-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Water Pollution and its Control: Water Pollutants, Effects of Water Pollution, Practice Problems and FAQs
“Water, water, everywhere and not a drop to drink”. Yes, you heard that right. Earth is 70% water and 30% land but guess the amount of water that is drinkable?
Just 3%! Astonished? This freshwater, safe for consumption, flows in rivers, glaciers, ponds, lakes etc. The remaining water is extremely polluted and as humans, the smartest creature of this planet, it is our responsibility to use this precious resource wisely. What has made the remaining water unfit for consumption? How can we treat polluted water? What are the initiatives we have taken so far to do so? All these questions will be answered as you read further.
Table of Contents:
- What is Water Pollution?
- Types of Water Pollutants
- Heat
- Biomagnification
- Practice Problems of Water Pollution and its Control
- FAQs of Water Pollution and its Control
What is Water Pollution?
Water pollution can be defined as contamination of water by harmful substances which make it unfit for consumption by living beings.

Water Pollutants
What are Water Pollutants?
Substances that make water unfit for consumption are known as water pollutants.
Types of Water Pollutants
Different types of water pollutants are listed below:
- Domestic waste
- Microbial contaminants
- Toxic waste
- Heat
- Petroleum products

Domestic Waste
All the wastes that we throw from our households can be considered as domestic waste. Can you name a few?? Domestic wastes can be solid such as plastic, kitchen waste, paper etc, or liquid such as cleaning chemicals, soapy water etc. Waste water containing domestic waste is said to be sewage water.
Domestic waste majorly includes biodegradable waste and hence can be easily decomposed using various microorganisms.
Biological oxygen demand (BOD)
It is the amount of oxygen used by the microorganisms in order to decompose the organic substrates present in one litre of water. Amount of organic matter and water pollution is directly proportional to the BOD of water while the amount of dissolved oxygen is inversely proportional to the BOD of water. Hence, sewage water will have higher BOD and less dissolved oxygen.
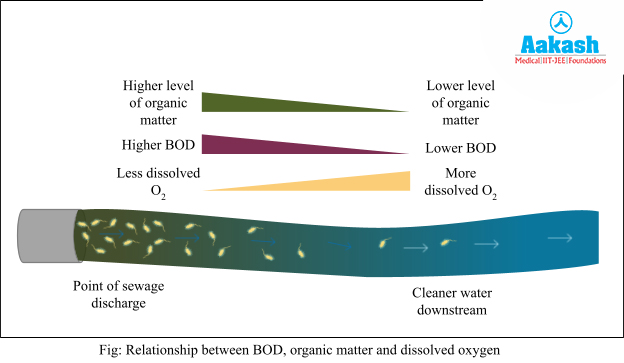
Sewage is composed of three types of components:
- Suspended solids: These can be removed easily by physical methods such as filtration, sedimentation, etc. Suspended solids include sand, clay, silt etc.
- Colloidal impurities: Biodegradable organic matter form the colloidal impurities. For example: faecal matter, microbes etc.
- Dissolved impurities: These impurities are hardest to remove as they are dissolved in water. For example: Metal ions, nitrates, ammonia etc.
Microbial Contaminants
Microbial contaminants include various harmful microorganisms that are disposed in water from sources like sewage and ill-disposed medical waste.
Various pathogenic bacteria, protozoa and viruses are some of the microbial contaminants that increase the chances of waterborne illness if such contaminated water is consumed.
Toxic Waste
Any poisonous, carcinogenic, radioactive and explosive chemicals that are disposed into water, hence making it polluted, are known as toxic waste.
Toxic waste mainly comes from commercial industries involved in production of paper, textile, pharmaceuticals, chemical processing etc. These industries dispose of heavy metals (elements with density greater than 5g/cm3) and various other organic compounds into the water.
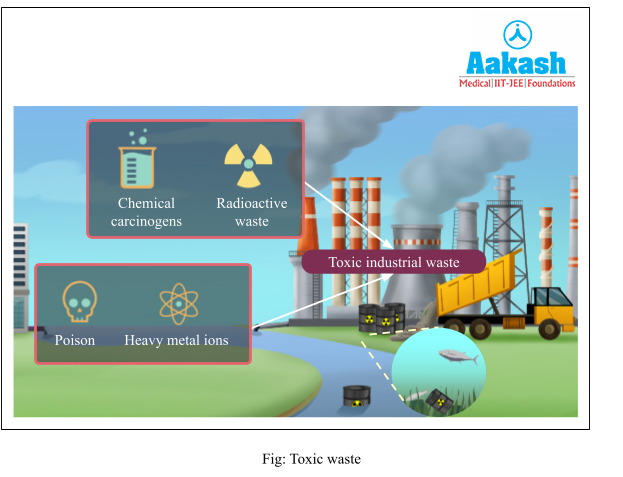
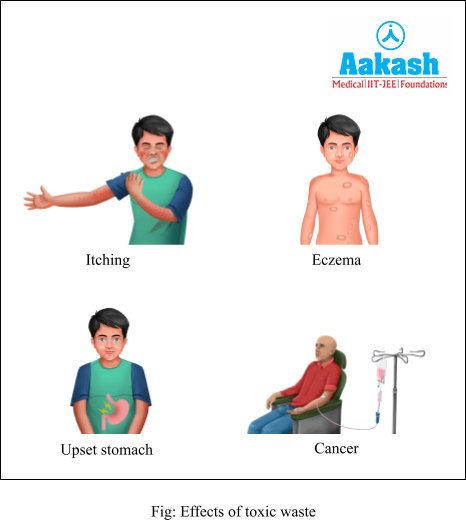
Frequent contact with toxic water results in itching, eczema, upset stomach, cancer etc.

Heat
Power plants release coolants directly into the water which are approximately 15oC warmer than the normal water. This increases the temperature of water, hence making it uninhabitable for flora and fauna and for consumption. This is also known as thermal pollution.
Release of coolants in water results in an increase in temperature of water which decreases the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water making it difficult for aquatic life forms to survive. This is because the solubility of oxygen in water decreases as the temperature increases.
Petroleum Products
Petroleum products that contribute to water pollution are as follows:
Plastic
Plastic is a non-biodegradable product of petroleum and one of the widely used products in daily life. Plastic breaks down into smaller pieces called microplastics which have higher surface area. This results in accumulation of toxic chemicals in water resulting in water pollution.
Oil Spills and Shipwrecks
These are the major sources of water pollution caused due to petroleum products. Oil, being insoluble in water, floats over the water, decreasing the dissolved oxygen concentration of water and hence causing the death of aquatic life forms of the respective ecosystem.
Effects of Water Pollution
Algal Blooms
What are Algal Blooms?
Excessive organic wastes present in the water lead to excessive growth of planktonic algae and hence forming algal blooms.

Effects of Algal Blooms
Algal blooms impart a distinct colour to the water bodies. Growth of algae in water bodies decreases the amount of dissolved oxygen which results in the death of aquatic lifeforms.
Similar effect is caused by water hyacinth, also known as ‘terror of Bengal’ as it has the ability to rapidly grow in polluted water, hence causing decrease in dissolved oxygen of water bodies. Water hyacinth is also called the world’s most problematic aquatic weed.

Eutrophication
Eutrophication is defined as the natural ageing of the lake caused due to the excess amount of nutrients (like nitrogen and phosphorus) in water.
When a lake is young, it has clear water and very few life forms. As streams drain into the lake, it increases the nutrient content of the lake which results in an increase in aquatic life forms of that particular lake. This, in turn, increases the organic content of the lake which gets deposited at the bottom of the lake. With time, the lake becomes shallower and warmer. Eventually, marsh plants bloom at the bottom of the lake and floating plants take over the top of the lake. Overtime, the lake gets converted into land.
Accelerated Eutrophication
The rate of eutrophication may vary depending on the size of the lake, climate etc. however, various anthropogenic activities may speed up the process of eutrophication which is termed as accelerated eutrophication.
Effect
Enrichment of nutrients results in the growth of algae in water. Algal growth blocks the sunlight making the aquatic flora and fauna devoid of sunlight. This results in the death of aquatic plants. The dead plants are further decomposed by decomposers. This may eventually lead to an increase in the number of decomposers who would consume the majority of the dissolved oxygen and increase he biological oxygen demand (BOD) in the aquatic ecosystem, hence destroying the aquatic ecosystem.

Biomagnification
Increase in concentration of harmful pollutants at each successive trophic level of the food chain is termed as biomagnification. DDT, mercury and heavy metals are some of the harmful substances that can undergo biomagnification.
Accumulation of the toxic substances mainly occurs due to the inability of an organism to metabolise or excrete harmful substances.
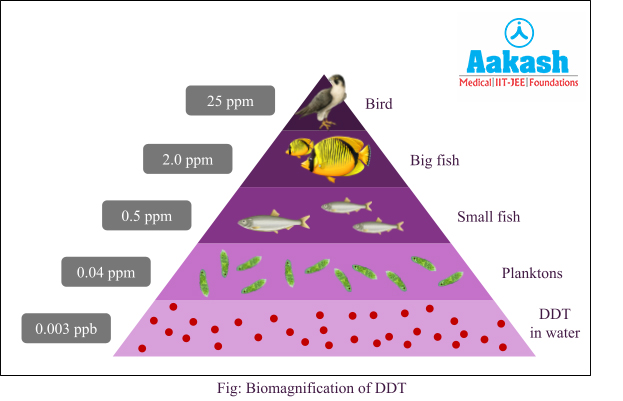
Effects
Biomagnification of DDT causes faulty calcium metabolism in birds which results in thinning and premature breaking of eggshells. This eventually causes a decline in the bird population.
Practice Problems of Water Pollution and its Control
Question 1. The ocean was affected by an oil spill which resulted in death of flora and fauna in the ocean. Which of the following statements justify the death of flora and fauna?
a. Decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water
b. Increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water
c. Decrease in the BOD of water
d. None of the above
Solution: Death of aquatic life forms is caused by the decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water. Oil, being insoluble in water, floats over the water, decreasing the dissolved oxygen concentration of water and hence causing the death of aquatic life forms of the respective ecosystem. Decrease is dissolved oxygen concentration increases the BOD of water.
Hence, the correct option is a.
Question 2. Which of the following options incorrectly represents the concentration of DDT at a particular trophic level?
a. Big fish - 2 ppb
b. Plankton - 0.04 ppm
c. Small fish - 0.5 ppm
d. Big fish - 25 ppm
Solution: DDT is a type of insecticide. It runs off through fields into water. In water bodies, it initially exists at a dilute concentration of 0.003 ppb and enters the food chain via phytoplankton and zooplankton (0.04 ppm) in water. As DDT cannot be metabolised by living organisms, its accumulation at successive trophic levels continues as zooplankton are consumed by small fishes (0.5 ppm), big fishes (2 ppm) and birds (25 ppm). Highest concentration of DDT is accumulated in birds.
Thus, the correct option is a.
Question 3. Which of the following unknown metals can be considered as a heavy metal?
|
Metal A |
Density greater than 5g/cm3 |
|
Metal B |
Density greater than 6g/cm3 |
|
Metal C |
Density greater than 4g/cm3 |
|
Metal D |
Density greater than 3g/cm3 |
a. Metal A
b. Metal B
c. Metal C
d. Metal D
Solution: Heavy metals are the elements with density greater than 5g/cm3.
Hence, the correct option is a. Density greater than 5g/cm3.
FAQs of Water Pollution and its Control
Question 1. What are different types of water pollutants? Mention the examples of each.
Solution: Substances that make water unfit for consumption are known as water pollutants.
Different types of water pollutants are:
- Domestic waste: Domestic waste includes wastes that come from residential areas. Example of domestic waste:
- Solid waste: Plastic, kitchen waste, paper etc.
- Liquid waste: Cleaning chemicals, soapy water etc.
- Microbial contaminants: Microbial contaminants include various harmful microorganisms that are disposed in water from sources like sewage and ill-disposed medical waste. Example: Pathogenic bacteria, viruses etc.
- Toxic waste: Any poisonous, carcinogenic, radioactive and explosive chemicals that are disposed into water, hence making it polluted, are known as toxic waste. For example: Mercury, cadmium, copper etc.
- Heat: Power plants release coolants directly into the water which are 15oC warmer than the normal water. This increases the temperature of water, hence making it inhabitable for flora and fauna and for consumption.
- Petroleum products: Plastic disposal in water, oil spills and shipwrecks are the petroleum products that cause water pollution.
Question 2. What is eutrophication? How is it harmful?
Solution: It is defined as the natural ageing of the lake caused due to the excess amount of nutrients (like nitrogen and phosphorus) in water. Enrichment of nutrients results in the growth of algae in water. Algal growth blocks the sunlight making the aquatic fauna devoid of sunlight. This results in the death of aquatic plants. The dead plants are further decomposed by decomposers. This may eventually lead to a negligible amount of dissolved oxygen in the aquatic ecosystem, hence destroying the aquatic ecosystem.
Question 3. How does biomagnification of DDT harm the living organisms?
Solution: DDT is a type of insecticide. It runs off through fields into water and exists at a dilute concentration of 0.003 ppb and enters the food chain via phytoplankton and zooplankton (0.04 ppm) in water. Accumulation of DDT continues as zooplankton are consumed by small fishes (0.5 ppm), big fishes (2 ppm) and birds (25 ppm). Highest concentration of DDT is accumulated in birds which causes faulty calcium metabolism in birds resulting in thinning and premature breaking of eggshells. This eventually causes a decline in the bird population.
Question 4. What are algal blooms? How do they affect aquatic life?
Solution: Excessive organic wastes present in the water lead to excessive growth of planktonic algae and hence forming algal blooms.
Algal blooms impart a distinct colour to the water bodies. Growth of algae in water bodies decreases the amount of dissolved oxygen which results in the death of aquatic lifeforms.
Question 5. What is thermal pollution?
Solution: The increase in the temperature of water, due to release of hot liquids into water bodies is known as thermal pollution. Power plants release coolants directly into the water which are approximately 15oC warmer than the normal water. This increases the temperature of water and makes it uninhabitable for the aquatic flora and fauna.
Increase in temperature of water decreases the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water making it difficult for aquatic life forms to survive. This is because the solubility of oxygen in water decreases as the temperature increases.


