-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Trapezoids: Definition, Types, Formulas, Practice Problems, FAQs
In this article, you will come across one of the quadrilaterals named trapezoid which is shown in the figure below. It is also known as trapezium. It is a two-dimensional convex figure which has four sides.
Varun has purchased a piece of land in the following shape:

Varun has to calculate the money he has to spend on cutting the grass and putting a fence around the land. Can we help Varun with the following calculations?
- Cost of cutting the grass at the rate
- Cost of putting a fence around the borders of the land at the rate
Let’s learn about trapezoids through this article and help Varun answer these questions. In this article, you will also learn about the types of trapezoids, and formulas related to trapezoids.
Table of contents:
- Definition of Trapezoid
- Types of Trapezoids
- Formulas related to a Trapezoid
- Practice problems
- FAQs
Definition of Trapezoid:
A trapezoid, commonly referred to as a trapezium, is a quadrilateral or a polygon with four sides.
Out of the four sides of the trapezoid, two sides are parallel and the other two sides are non-parallel.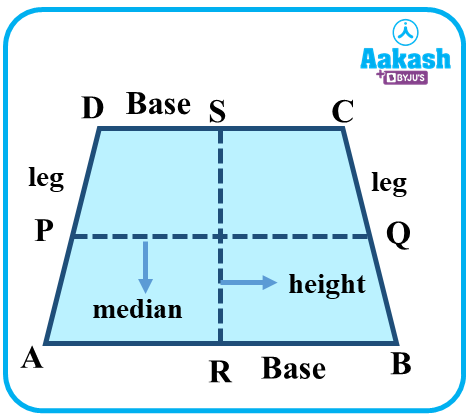
Terms used in Trapezoid:
- Bases: The parallel sides of the trapezoid are referred to as bases.
- Legs or lateral sides: The non-parallel sides of the trapezoid are referred to as legs or lateral sides.
- Height or altitude: The perpendicular distance between the two bases of the trapezoid is referred to as height or altitude.
- Midsegment or median: It is a line segment that connects the midpoints of the two non-parallel sides of the trapezium. It is always parallel to both the bases of the trapezoid.
Types of Trapezoids:
Trapezoids are classified into the following three types:
- Right trapezoid
- Isosceles trapezoid
- Scalene trapezoid
Right trapezoid: A trapezoid with at least one right angle is known as a right trapezoid. It is also called a right-angled trapezoid. Right trapezoids are used to estimate the areas under the curve.

Isosceles Trapezoid: A trapezoid is considered to be isosceles if the lengths of its non-parallel sides (legs) are equal. In an isosceles trapezoid, base angles are equal and diagonals are also of equal length.

Scalene Trapezoid: A trapezium is referred to as a scalene trapezoid when neither its sides nor its angles are equal.

Formulas related to Trapezoid:
Perimeter of Trapezoid: A trapezoid's perimeter equals the sum of all of its side lengths.
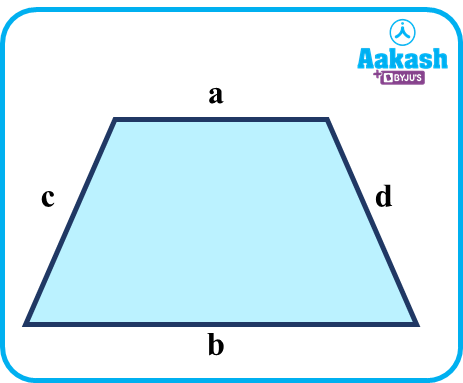
Let a and b be the length of the bases, and c and d be the lengths of the legs.
Then, the Perimeter of the Trapezoid (P)= Sum of all the side lengths of the trapezoid
P=a+b+c+d
Area of Trapezoid:
Area of Trapezoid

Proof:
Consider a trapezium ABCD as shown in the above figure.
To find the area of the trapezium divide it into three parts by drawing AP and BQ which are heights or altitudes.
Let AP=BQ=h
Then the area of the trapezium is the sum of the area of △ APD, △ BQC and rectangle ABQP.
A= Area of △ APD + Area of rectangle ABQP + Area of △ BQC
…(1)
We know, b=r+a+s
Hence on substituting the value of b in equation (1) we get,
Where a is the smaller base of the trapezoid and b is the longer base of the trapezoid.
Let us now solve Varun’s land problem which is mentioned at the start.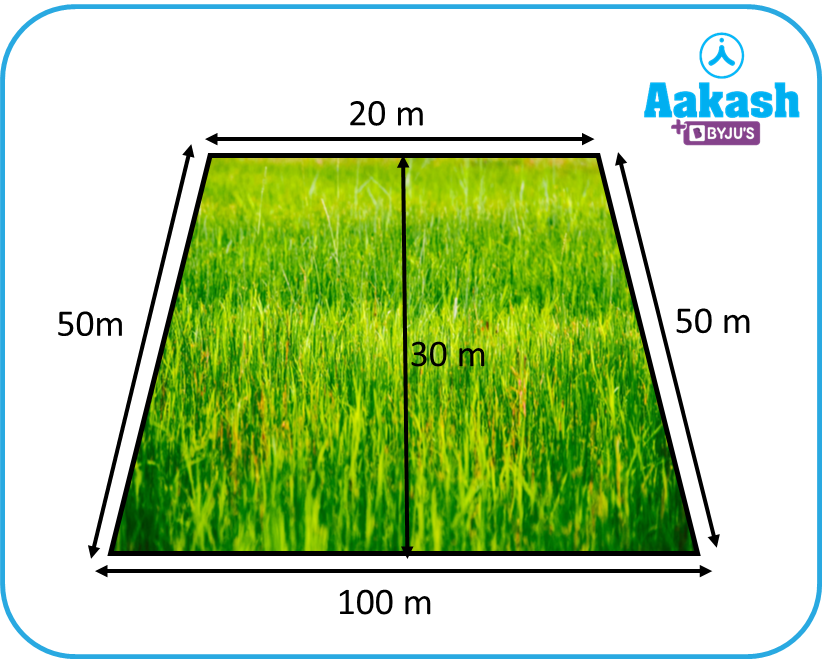
Problem 1: What will be the cost of cutting the grass at the rate
Solution:
To find the total cost of cutting the grass we need to calculate the total area of the land.
a=20 m
b=100 m
h=30 m
Total costs of cutting the grass
Hense Rs.36,000 is required for cutting the grass.
Problem 2: What will be the cost of putting a fence around the borders of the land at the rate .
Solution:
To find the total cost of the fence we need to find the perimeter of the land,
P=a+b+c+d
P=20+100+50+50=220 m
Total costs of fencing
=Rs. 2200
Rs.2200 is required to put the fence around the boundaries of the land.
In total Varun has to spend Rs. 38,200 for cutting the grass and putting the fence around the land he has bought.
Midsegment Theorem:
It states that “If a line connects the midpoints of the two legs of a trapezoid, then it is parallel to the bases and its length is half the sum of the length of bases”.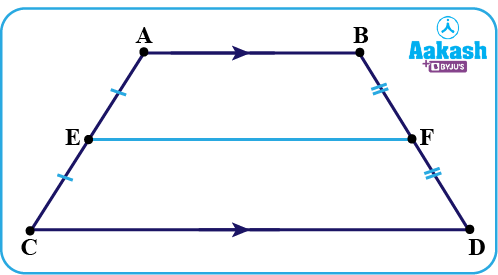
Proof:
Consider a trapezoid ABCD as shown in the above figure.E is the midpoint of the leg AC and F is the midpoint of the leg BD. Hence, EF is the midsegment of the trapezoid.

Draw a line through AF which intersects the extension of CD at point G.
As,
Consider △ ABF and △ GDF
∠BAF=∠DGF (Alternate interior angles)
∠AFB=∠DFG (Vertically opposite angles)
BF=FD (given)
∴ By Angle- Angle-Side(AAS) congruence rule, △ ABF ≌ △ GDF.
AF=FG (CPCT)
AB=DG (CPCT)
Now consider the △ AGC,
E is the midpoint of the leg AC and F is the midpoint of AG,
Then by mid-point theorem, and
Now,
Also, from (1), we have i.e. . But
Hence EF is parallel to both AB and CD and is equal to half of the sum of AB and CD.
How to find the area of trapezium when all the sides are given?
We have learnt how to calculate the area of a trapezium when both the bases and height are given. Let’s understand how to calculate the area of the trapezium when all sides are given but height is not given through the below example.
Example: Find the area of the below-given trapezoid.
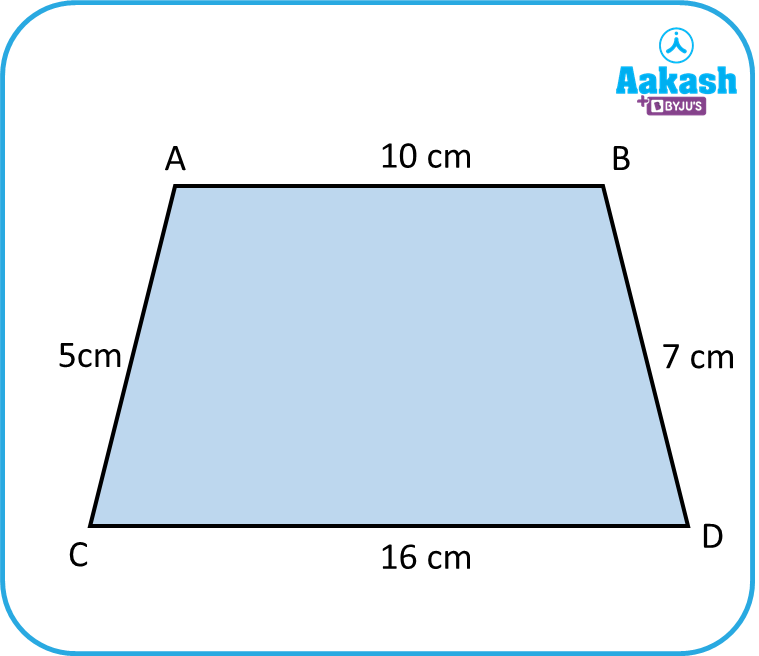
Solution:
Through point B, draw a line parallel to AC, which intersects CD at E.
As, and , then ABEC will become a parallelogram.
and BE=AC=5cm.
Now consider the △ BED. In this triangle, we know all three sides. So, we will use Heron’s formula to calculate the area.
Let a=5cm, b=6cm and c=7cm.
Area of triangle
Where
Now we know the area of △ BED, So let’s calculate the height (h) of the triangle.
Now we know all the data to calculate the area of trapezoid ABDC.
Smaller base (a)=10 cm
Larger base (b)=16 cm
Height
Area of trapezoid=
∴ The area of the given trapezoid ABDC is
Practice problems:
Q1. Find the area of a trapezoid whose bases are 15 cm and 12 cm and the height of the Trapezoid is 6 cm.
Solution:
Larger base (b)=15 cm
Smaller base (a)=12 cm
Height of trapezoid (h)=6 cm
Area of trapezoid
Q2. The sides of a trapezoid measure 7 cm, 10 cm, 5 cm and 4 cm. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
Let a=7 cm, b=10 cm, c=5 cm, d=4 cm
Perimeter of trapezoid (P)=a+b+c+d=7+10+5+4=26 cm
Q3. Find the length of the midsegment of the trapezoid if its bases are of length18 cm and 13 cm.
Solution:
From the Midsegment Theorem, the length of the midsegment is the average of its bases.
So, the Length of midsegment
Q4. Find the height of the trapezoid which has an area of 112 cm2 and the bases of the trapezoid are 22 cm and 10 cm.
Solution:
Larger base of trapezoid (a)=22 cm
Smaller base of trapezoid (b)=10 cm
Area of trapezoid (A)=112 cm2
The formula for the area of a trapezoid is
FAQs:
Q1. Can there be only one right angle in a trapezoid?
Answer: No, Trapezoids can't have only one right angle. They can either have two right angles or none.
Q2. Is regular trapezoid possible or not?
Answer: Because all sides of a trapezoid can’t be of the same length and its angles are also not of the same measure. Hence, a trapezoid or a trapezium cannot be a regular polygon.
Q3. How can a trapezoid be verified?
Answer: Remember that a trapezoid is a quadrilateral with precisely one pair of parallel sides. So you need to check in the given figure whether there is exactly one pair of parallel sides or not.
Q4. What is the sum of the internal angles of a trapezoid?
Answer: A trapezoid is a quadrilateral so the sum of its internal angles is 360.
Q5. Do the diagonals of a trapezoid divide each other in an equal ratio?
Answer: Yes, the diagonals of a trapezoid always divide each other in an equal ratio.


