To begin with, how do we heat water? Or how do our electrical appliances work? Not just these questions, but we experience thousands of similar activities daily, and to answer such questions, let’s see about different levels of conductivity.
There are three levels of conductivity. They are
- Conductors
- Semiconductors
- Insulators
Conductivity could be anything. It could be heating water, electricity in households, cooking using wood, etc. In this article, let us look at conductivity in a brief while understanding all its related concepts in detail. It will be very much useful for the aspirants of JEE.
What is Conductivity?
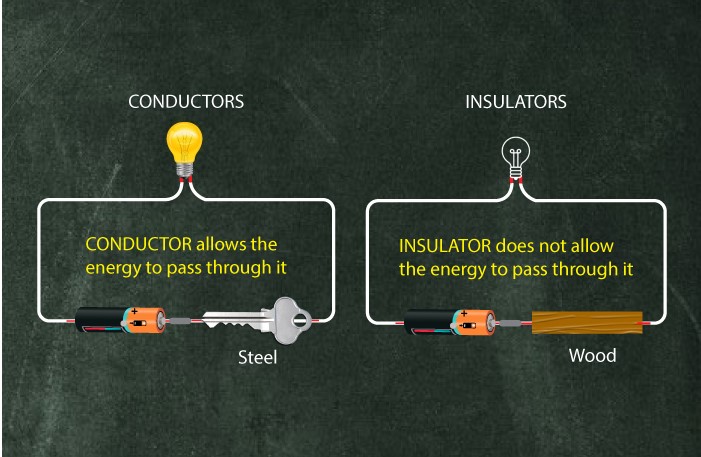
In Physics, conductivity is a term used to demonstrate the principle differences between conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. A conductor is a phenomenon in which it allows heat, electricity, light, water, etc. to pass through them completely. In contrast, semiconductors are the ones that only have a partial conductivity nature in them. On the other hand, insulators do not conduct anything, and their conductivity is zero.
Band Theory
Students of the JEE 2022 exam should be able to understand what a Band theory is, at first. Band theory is one of the fundamental ways of describing differences in conduction. Band theory involves the ‘band’ of materials which could help explain a certain number of physical properties of conduction.
The electrons present in an atom can orbit the positive nucleus within the allotted energy levels. The energy levels have been reorganized into valence bands and conduction bands in many of those atoms. The conduction band can be seen as the higher level of electrons, whereas the valence bond is at the lower electron levels.
In-between both the bands, there exists an energy gap where no electrons are present. While conduction takes place, the electrons roam around, but there should be spaces present in the energy bands for this to happen. Therefore, the electrons can move into the areas of the energy bands.
Conductor – Definition
For the JEE Physics aspirants to understand the concepts of Semiconductors and Insulators, they need to learn about conductors first. The following is the brief definition given for it.
A conductor is a conduction device that facilitates the smooth flow of electrons from one atom to the other when voltage application is proper. It only happens when there are no band gaps between the conduction bands and valence bands.
However, some materials have the overlapping formation of valence and conduction bands. It indicates that the movement of electrons between both the overlapping gaps would be possible. Since there is enough space to move into the conduction band for the electrons, the electrons with the valence band can easily move into the other space, making way for the conduction to occur.
Conductor materials and substances
One of the best electrical conductors is silver. Other than silver, some other metals that provide good conductivity are copper, brass, aluminum, gold, steel, etc. All these materials are found in daily life in various electrical equipment. They are mostly in the form of wires.
In addition to this, solids are the best conductor types; however, sometimes liquid metals, namely mercury, are also good at transmitting energy. Some materials are classified as superconductors because, during extremely low-temperature conditions, these materials are capable of conducting without resistance.
Semiconductor – Definition
Understanding semiconductor concepts would be much simpler as we have seen what a conductor is. The conductivity value of the semiconductor would be moderate, which means the value lies between the conductors and the insulators.
Moreover, when there is a temperature rise, the resistance of a semiconductor drops drastically. Given below are some of the instances of semiconductors:
- Indium antimonide (InSb)
- Gallium arsenide (GaAs)
- Silicon (Si)
- Selenium (Se)
- Germanium (Ge)
In this, silicon is the most commonly used semiconductor in the world.
A semiconductor presents a gap between the valence bands and conduction bands. However, this gap would enable the conduction of electron movements at room temperature.
Furthermore, temperature rise increases the semiconductor’s conductivity. More electrons will have the required energy to move into the conduction band. Usually, due to spaces between the gas atoms, they are considered poor conductors. Although, in certain circumstances, gases can be seen as fair conductors and could act as semiconductors.
Types of semiconductors
Semiconductors are of two types. They are
- Intrinsic semiconductors: They are made up of only a single element type. Intrinsic semiconductors are made to contain zero impurities in them.
- Extrinsic semiconductor: In extrinsic semiconductors, we add up some small amounts of impurities to improve their conductivity nature.
With this, JEE 2022 aspirants would be able to comprehend the total understanding of semiconductors.
Insulator – Definition
In JEE Physics, the main objective of an insulator is to prevent the energy flow between two or more objects. These can control the flow of sound, heat, electricity, etc. Furthermore, thermal insulators help reduce the heat transfer between two bodies having two different temperatures when we take thermal insulators. Thermal insulators are capable of performing this by reflecting thermal energy.
In addition to this, a material’s insulating capacity can be termed as the inverse of thermal conductivity (k). Therefore, the materials that contain low thermal conductivity will consist of high resistance value or insulating ability. In addition to this, other fundamental properties such as the product’s density and specific heat capacity are taken into account.
In insulators, dielectric materials are substances that do not conduct electricity. The polarisation of these substances can be easily attained by applying an electric field. The electric charges could not flow through them like they could with conductors. Ultimately, the internal electric field can decrease the overall area inside the dielectric.
There are wider gaps between the insulators’ valence bands and conduction bands. Due to that reason, the electrons are not permitted to move into the conduction band. Therefore, the materials do not conduct electricity.
Conductors in everyday life
We can see many items that act as conductors in our daily lives. Below mentioned are some of the examples of conductors:
1. Thermometers:
To measure body temperature, we use thermometers. It consists of a liquid substance called mercury.
2. Cooking pans:
In cooking pans, iron has been traditionally used. It is to conduct heat from a flame at a higher pace. It is ultimately used to cook the food which is in the pan.
3. Radiators:
Radiators have been traditionally used in central heating systems. The reason is that radiators are good conductors of heat and can help transfer the heat into the room.
Usage of semiconductors in daily life
Semiconductors might not be very common among general people as only the usage of conductors and insulators has been normalized among us. Although, there are certain cases where we use semiconductors. They are as follows:
1. Solar cells:
Solar cells are made of n-type and p-type semiconductor materials. They are utilized in solar panels, which could turn sunlight into electricity.
2. Transistors:
Transistors are present in many gadgets that we use in our daily lives. The technology utilized in the transistors is known as VLSI technology. The abbreviation of this is Very Large Scale Integration.
Common insulators in everyday life
The usage of insulators is tremendous, be it in any daily life household applications or industrial applications. Now, let us see the places where they are being used:
1. Electrical insulation:
These insulators are used mainly in wire coating of circuitry in the household. Apart from that, they are also used to insulate capacitors in consumer and commercial goods.
2. Wall insulation:
Wall insulation usually comes in the thermal insulation variant. It is used to maintain the flow of heat flow between a commercial or a residential building and the outside surroundings.
3. Sound insulation:
It is usually used in recording studios and stages. However, its usage does not just stop there. Nowadays, many people use it in different circumstances, such as to prevent causing any noise disturbances between residential properties and private rooms.
Hence, the JEE 2022 aspirants can understand the usage of insulators in detail.
Difference between Semiconductors and Insulators
A differentiation table is provided for the JEE Physics students to comprehend the differences between semiconductors and insulators.
| Semiconductors | Insulators |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
In a nutshell, JEE 2022 Physics aspirants can understand all the concepts related to conductivity, starting from what is meant by conductivity to the difference between semiconductors and insulators. The students have learned the definitions of conductor, semiconductor, and insulator while understanding the Band theory.
In addition, the JEE 2022 students are taught the usage of conductors in everyday life, the applications of semiconductors in daily life, and the importance and benefits of insulators.