-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Cancer: Types, Causes, Detection, Diagnosis, Treatment, Practice Problems and FAQs
Human body is made up of numerous cells, right? These cells multiply and coordinate together to form tissues. Cell growth and differentiation are tightly controlled and regulated in our bodies. What will happen if regulation of cell division gets disrupted?
Cells will grow abnormally due to uncontrolled cell division. This leads to the formation of mass of undifferentiated cells called tumours. You must be wondering, what gives rise to cancer? How can a tumour become cancerous? When a tumour starts spreading from one organ to another organ, it is called cancer.
Cancer is one of the most dreaded diseases nowadays and it is a leading cause of death around the world. Every year, a huge number of people develop cancer and die as a result. Some of the most active fields of research in biology and medicine have been the mechanisms that underlies the genesis of cancer or oncogenic cell transformation, as well as its therapy and management.
Table of Contents
- Tumours
- Causes of Cancer
- Detection of Cancer and its Diagnosis
- Treatment of Cancer
- Practice Problems of Cancer
- FAQs of Cancer
Tumours
Normal cells have the property of contact inhibition due to which contact with other cells prevents them from dividing uncontrollably. Cancer cells do not possess contact inhibition. Tumour is the abnormal mass of undifferentiated cells produced by the uncontrolled division of such cells.
Tumours can be classified as - benign tumours and malignant tumours.
Benign Tumours
Tumours that are confined to one location and do not spread to other parts of the body. They do not cause much damage to the body.

Malignant Tumours
Tumour cells that multiply quickly, invading and destroying normal tissues are called malignant tumours. They are a mass of growing cells known as neoplastic or tumour cells. By competing for crucial nutrients, these cells starve the regular cells as they reproduce and expand.

Sloughed cells from these tumours travel through the bloodstream to other parts of the body, where they create a new tumour. This is known as metastasis and is one of the most dangerous properties of malignant tumours.

Difference between normal and tumour cells
The regulatory processes such as cell growth, cell division, cell differentiation are disrupted in cancer cells.
|
Normal cell |
Tumour cell |
|
They show definite cell division. |
They show indefinite cell division. |
|
They show the property of contact inhibition which prevents them from growing out of control when they come into contact with other cells.
|
This property appears to have been lost in tumour cells.
|
|
Normal cells differentiate in the presence of positive growth factor and differentiation decreases in the presence of negative growth factors. |
Tumour cells do not get affected by the negative growth factors.
|
|
They do not show the property of angiogenesis. |
They show the property of angiogenesis, that is, formation of new blood vessels from the existing blood vessels to meet the nutrient requirements.
|
Causes of Cancer
Normal cells can be induced to transform into malignant neoplastic cells by various physical, chemical, or biological factors. These factors are known as carcinogens.
Physical Factors
Physical factors such as X-rays and gamma rays (ionising radiations), UV rays (non-ionising radiations) cause DNA damage which leads to neoplastic transformation. These rays also lead to the formation of free radicals in tissues which eventually destroys the DNA.

Chemical Factors
Chemical factors such as tobacco contain chemical carcinogens, which have been established as a primary cause of lung cancer. Additionally, other chemicals such as benzopyrene and N-nitrosodimethylamine are dangerous carcinogens.
Biological Factors
Biological factors include oncogenic viruses such as Epstein-Barr and Herpes simplex type-2 viruses which can incorporate their genome within the host DNA, thus transforming host DNA. Oncogenic viruses have genes termed viral oncogenes that cause cancer.
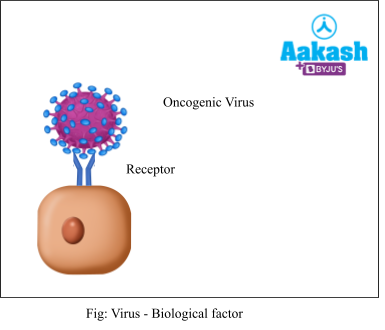
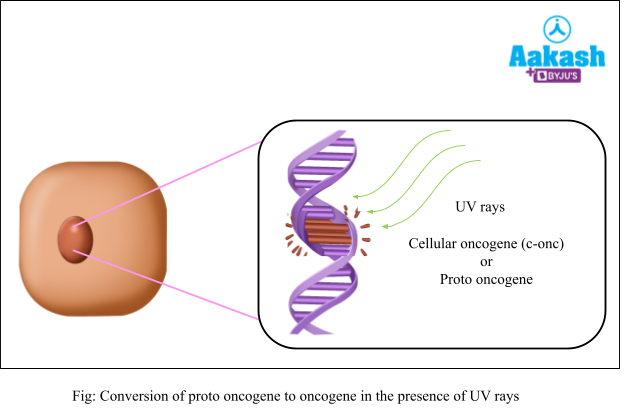
In addition, numerous genes known as cellular oncogenes (c-onc) or proto-oncogenes have been discovered in normal cells that, when activated under particular conditions, might cause the cells to become cancerous. Once they get activated by carcinogens, they cause cancer.
Detection of Cancer and its Diagnosis
Symptoms of cancer mimic the symptoms that can be caused due to other anomalies and hence often go undetected. Early cancer detection is critical because it permits the disease to be successfully treated in many cases. Biopsy and histological analyses of tissue, as well as blood and bone marrow testing for elevated cell counts in the case of leukemias, are used to diagnose cancer.
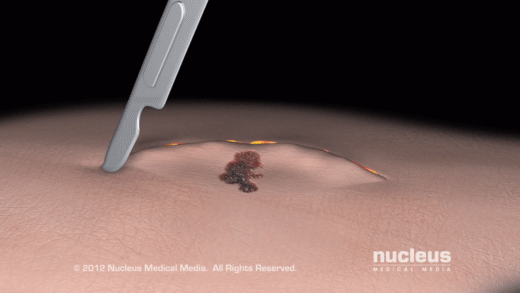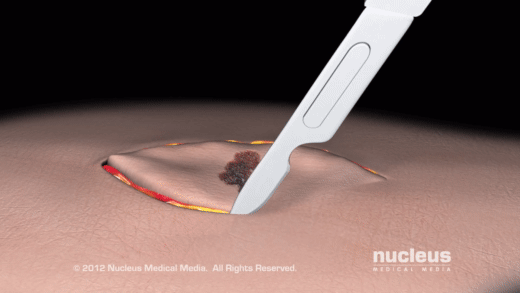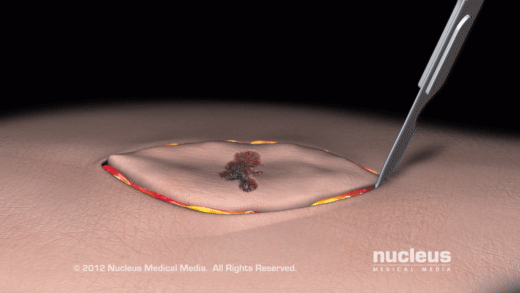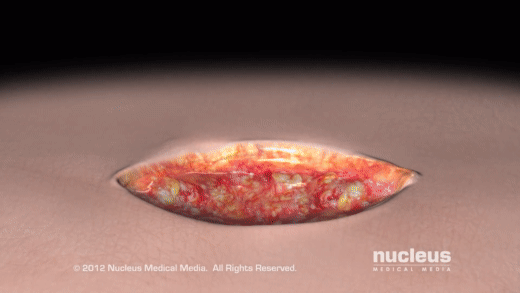
Biopsy
A pathologist examines a portion of suspicious tissue sliced into thin pieces under a microscope (histopathological tests) during a biopsy. It involves taking out a sample of tissue from the area where abnormality is detected.
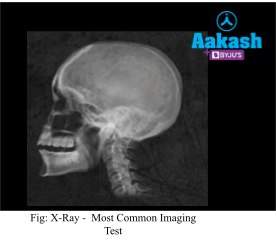
Radiography
Tests such as X-ray radiography and others assists doctors in the detection of cancer in several regions of the body, including the bones, stomach, liver, kidneys, and other organs.
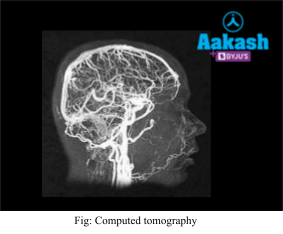
Computed Tomography (CT)
Computed tomography is a method for creating a three-dimensional image of the inside of an object by combining many X-ray images. It helps to generate a three-dimensional image that aids in the identification and location of basic components as well as suspected tumours or anomalies.
MRI
MRI detects pathological and physiological changes in living tissue using intense magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is used to guide the needle during biopsy and in circumstances where tumours are difficult to see on an X-ray. An ultrasound can't identify whether a tumour is benign or malignant, which is a disadvantage. As a result, it is ineffective in cancer detection.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is used to diagnose stomach cancer.
ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
ELISA helps in the detection of either cancer specific antigens or antibodies in the blood.

Molecular Biology
Techniques such as PCR can help in identifying tumour suppressor genes at the DNA and the mRNA level. Mutated or damaged tumour suppressor genes cause cancer by inducing the cells to divide uncontrollably.
Treatment of Cancer
Cancer treatment includes radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy or surgical removal of cancerous tissues.
Radiotherapy
It is a cancer treatment method that uses ionising radiation. Tumour cells are given a deadly dose of irradiation. Thus, the tumour mass is killed by targeting diseased cells more than normal cells and taking care to aim radiation precisely using shielding, collimation, and other ways.
Chemotherapy
Cancer cells are actively dividing cells. Thus, chemotherapy includes drugs that target actively dividing cells and stop their cell division. Chemotherapy attempts to strike a balance between destroying cancer cells (in order to cure or treat the disease) and sparing healthy cells to lessen side effects such as destruction of RBCs, loss of hair, scarring of the skin etc.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy includes the administration of interferon-alpha, a cytokine, to treat cancer. It activates immune cells to target and kill tumour cells. Thus, they are called biological immune modifiers. They produce long-term antitumor response.
Surgical removal
Surgery is used to remove only the tumour or cancerous tissue from the body. It can be performed through various methods such as:
- Laser surgery
- Laparoscopic surgery
- Cryosurgery
- Electro-surgery and many new methods recently introduced
Cancer cannot be completely treated with one type of treatment. Majority of patients receive a combination of treatments such as surgical procedures coupled with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
Practice Problems of Cancer
Question 1. Which of the following statements are true for cancer cells?
a. They show the property of contact inhibition.
b. Growth inhibitors can arrest the growth of cancer cells.
c. They do not show angiogenesis.
d. They can metastasise.
Solution: The properties of cancer cells are -
- They do not exhibit contact inhibition.
- They remain unaffected by growth regulators (promoters or inhibitors).
- They show the property of angiogenesis, that is, formation of new blood vessels from the existing blood vessels to meet the nutrient requirements.
- Cancer cells travel through the bloodstream to other parts of the body, where they create a new tumour. This is known as metastasis.
Hence, option d is correct.
Question 2. Observe the picture given below carefully and identify the method of diagnosis of cancer.
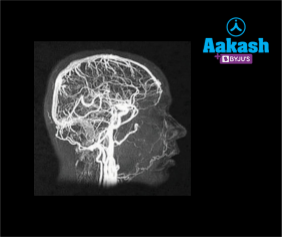
a. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
b. Computer tomography (CT scan)
c. X-rays
d. Biopsy
Solution: The image given in the question is formed by computed tomography (CT scan). It is a method for creating a three-dimensional image of the inside of an object by combining many X-ray images. It helps in the identification and location of basic components as well as suspected tumours or anomalies.
Question 3. Which of the following correctly defines a benign tumour?
a. Surgically removable, cancerous
b. Confined to the tissue, highly curable
c. Not curable, confined to the tissue
d. Not curable, cancerous
Solution: Benign tumour is confined to a particular tissue and does not spread from one body part to the other through the bloodstream. Thus, it is non-cancerous and can be cured easily by surgical removal or any other cancer treatment. Hence, option b is correct.
FAQs of Cancer
Question 1. What are proto-oncogenes?
Solution: Proto oncogenes are cancer causing genes which are present in inactive state and can lead to the formation of cancer in the body when exposed to carcinogens (cancer causing agents).
Question 2. How does cancer spread from one organ to another? What is this property called?
Solution: Malignant tumour cells are cancer cells that multiply, expand and sometimes slough off and enter the bloodstream through which they travel to other body parts and form new tumours there. This property of tumour cells is called metastasis.
Question 3. Why do cancer patients suffer from hair loss, anaemia while under chemotherapy?
Solution: Cancer cells are actively dividing cells. Drugs given to cancer patients during chemotherapy do not target the cancer cells only but they also target actively dividing cells to stop the cell division of cells at different phases of cell division. During this treatment, other actively dividing cells such as hair follicles, red blood cells are also affected and stop dividing. This leads to side effects such as hair loss, anaemia etc.
Question 4. What is contact inhibition?
Solution: Contact inhibition is the property shown by normal cells in which they stop dividig when they are in contact with other neighbouring cells.
Question 5. What is biopsy?
Solution: During biopsy, a pathologist examines a portion of suspicious tissue sliced into thin pieces under a microscope (histopathological tests). It involves taking out a sample of tissue from the area where abnormality is detected.






