-
Call Now
1800-102-2727
Progressive wave : Amplitude, Wavefunction, phase, wavelength,Angular wave number, period, Frequency, angular frequency, Wave velocity and frequency
As you know, many forms of energy like light and sound travel in waves. A wave is defined through various characteristics like amplitude, phase, wavelength etc. In wave mechanics, any given wave enfolds parameters like – frequency, time period, wavelength, amplitude etc. But what does it actually mean?
Table of content
- Progressive wave
- Amplitude
- Wavefunction
- Phase
- Wavelength
- Angular wave number
- Time period
- Frequency
- Angular frequency
- Wave velocity or phase velocity
- Relationship between the wavelength, frequency, and velocity of a wave
- Practice problem
- FAQs
Progressive wave
A wave that travels in medium and can be represented by any of the following equations is called traveling or Progressive wave.

The graphical representation of Progressive wave is shown in figure
Amplitude
Since the sine function varies between 1 and -1 , So the displacement of a Progressive wave y(x,t) will vary between a and -a. Then ‘a’ represents the maximum displacement of a particle in medium.
Hence , the magnitude of maximum displacement of each particle from its mean position is known as the amplitude of the transverse wave.
In the figure, OA is the amplitude of the wave. Every particle of the string will have an amplitude similar to that of the source.
Wavefunction
The functions that represent the waves are known as wavefunctions. The wavefunctions for the traveling waves moving with velocity v are sin ![]()
Phase
The quantity (t-kx+) is known as the phase of the wavefunction. For a wave pulse, the phase remains constant because the shape of the pulse does not change. In other words, a phase is nothing but the shape of the wave pulse.
Wavelength ()
The crest-to-crest or the trough-to-trough distance is known as the wavelength of a Progressive wave. Sometimes, this distance is known as the peak-to-peak distance.
Symbolically, the wavelength is represented by λ.
Angular wave number (k)
In a Progressive wave equation K is known as angular wave number.
![]()
Time period (T)
The time taken for one complete oscillation, the time interval between two successive wave pulses to come out from the source, or the time between two successive crests or troughs is known as the time period of the Progressive wave.
Frequency (f)
We define the frequency of a Progressive wave as the number of complete oscillations made by any wave element in per unit time. By the definition of frequency, we can understand that if a body is in periodic motion, it has undergone one cycle after passing through a series of events or positions and returning to its original state. Thus, frequency is a parameter that describes the rate of oscillation and vibration.
Period and frequency are reciprocal of each other,
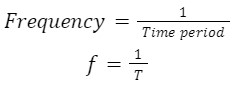
Its SI unit is s-1 or Hertz.
Angular frequency ()
For a Progressive wave, the angular frequency is the angular displacement of any particle of the wave per unit time or the rate of change of the phase of the waveform. It is represented by . Angular frequency formula
![]()
Its SI unit is rad/s.
Wave velocity or phase velocity (v)
Velocity of a Progressive wave is actually the measurement of the rate of propagation of energy in the direction of wave propagation.
- A wave borrows every single property from the source except velocity because the wave propagates through a medium. Hence, the velocity of the wave depends on the property of the medium.
- Since the velocity (v) of a wave depends on the medium and the frequency (f) of the wave solely depends on the source, the wavelength (λ) depends on both the medium and the source.
- A wave imitates every property of source except velocity.
Relationship between the wavelength, frequency, and velocity of a wave
Let the wavelength, frequency, and velocity of a wave be λ, f, and v, respectively. Then, they are related as follows:
Wave velocity (v) mathematically is given by

Where,
- The angular velocity
k - the angular wavenumber or propagation constant
We know that, angular velocity =2f
Where = frequency of wave
The wavenumber k=2
Where = wavelength
Substituting these value in eq (i)

If we know the frequency and wavelength then with the help of this formula we can find velocity.
Practice problem
Q 1. A wave is propagating on a long, stretched string along its length taken as the positive x-axis. The wave equation is given as y=y0 e-(tT-x)2 , where y0 = 4 cm, T = 1 s, and λ = 4 cm. Find the function f(t) giving the displacement of the particle at x = 0
Answer: Given equation is,
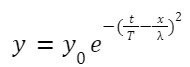
where y0 = 4 cm, T = 1 s, and λ = 4 cm
On putting value in equation, we have
![]()
Now at x = 0 displacement of particle

Hence f(t) represents displacement of particles at x=0.
Q 2 . A sinusoidal wave is traveling along a rope. The oscillator that generates the wave completes 60 vibrations in 30 s. Also, a given pulse travels 425 cm along the rope in 10 s. What is the wavelength?
Answer: We know that frequency is defined as the number of oscillations per unit time.
Therefore, the frequency is, ![]()
Given,
The wave pulse travels 425 cm along the rope in 10 s.
Hence, the wave velocity is, ![]()
Thus, the wavelength is, ![]()
Q 3. A wave is propagating on a long, stretched string along its length taken as the positive x-axis. The wave equation is given as y=y0 e-(tT-x)2 , where y0 = 4 cm, T = 1 s, and λ = 4 cm. Find the function g(x) giving the shape of the string at t = 0
Answer: Given equation is,
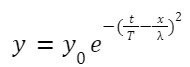
Where y0 = 4 cm, T = 1 s, and λ = 4 cm
On putting value in equation, we have
![]()
Now at t = 0 shape of string is given as
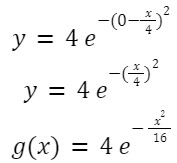
Hence g(x) represents the shape of the string at t=0.
Q 4. A sinusoidal wave traveling in the positive x-direction has an amplitude of 15 cm, a wavelength of 40 cm, and a frequency of 8 Hz. The vertical displacement of the medium at t = 0 and x = 0 is also 15 cm. Find the angular wave number, period, angular frequency, and speed of the wave
Answer: The angular wave number of the wave is, ![]()
The time period of the wave is, ![]()
The angular frequency of the wave is, =2f=28=16 s-1 (the unit of angular frequency is rad s-1, but here, π is expressed in rad; so, the unit is written as s-1 only.)
The speed of the wave is, ![]()
FAQs
Q 1. What is the formula for finding frequency ?
Answer: ![]()
Q 2. What is the relation between wavelength and frequency?
Answer: The relation is given as v=f . For the same velocity of wave, wavelength is more then frequency will be less and vice versa (see figure).
Q 3. Which parameter of Progressive wave depends on the medium?
Answer: Velocity of a wave depends on the medium.
Q 4. What is the speed of sound waves in air?
Answer: The speed of sound waves is approximately 332 m/s.
Related link
|
Type of Waves,Terms related to Waves,Practice Problems, FAQs |
Transverse Wave-definition,Practice problem,FAQs |
|
Longitudinal waves-Practice Problems,FAQs |
Progressive wave : Displacement Relation |


