryo and aids in the movement of substances to and from the embryo. The placenta also functions as an endocrine organ, producing hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogens, and progestogens. The ovary also secretes a hormone called relaxin in the later stages of pregnancy which relaxes the ligaments of the pelvis and helps in widening of the cervix during childbirth. Women generate hCG, hPL, and relaxin exclusively during pregnancy.
In addition, additional hormones such as estrogens, progestogens, cortisol, prolactin, thyroxine, and others are elevated several fold in the maternal blood during pregnancy.
Increased production of these hormones is required to promote foetal growth, maternal metabolic alterations, and pregnancy maintenance.
hCG
It promotes progesterone secretion by corpus luteum and helps in maintaining the pregnancy. The strip of the pregnancy test kit has antibodies that help in measuring the presence of hCG in the urine.
hPL
It breaks down fats in mother to supply energy to the foetus
Parturition
Parturition refers to the process of delivering a foetus (childbirth). Expulsion/delivery of the foetus is caused by uterine contractions at the end of pregnancy.

Oestrogen, oxytocin, relaxin, prostaglandins, and other hormones play an important role in the process of parturition. It is stimulated by a complicated neuroendocrine mechanism. The fully grown embryo and placenta send out parturition signals, which cause moderate uterine contractions known as the foetal ejection reflex. This causes the release of oxytocin from maternal pituitary gland under the influence of the hypothalamus.
Oxytocin causes the uterine muscles to contract which further stimulates pituitary to release more oxytocin. The uterine contraction and oxytocin secretion creates a reflex which results in stronger and stronger contractions of the uterus eventually leading to the expulsion of the foetus from the uterus via the birth canal. The placenta is also ejected out of the uterus shortly after the baby is born.
Lactation
During pregnancy, the mammary glands of the female undergo differentiation and begin to produce milk through a process known as lactation under the influence of the prolactin hormone released by . Oxytocin plays an important role in lactation by assisting in the release of milk from the mammary glands.
Breast-feeding is a process of feeding the breast milk to the baby. Breast-feeding throughout the first six months of an infant's life is suggested by doctors for a healthy child's development.
Colostrum
Colostrum is the yellowish milk produced during the first few days of breastfeeding, and it contains many antibodies especially (IgA) that are critical for the development of resistance in newborns.
Practice Problems of Pregnancy
1. Which of the following structures is most likely to not develop if the germ layer creation in an embryo occurs without the formation of a separate ectoderm?
a. Neurons
b. Cardiac muscle tissue
c. Gonads
d. Bones
Solution: The three germ layers of ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm are formed during the gastrulation process. Specific tissues, organs, and organ systems arise from each of the three germ layers. The ectoderm undergoes multiplication and differentiation to form the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and brain. Ectoderm also produces neurons, epidermal skin cells, pigment cells, and other cells. Hence, option a is correct.
2. Which of the following is not a placental function?
a. Nutrient transfer to foetus
b. Respiratory gas exchange between foetus and mother
c. Waste elimination of foetus
d. Oxytocin production
Solution: Placenta connects the mother to the foetus and via the umbilical cord. It helps in the exchange of respiratory gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, allows diffusion of nutrients to the foetus from the mother’s blood and helps in elimination of nitrogenous waste from the foetus.
Oxytocin is a hormone secreted by the pituitary gland of the mother.
Thus, the correct option is d.
3. In humans, the foetal ejection reflex causes ___________ to release the hormone ____________ which is responsible for parturition.
a. placenta, human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
b. foetal pituitary, oxytocin
c. placenta, human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
d. maternal pituitary, oxytocin
Solution: The placenta and the fully grown foetus initiates foetal ejection reflex. This induces oxytocin release from the mother's posterior pituitary, which causes moderate uterine contractions. As a result, myometrium of the uterus contracts vigorously. Hence, option d is correct.
4. Match the following:
|
Period of pregnancy |
Development of foetus |
|
A. 3rd month |
I. Hair appears on the head |
|
B. 5th month |
II. Increase in the frequency of eye movements |
|
A. 7rd month |
III. External genitals begin to develop |
a. A - II, B - III, C - I
b. A - III, B - I, C - II
c. A - I, B - III, C - II
d. A - II, B - I, C - III
Solution: The external genitalia begin to develop during the 3rd month, hair appears on the foetus’ head during the 5th month and the frequency of eye movements increase during the 7th month of pregnancy.
Hence, option b is correct.
FAQs of Pregnancy
1. Placenta is an important endocrine tissue. What are the roles played by placenta?
Solution: Placenta is a connecting tissue that joins the mother and the foetus via the umbilical cord. It helps in the exchange of respiratory gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, allows diffusion of nutrients to the foetus from the mother’s blood and helps in elimination of nitrogenous waste from the foetus. It also produces hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), oestrogens, and progesterone and functions as an endocrine gland.
2. What is colostrum and why is it important for newborns?
Solution: Colostrum is the yellowish milk produced by the mammary glands during the first few days of lactation. It contains a number of antibodies, particularly IgA, that are important for providing immunity against microbes to the newborn.
3. How does foetal ejection reflex help in parturition?
Solution: The completely developed embryo and placenta send out parturition signals, which trigger the foetal ejection reflex, which is characterised by moderate uterine contractions. The uterine contractions triggers the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary gland. The uterine muscles contract as a result of oxytocin, which stimulates the pituitary to release more oxytocin. The uterine contraction and oxytocin production trigger a response that causes the uterus to contract more and harder, eventually resulting in the foetus being expelled from the uterus through the birth canal.
4. What is the role of hCG and how is it used for pregnancy test?
Solution: hCG is human Chorionic Gonadotropin hormone secreted by the placenta during pregnancy and is present in the urine. It induces the secretion of progesterone from corpus luteum to maintain pregnancy. Pregnancy test kits contain a strip of antibodies that can detect presence of hCG in urine.


